-
国外从20世纪50年代末期和60年代初期最早开始关注研究风暴岩。Ager[1]和Kelling et al.[2]首先提出了“风暴岩”的概念,系指经历风暴流扰动后再沉积形成的一套沉积物组合,进一步分为海相和湖相风暴岩[3]。国内对于风暴岩的研究起步较晚,最早是在20世纪80年代孟祥化等[4]和刘宝珺等[5]开始引进风暴岩的研究成果,对国内的风暴岩进行研究,国内对于风暴岩的研究在20世纪末期达到高潮,在重建风暴沉积演化模式、恢复古板块、古地理及古环境等多方面取得了诸多进展与成果[6]。如马瑞申等[7]据豫北地区寒武纪发育的风暴岩推断当时该区位于赤道低纬度(5°~20°)的风暴作用带,属于热带气候;马志鑫等[8]通过黔东镇远地区风暴沉积研究认为该区清虚洞组为潮坪环境,完善了早寒武世清虚洞期湘西—黔东地区风暴沉积类型。景宇轩等[9]根据北京西山下苇甸剖面风暴沉积类型恢复了海平面变化。冯宇翔等[10]通过中三叠世扬子地台西缘雷口坡组风暴沉积证实龙门山古隆起与川西斜坡古海湾的存在。
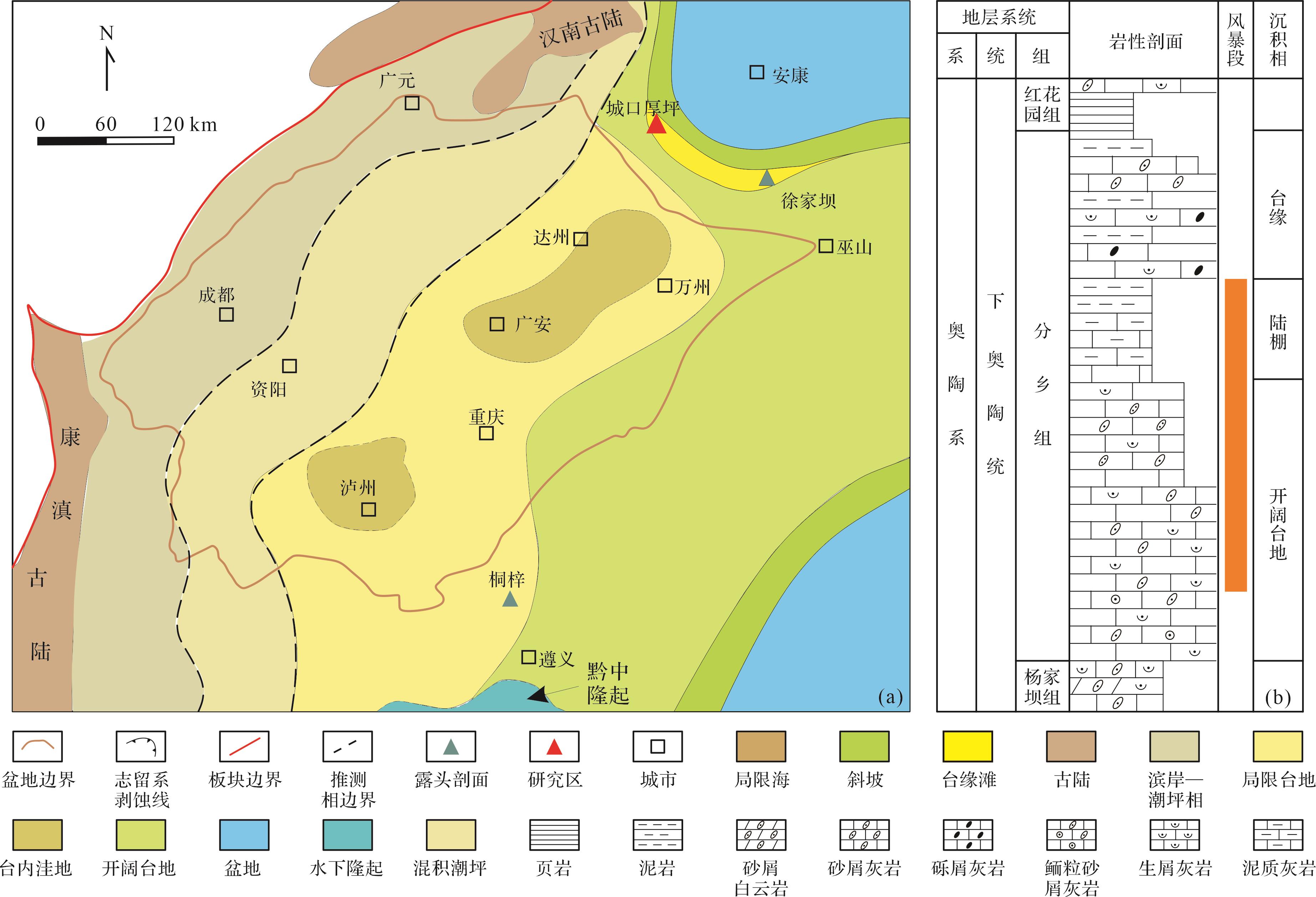
扬子板块中具有十分丰富的风暴沉积,在震旦纪[10⁃12]、寒武纪[13⁃15]、奥陶纪[1⁃19]、志留纪[20⁃21]、泥盆纪[22⁃25]、石炭纪[26]和三叠纪[27⁃33]均发现风暴沉积。目前对于扬子板块风暴岩的研究主要集中在寒武纪地层,志留纪次之,奥陶纪时期风暴沉积的报道主要在扬子板块西南部,集中在下奥陶统层位[17⁃19];扬子板块北缘地区的风暴沉积仅在寒武纪[14],志留纪[21],三叠纪[28,32]中报道,尚未发现奥陶系风暴岩的相关报道。目前对扬子板块北缘地区奥陶系分乡组的沉积环境、油气探勘、古环境与古地理特征等方面的研究较为薄弱。笔者在城口厚坪剖面的下奥陶统分乡组中发现了风暴沉积,这对于认识该区下奥陶统沉积环境、古海洋条件、古地理和沉积古地貌具有重要意义。本文在薄片鉴定和实测剖面的基础上,阐明下奥陶统分乡组风暴沉积构造、沉积序列以及沉积模式,分析分乡组风暴沉积的地质意义。
-
四川盆地是一个叠合盆地,在震旦纪到三叠纪为一个海相克拉通盆地,三叠纪后变为前陆盆地[34]。受Rodinia大陆裂解影响,南华纪四川盆地普遍发生张裂作用,晚震旦世时构造运动减弱,盆地内部稳定沉降,加里东运动早期的拉张—伸展作用逐渐替代晋宁期板块汇聚作用,此时盆地外缘方向逐渐变深,转变为克拉通内坳陷盆地[35]。早奥陶世,四川盆地继承了寒武纪末期的地理格局,主体位于稳定克拉通内坳陷盆地中。到了中奥陶世,由于华夏板块与扬子板块再次碰撞拼合,盆地内部从伸展构造背景逐渐被挤压构造背景替代,此时中上扬子地区盆内及盆缘开始隆起,四川盆地成为挤压环境下的克拉通盆地[36]。晚奥陶世,由于华夏板块与扬子板块的汇聚过程,此时四川盆地基底快速沉降[37],盆地北西部康滇古陆和川中隆起同时发展使得盆地中海域被围限,形成局限海[35],在志留纪末期华夏板块与扬子板块逐渐统一成为华南板块,盆地主体基本消亡。
研究区位于北大巴山逆冲推覆构造带前缘、城口断裂带南侧的城口厚坪一带,隶属于扬子地台北缘(图1a)。扬子地台区奥陶纪主要发育浅海稳定型灰岩,沉积环境为镶边碳酸盐岩台地,奥陶世早期海水较浅,生物繁盛,气候温暖;奥陶世中晚期海平面逐渐上升,海水加深,气候炎热;奥陶世末期地台持续上升,南部抬升至海平面以上,北部形成闭塞海湾[35]。研究区内下奥陶统发育地层自下而上为杨家坝组、分乡组、红花园组、大湾组、牯牛潭组(图1a)。研究区分乡组的沉积相主要是开阔台地,沉积的岩性主要是粒屑生屑灰岩、粒屑鲕粒灰岩、泥晶灰岩夹泥灰岩和泥岩。
通过对城口地区厚坪剖面分乡组野外露头进行实测,发现在厚坪剖面的分乡组与上伏地层红花园组及下伏地层杨家坝组均呈整合接触,厚度为33.6 m,其中部约有16.9 m的灰岩段具有明显的风暴沉积特征(图2)。岩性主要为灰色中层—薄层状泥晶灰岩,发育约25个风暴沉积序列(图2),每个序列的厚度介于20~200 cm。其中砾屑段主要发育于风暴段下部到中部,砾屑层厚度介于8~11 cm,粒径介于6~12 mm,反映出风暴强度在沉积时期由强变弱的特征。风暴段划分出2个海侵(TST)—海退(HST)旋回,整体上旋回下部发育灰色中层状砾屑生屑灰岩,中部发育灰色薄层状砂屑生屑灰岩,上部发育灰色薄层状泥灰岩与薄层—极薄层状泥岩互层,自下而上泥质含量增多。
-
风暴常发生于浅海陆棚区,形成的风暴流动力强,会搅动、搬运、侵蚀、悬浮海底沉积物,将其携带沉积至不同环境[38],形成如风暴粒序段等风暴沉积构造。城口厚坪剖面发育有典型的底冲刷构造、风暴砾屑段、风暴撕扯构造、菊花状构造、风暴层理等沉积构造。
-
底冲刷构造是由于风暴高峰期产生的风暴流对风暴浪基面以上的海底沉积物进行冲刷、淘洗,形成一个与下伏地层突变的底面和冲刷—充填构造,发育于风暴沉积底部[17]。厚坪剖面发育的底冲刷构造波型较缓(图3a,b),单一波长为20~80 cm,波峰为3~5 cm,反应风暴涡流强度较大,侵蚀能力强,上覆岩性为生屑砾屑灰岩,可见叠瓦状砾石,以颗粒支撑为主,见大量介壳生屑。
-
风暴砾屑层是风暴沉积的重要识别标志。厚坪剖面砾屑层厚度为30~50 cm,其中的砾屑颗粒成分主要为暗色泥晶白云岩,形态主要呈短柱状以及椭圆状,粒径为1 mm~3 cm,多集中在2 mm;分选性较差,次棱角—次圆状,基质支撑,砾屑的含量介于30%~50%,并且发育厚度较大的风暴生屑层,层厚介于40~60 cm。同时发育菊花状构造,该构造类型也是风暴涡流沉积的指相标志[38⁃39],表现为竹叶状砾屑呈放射状(图3c)。生物类型主要是双壳类(图3c,d,i)。
-
风暴浪摆动波和旋涡流触及浅海底床形成各种风暴层理构造,主要包括丘状交错层理、洼状交错层理、平行层理和水平层理等。在厚坪剖面分乡组的风暴岩中主要发育平行层理和丘状交错层理(图3g,h,l)。丘状交错层理是风暴沉积的特征标志,其底部为倾角很小的侵蚀冲刷面,其上层系与底面平行,上凸的为丘状交错层理,下凹的为洼状交错层理;纹层在横向上有规律地变厚,倾角有规律地向上减小或散乱,顶面呈丘状起伏,丘状交错层理多发育于风暴序列的上部单元[40]。在厚坪剖面分乡组风暴岩中发现的丘状交错层理岩性以泥质灰岩为主,厚度介于6~40 cm,单个波长介于19~40 cm,波峰介于2~4 cm。水平层理岩性主要以深灰色薄层灰岩与黑色薄层泥岩互层为主,厚度介于3~24 cm,夹有灰色透镜状灰岩,长轴介于2~9 cm,短轴介于0.5~1.0 cm。
-
风暴沉积序列是由于风暴岩在沉积过程中风暴作用在不同阶段的方式、持续时间以及强度的不同而使得风暴岩在纵向上形成的一系列有规律的沉积组合。一个典型的浅水碳酸盐岩完整风暴序列[38],从底至顶由以下5个沉积单元构成:(A)底冲刷和砾屑段,颗粒较大、破碎的砾屑沉积物;(B)粒序段,具有粒序的砂屑沉积物;(C)平行层理,粒度较细的粉砂屑沉积物;(D)丘状层理,具有特殊层理结构的粉砂屑沉积物;(E)泥质泥晶灰岩段,薄层的泥晶灰岩与泥岩。城口厚坪剖面分乡组可识别出5类风暴沉积序列。
-
主要由底冲刷和砾屑层A、粒序层B、平行层理段C组成(图4),风暴砾屑段(A段)主要为泥质灰岩,砾屑呈透镜状顺层分布,可见菊花状构造和叠瓦状构造。砾屑大小长轴为2~3 cm,短轴为0.2~0.5 cm,局部含生屑、鲕粒和砂屑(图3f,i,k),含砾率介于50%~60%,单层厚度在4~8 cm,向上粒度减小,颗粒间杂基支撑,可见大型的底冲刷面,单个波长可达60~80 cm,波峰为4~6 cm。粒序段(B段)为正粒序结构,总体为砾屑—砂屑—粉屑的正韵律结构,可见生物介壳在下部,为腹足类。上部主要为砂屑灰岩,杂基支撑。平行层理段(C段)主要是钙质泥岩与灰岩互层,泥岩厚度介于2~5 cm,灰岩层厚介于1~3 cm,向上泥质增加,夹灰岩透镜体。
-
主要由粒序层(B)、平行层理段(C)组成(图4),粒序段岩性主要是深灰色薄层状含生屑砂屑灰岩,局部呈透镜状,生屑以介壳为主,并且可见生屑呈倒小字分布。平行层理段(C)主要以灰岩夹泥质灰岩为主,局部灰岩呈透镜状,层厚介于2~5 cm,宽介于1~2 cm,顶部见页岩薄层,并且可见波状层理。
-
由底冲刷、砾屑层(A)、粒序层(B)、平行层理(C)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成(图4),砾屑层(A)下伏为薄层状泥质灰岩,底冲刷构造发育,形成砂屑、砾屑混杂沉积,砾屑和生屑顺层分布,层厚介于20~45 cm,可见菊花状构造。砾屑之间杂基支撑,杂基内部可见沙纹层理,砾屑呈椭圆状,短轴为2 cm,长轴为3~4 cm,长条状的砾屑短轴为0.5 cm,长轴为1~9 cm。粒序段(B)主要是由砂屑—粉屑的正粒序结构,局部呈透镜状,厚度介于2~7 cm。平行层理段(C)主要是钙质泥岩与灰岩,单层灰岩厚度介于1~2 cm,泥岩厚度介于0.5~1.0 cm。泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)厚度介于3~4 cm,可见水平层理发育。
-
由粒序段(B)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成(图4),粒序段(B)主要以砂屑灰岩为主,砂屑短轴一般为0.2~1.0 cm,长轴为1.5~3.0 cm。泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)以钙质泥岩为主,夹透镜状灰岩,长介于2~9 cm,宽介于0.5~1.0 cm。发育风暴远源浊流泥岩,其中见多个风暴浊流旋回,岩性为深灰色薄层泥岩夹透镜状灰岩,宽度介于2~3 cm,长介于5~12 cm,可见沙纹层理和水平层理,上段发育灰色薄层灰岩与泥岩互层,灰岩单层厚度介于1.0~1.5 cm,泥岩单层厚度介于1~2 cm。
-
由粒序段(B)、丘状层理段(D)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成(图4),粒序段(B)主要为砂屑灰岩,厚度介于12~14 cm,正粒序结构发育,从下部到上部主要呈砾屑到砂屑的过渡,下部砾屑长轴为2~4 cm,短轴为5~10 cm,上部砂屑长轴为0.2~1.0 cm,长轴为1.5~2.0 cm,其中生物介壳发育在下部,主要为腹足类,上部砂屑为颗粒杂基接触支撑;丘状层理段(D)岩性以泥晶灰岩为主,厚度介于5~8 cm,单个波长介于25~40 cm,波峰介于2.5~3.0 cm。泥质泥晶灰岩段(E),岩性主要是深灰色薄层泥岩夹薄层钙质泥岩,泥岩单层厚度小于1 cm,夹透镜状灰岩,水平层理发育。
基于剖面、镜下鉴定及风暴岩段统计,分析分乡组风暴序列的纵向展布特征:城口地区分乡组风暴沉积序列主要为序列Ⅰ—Ⅴ,纵向上呈序列Ⅰ→序列Ⅲ→序列Ⅴ→序列Ⅳ的演化特征,自下而上沉积环境演化为开阔台地→台地边缘→斜坡→陆棚,在纵向上表现为沉积水体加深的沉积特征。Ⅰ型序列结构主要发育在剖面下部,向上逐渐减少,至中部逐渐发育Ⅲ型序列结构,其中Ⅰ型序列发育规模较大,厚度相对于Ⅲ型序列较大,见大型冲刷面,波长可达70~80 cm,中下部夹有少量Ⅱ型序列结构,显示沉积早期风暴较强,水体较浅。而在分乡组中上部主要发育Ⅳ、Ⅴ型序列结构,在顶部发育两期Ⅰ型序列结构,规模均较大,厚度可达50~80 cm。分乡组沉积时期总体上呈现海平面逐渐上升,水体加深,风暴减弱的特征。
-
奥陶系分乡组沉积时期,城口地区为台缘滩—斜坡沉积[35]。通过总结厚坪剖面风暴沉积序列特征及类型与沉积特征,本文建立了城口地区分乡组风暴沉积模式(图5)。

图 5 城口地区下奥陶统分乡组风暴沉积模式图
Figure 5. Storm deposition model of the Lower Ordovician Fenxiang Formation, Chengkou area
序列Ⅰ发育大型的冲刷面以及砾屑层,表明风暴侵蚀能力较强,受到强烈风暴涡流对台缘的生屑滩进行剥蚀、撕裂,并发育大量的生物碎屑,距离风暴中心较近,水体较浅;其上又发育粒序段,顶部含有少量陆源碎屑,说明该序列为风暴回流沉积,位于风暴浪基面以上,部分碎屑颗粒向离岸地区搬运,因此该序列主要位于台缘浅滩。
序列Ⅱ下伏岩性主要是含生屑砂屑灰岩,底部无冲刷面,可见破碎状生物碎屑,砂屑分选性中等—较好,磨圆为次棱角—次圆状,可见撕扯构造,粒序层上部发育平行层理,说明该序列位于正常浪基面之下,风暴浪基面之上,且更靠近正常浪基面,为台地前缘斜坡的上部沉积。
序列Ⅲ可见明显的底冲刷界面,砾屑分选一般,磨圆为次棱角—次圆,可能是被风暴回流搬运的异地沉积。上部的粒序段形成与风暴回流搬运有关,呈正粒序,重力分异使沉积物粒度变细,顶部的水平层理及薄层钙质泥岩主要受风暴下部回流作用影响,表明水体较深,应该是形成于风暴浪基面附近且在风暴浪基面之上水体相对较深的台缘斜坡下部沉积。
序列Ⅳ粒序段的形成与风暴浊流的搬运有关,重力分异使沉积物粒度变细,同时上部的发育泥岩与灰岩互层受远源风暴浊流沉积控制,表明风暴流强度较弱,距离风暴中心较远,应该是位于水体较深的风暴浪基面之下的深海陆棚沉积。
序列Ⅴ下部主要是砂屑灰岩,表现出正粒序结构,与风暴回流有关的异地沉积;丘状交错层理是在风暴浊流和风暴远端震荡作用下形成,同时顶部发育薄层泥质泥晶灰岩,也是风暴浊积成因,分析表明沉积水体较深。因此,该序列的沉积环境应该是位于风暴浪基面附近的台地前缘斜坡下部。
通过分析扬子地台北缘城口地区分乡组风暴沉积特征,建立了分乡组风暴沉积模式。风暴沉积自下而上可以划分出侵蚀底面及砾屑段(A)、粒序段(B)、平行层理段(C)、丘状交错层理段(D)及远源风暴浊流沉积(E),该序列总体上反应了风暴能量由高到低的过程。
-
前人对扬子板块古地磁重建发现,扬子板块在早古生代位于受风暴强烈影响的热带低纬度区,到寒武纪扬子板块开始漂移,逐渐向北高纬度运动,在奥陶纪,扬子板块处于北纬6.5°~7.3°附近[41⁃42],而风暴活动常出现在纬度5°~35°之间[43]。因此,风暴流改造海底原始沉积物形成的风暴岩可作为恢复板块古纬度位置的重要证据。城口地区下奥陶统分乡组风暴岩的发现,表明研究区分乡组沉积时期扬子板块位于风暴频繁发生的热带、亚热带海域的低纬度区域。与古地磁资料[41⁃42]以及前人在贵阳乌当下奥陶统湄潭组[19]和湖北松滋刘家场下奥陶统红花园组[18]发现的风暴岩得出的扬子板块在奥陶纪处于低纬度赤道附近飓风带地区结论相一致。
-
目前报道的绝大多数风暴岩主要分布于浅海陆棚—缓坡、潮坪—滨岸带[38],因此风暴岩的发现可以指示沉积时期的古地理背景。早奥陶世,四川盆地主体位于稳定克拉通内坳陷之中,基本继承了寒武纪末期的岩相古地理格局,具有西高东低的特征,以碎屑滨岸、混积潮坪和清水碳酸盐岩台地环境为主[35]。由于风暴作用常发生在向开阔海方向的斜坡附近,使得在正常浪基面斜坡附近侵蚀、上扬卷起的原地沉积物被风暴流搬运到水体较深的正常浪基面之下再沉积。结合前人对扬子地台下奥陶统岩相古地理研究和城口地区分乡组沉积风暴岩特征进行综合分析,风暴岩在分乡组沉积时期的发现表明分乡组处于浅海陆棚—缓坡相带。根据早奥陶世古地理格局,该时期扬子板块正处于海侵时期,研究区位于台地边缘浅海地区,并且靠近斜坡位置,风暴频发。序列Ⅰ、序列Ⅱ、序列Ⅲ均与风暴回流有关,这种回流的产生要具有一定的坡度[13],处于台缘斜坡上部和下部;序列Ⅳ沉积环境为深水环境,为陆棚沉积;序列Ⅴ沉积环境位于水体较深的台缘斜坡下部的风暴浪基面附近,因此城口地区分乡组时期沉积环境应为台缘相带。同时,分乡组在扬子地台北缘厚坪西南方向是台地内部沉积,而在厚坪地区是台地边缘滩沉积,在厚坪东北方向是斜坡沉积。在扬子地台内,前人在寒武系及志留系均发现风暴沉积,分乡组风暴沉积环境与寒武系风暴岩沉积环境较为一致,以浅海陆棚—缓坡环境为主,而志留系已发现风暴沉积以浅水—滨岸环境为主,因此两者在风暴沉积序列上会有所不同。最近研究表明,随着热带海面温度的升高,大多数强烈的风暴频率会增加[44],而在扬子地台内寒武系及奥陶系所发现风暴岩的数量远高于志留系,因此寒武系奥陶系频繁发生的风暴岩可能与全球变暖时期相对应。这为早奥陶世扬子地台北缘提供了重要的岩相古地理证据。
-
扬子地台下奥陶统的有效储集层优势相带在波浪、潮汐水动力作用下发育的大规模台缘滩微相[17]。根据奥陶系扬子地台北缘古地理发现台地边缘微高地貌地区发育方向整体为北西到南东方向,且据上述风暴沉积对于岩相古地理的约束,城口地区下奥陶统主要为台地边缘沉积,处于正常浪基面附近,是台缘滩发育的有利相带。笔者通过对厚坪剖面实测发现分乡组与下部杨家坝组及上部红花园组皆发育厚层生屑灰岩和颗粒灰岩,并在分乡组见大量生屑呈破碎状分布,集中在分乡组中下部,认为其台缘滩颗粒岩发育于风暴减弱时期,整体厚度在35~40 m。同时,分乡组台缘滩分布应与下奥陶统扬子地台北缘台地边缘微高地貌发育方向一致,即分乡组在扬子地台北缘具备发育北西到南东向的优质颗粒滩型储层的古地理背景。
-
(1) 扬子地台北缘城口地区分乡组发育五个期次的风暴岩,具体划分出五种沉积风暴序列:序列Ⅰ主要由底冲刷和砾屑层(A)、粒序层(B)和平行层理段(C)组成,主要发育在台地边缘相带;序列Ⅱ相较于序列Ⅰ更加靠近斜坡和风暴浪基面一点,由粒序层(B)、平行层理段(C)组成,发育在靠近斜坡的台地边缘相带;序列Ⅲ由底冲刷和砾屑层(A)、粒序层(B)、平行层理(C)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成,主要沉积于台地边缘斜坡相带;序列Ⅳ主要由粒序段(B)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成,主要沉积在台地边缘斜坡下部;序列Ⅴ由粒序段(B)、丘状层理段(D)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成,主要发育在深海陆棚相带。
(2) 风暴层序自下而上的沉积环境演化为台地边缘、台地边缘斜坡、深海陆棚,纵向上表现为一个水体逐渐加深的沉积特征。
(3) 扬子地台北缘分乡组风暴岩的发现说明扬子板块在早奥陶时期位于低纬度风暴发育地区,并且证明分乡组沉积时期处于台缘—斜坡相带。这为早奥陶世扬子地台北缘提供了重要的岩相古地理证据。
(4) 扬子地台北缘分乡组在台地边缘沉积,处于正常浪基面附近,是台缘滩发育的有利相带。因此,扬子地台北缘分乡组具备发育大规模优质颗粒滩型储层的古地理背景。
Characteristics and Geological Significance of the Tempestites in the Lower Ordovician Fenxiang Formation, Upper Yangtze Platform
-
摘要: 目的 扬子板块中发育有十分丰富的风暴沉积,但对上扬子板块北缘奥陶系风暴岩的发育特征以及该区下奥陶系沉积环境、古海洋条件、古地理和沉积古地貌的研究较为薄弱。 方法 以上扬子地台北缘城口地区厚坪剖面分乡组中发育典型的风暴岩为研究对象,进行野外剖面详测和镜下薄片鉴定,研究分乡组风暴沉积序列和沉积模式并揭示其地质意义。 结果 城口地区分乡组风暴沉积构造主要有底冲刷构造、风暴砾屑层、粒序层理、丘状交错层理等。同时识别出5种风暴沉积序列:序列Ⅰ主要由底冲刷和砾屑层(A)、粒序层(B)和平行层理段(C)组成,主要发育在台地边缘相带;序列Ⅱ由粒序层(B)、平行层理段(C)组成,发育在靠近斜坡的台地边缘相带;序列Ⅲ由底冲刷和砾屑层(A)、粒序层(B)、平行层理(C)和泥质灰岩段(E)组成,主要沉积于台前斜坡相带;序列Ⅳ主要由粒序段(B)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成,主要沉积在台前斜坡下部;序列Ⅴ由粒序段(B)、丘状层理段(D)和泥质泥晶灰岩段(E)组成,主要发育在深水陆棚相带。风暴岩的发育指示上扬子地台在早奥陶世分乡期位于低纬度地区,城口地区以台缘—斜坡沉积为主,自下而上的沉积环境演化为台地边缘→台前斜坡→深水陆棚。 结论 上扬子地台城口地区分乡组风暴岩的发育表明上扬子地台在奥陶纪处于低纬度赤道附近,沉积环境为台缘带且具备发育大规模台缘滩的地质条件。Abstract: Objective The purpose of this study is to study the development characteristics of the Ordovician stormrock in the northern margin of the Upper Yangtze Plate, and the sedimentary environment, paleomarine conditions, paleogeography and sedimentary paleogeomorphology of the Lower Ordovician in this area. Methods The typical storm rocks in Fenxiang Formation of Houping section in Chengkou area of the upper Yangtze Platform are studied. Detailed field profile survey and microscopic thin section identification are carried out to study the sedimentary sequence and sedimentary model of Fenxiang Formation and reveal its geological significance. Results The tempestite sedimentary structures of the Fenxiang Formation in the Chengkou area include bottom scour structure, storm gravel layer, grain sequence bedding, and mound cross-bedding. In total, five tempestite sedimentary sequences were identified: Sequence I was composed of a bottom erosion and gravel layer (A), grain sequence (B), and parallel bedding segment (C) and developed in the platform margin facies; Sequence II consisted of a grain sequence (B) and parallel bedding segment (C), which developed in the platform margin facies near the slope. Sequence III was composed of a bottom erosion and gravel layer (A), grain sequence layer (B), parallel bedding (C), and argillaceous limestone segment (E) and primarily deposited in the fore-platform slope facies zone. Sequence Ⅳ consisted of a grain sequence segment (B) and argillaceous micrite segment (E), which were primarily deposited in the lower the fore-platform slope. Sequence V was composed of a grain sequence (B), mound bedding segment (D), and argillaceous micrite segment (E), which mainly developed in the deepwater shelf. The development of tempestites indicate that the Upper Yangtze platform was located at a low latitude in the Early Ordovician, and the Chengkou area was dominated by platform margin and slope deposits. The bottom-up sedimentary environment evolved into platform margin → platform front slope → deep water shelf. Conclusions The development of storm rock of Fenxiang Formation in Chengkou area of Upper Yangtze Platform indicates that the Upper Yangtze platform was near the equator of low latitude in Ordovician period, and the sedimentary environment was platform margin zone with geological conditions for developing large-scale platform margin shoals.
-
Key words:
- Upper Yangtze Platform /
- Sichuan Basin /
- storm rock /
- Fenxiang Formation /
- Ordovician
-
-
[1] Ager D V. The nature of the stratigraphical record[M]. London: MacMillan, 1973: 114. [2] Kelling G, Mullin P R. Graded limestones and limestone-quartzite couplets: Possible storm-deposits from the Moroccan Carboniferous[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1975, 13(3): 161-190. [3] 赵聪. 四川盆地碳酸盐风暴岩发育特征及地质意义[J]. 天然气技术与经济,2018,12(3):1-4. Zhao Cong. Development characteristics and geological significance of carbonate empestites, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2018, 12(3): 1-4. [4] 孟祥化,乔秀夫,葛铭. 华北古浅海碳酸盐风暴沉积和丁家滩相序模式[J]. 沉积学报,1986,4(2):1-18. Meng Xianghua, Qiao Xiufu, Ge Ming. Study on ancient shallow sea carbonate storm deposits (Tempestite) in North China and Dingjiatan model of facies sequences[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1986, 4(2): 1-18. [5] 刘宝珺,张继庆,许效松. 四川兴文四龙下二叠统碳酸盐风暴岩[J]. 地质学报,1986,60(1):55-67. Liu Baojun, Zhang Ji-qing, Xu Xiaosong. On the calcareous tempestites in the Lower Permian of Silong, Xingwen, Sichuan[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1986, 60(1): 55-67. [6] 刘明博,林晋炎,高硒,等. 陕西宁强胡家坝地区震旦系灯影组风暴沉积特征[J]. 城市地质,2018,13(2):57-63. Liu Mingbo, Lin Jinyan, Gao Xi, et al. The characteristics of storm deposit about Dengying Formation of Sinian System in Hujiaba, Ning-qiang county, Shaanxi[J]. Urban Geology, 2018, 13(2): 57-63. [7] 马瑞申,张良,杜远生,等. 豫北地区寒武系风暴岩沉积特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2011,30(4):15-20. Ma Rui-shen, Zhang Liang, Du Yuansheng, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and its geological implications of Cambrian tempestite in northern Henan province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(4): 15-20. [8] 马志鑫,张万平,刘伟,等. 黔东镇远地区早寒武世清虚洞组潮坪风暴沉积特征及古地理意义[J]. 沉积学报,2012,30(5):787-794. Ma Zhixin, Zhang Wanping, Liu Wei, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of tidal storm deposit of early Cambrian Qing-xudong Formation in the Zhenyuan area, eastern Guizhou and its palaeogeographical implications[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(5): 787-794. [9] 景宇轩,刘建波,闫振,等. 利用风暴沉积类型恢复海平面变化:以北京西山下苇甸剖面寒武纪中晚期风暴沉积为例[J]. 古地理学报,2015,17(5):653-668. Jing Yuxuan, Liu Jianbo, Yan Zhen, et al. Reconstructing sea-level changes from types of storm deposits: An example of the Middle and Late Cambrian at Xiaweidian section of western Hills, Beijing[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(5): 653-668. [10] 冯宇翔,宋金民,刘树根,等. 川西地区雷口坡组风暴沉积特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报,2023,41(3):661-672. Feng Yuxiang, Song Jinmin, Liu Shugen, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and geological significance of tempestites in the Leikoupo Formation, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(3): 661-672. [11] 李壮福,郭英海. 徐州地区震旦系贾园组的风暴沉积[J]. 古地理学报,2000,2(2):19-27. Li Zhuangfu, Guo Yinghai. Storm deposits in the Sinian Jiayuan Formation of Xuzhou area[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2000, 2(2): 19-27. [12] 赵灿,陈孝红,李旭兵,等. 峡东地区埃迪卡拉系灯影组风暴岩的发现及其环境意义[J]. 地质学报,2013,87(12):1901-1912. Zhao Can, Chen Xiaohong, Li Xubing, et al. Characteristics of tempestite of Ediacaran Dengying Formation, in the eastern Yangtze gorges area and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(12): 1901-1912. [13] 宋金民,刘树根,赵异华,等. 川中地区中下寒武统风暴岩特征及沉积地质意义[J]. 石油学报,2016,37(1):30-42. Song Jinmin, Liu Shugen, Zhao Yihua, et al. Characteristics and sedimentary geological significances of Lower-Middle Cambrian tempestites in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(1): 30-42. [14] 王瀚,李智武,刘树根,等. 扬子地台北缘城口地区上寒武统洗象池组风暴沉积特征及其地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质,2019,41(2):176-184. Wang Han, Li Zhiwu, Liu Shugen, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and geological significance of tempestites in the Upper Cambrian Xixiangchi Formation, Chengkou area, northern margin of the Yangtze Platform[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(2): 176-184. [15] 周琦,颜佳新,张命桥. 黔东北地区寒武系清虚洞组钙质风暴岩及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报,2006,25(2):25-28. Zhou Qi, Yan Jiaxin, Zhang Mingqiao. Calcareous tempestite from the Cambrian Qingxudong Formation in northeastern Guizhou province and their geological implications[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(2): 25-28. [16] 黄乐清,刘伟. 湘西北龙山地区下奥陶统桐梓组潮坪风暴岩的发现及其意义[J]. 沉积学报,2016,34(5):830-841. Huang Leqing, Liu Wei. Characteristics of tempestite of Lower Ordovician Tongzi Formation, in the Longshan area, northwestern Hunan and its geological significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 830-841. [17] 金鑫,宋金民,刘树根,等. 西昌盆地新基姑地区大箐组风暴岩特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报,2021,39(4):908-918. Jin Xin, Song Jinmin, Liu Shugen, et al. Characteristics and geological significance of tempestites in the Daqing Formation, Xinjigu area, Xichang Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(4): 908-918. [18] 李维锋,肖传桃,孟宪富. 湖北刘家场下奥陶统碳酸盐岩风暴沉积[J]. 江汉石油学院学报,1993,15(2):9-14. Li Weifeng, Xiao Chuantao, Meng Xianfu. The carbonate tempestites within the Lower Ordovician in Songzi, western Hubei[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 1993, 15(2): 9-14. [19] 蒙锡龙,杨积琴. 贵阳乌当地区奥陶系湄潭组风暴岩特征[J]. 贵州地质,1988,5(2):143-146. Meng Xilong, Yang Jiqin. The characteristics of tempestites in the Meitan Formation of Ordovician in Wudang, Guiyang[J]. Geology of Guizhou, 1988, 5(2): 143-146. [20] 陈世悦,张鹏飞,杨怀宇. 湘西北江坪地区志留系风暴沉积特征及意义[J]. 古地理学报,2009,11(1):51-57. Chen Shiyue, Zhang Pengfei, Yang Huaiyu. Silurian storm deposits in Jiangping area, northwestern Hunan province: Characteristics and geological significances[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2009, 11(1): 51-57. [21] 张廷山,侯方浩,高卫东,等. 川西北地区早志留世风暴岩及其环境与古生态意义[J]. 沉积学报,1993,11(2):66-74. Zhang Tingshan, Hou Fanghao, Gao Weidong, et al. Tempestites and the environmental paleoecological significance of Early Silurian, NW Sichuan area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1993, 11(2): 66-74. [22] 魏钦廉,郑荣才,周刚,等. 龙门山甘溪组谢家湾段风暴岩沉积特征及其意义[J]. 中国地质,2011,38(5):1282-1288. Wei Qinlian, Zheng Rongcai, Zhou Gang, et al. Clastic tempestite in Xiejiawan member of Ganxi Formation within Longmenshan area and its significance[J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(5): 1282-1288. [23] 许安涛,李凤杰,刘奎,等. 北川甘溪下泥盆统风暴岩沉积特征及其沉积模式[J]. 中国地质,2018,45(5):1049-1061. Xu Antao, Li Fengjie, Liu Kui, et al. The characteristics and sedimentary model of storm deposits in the Lower Devonian strata of Beichuan[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(5): 1049-1061. [24] 屈雪林. 四川北川甘溪地区下泥盆统风暴沉积研究及其地质意义[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2017. Qu Xuelin. The research of storm deposits in the Lower Devonian of Ganxi, Beichuan, Sichuan and its geological significance[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017. [25] 张昊,李凤杰,沈凡,等. 四川盆地龙门山区甘溪石沟里泥盆系养马坝组风暴沉积特征及其地质意义[J]. 古地理学报,2019,21(3):441-450. Zhang Hao, Li Fengjie, Shen Fan, et al. Storm deposits characteristics and its geological significance in the Devonian Yangmaba Formation from Shigouli section, Longmenshan area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2019, 21(3): 441-450. [26] 徐锦龙,洪天求,贾志海,等. 川西北江油马角坝地区黄龙组下部风暴沉积特征[J]. 地质科学,2012,47(2):422-439. Xu Jinlong, Hong Tianqiu, Jia Zhihai, et al. The characteristics of storm deposits in the Lower Huanglong Formatiom of Majiaoba area, northwestern Sichuan province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2012, 47(2): 422-439. [27] 林彤,刘树根,宋金民,等. 川北南江地区下三叠统飞一段风暴沉积特征及地质意义[J]. 沉积学报,2015,33(5):899-908. Lin Tong, Liu Shugen, Song Jinmin, et al. The sedimentary characteristics and geological significances of carbonate tempestites near the boundary of Late Permian to Early Triassic at Nanjiang section, North of Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(5): 899-908. [28] 陈林洲,罗新民,肖劲东. 鄂东南早三叠世钙质风暴沉积特征及其初步研究[J]. 岩相古地理,1991(3):1-9. Chen Linzhou, Luo Xinmin, Xiao Jindong. Early Triassic calcareous storm deposits in southeastern Hubei[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 1991(3): 1-9. [29] Li Zhenyu. The tempestite sedimentary characters of Early Triassic Induan Formation in northwestern Sichuan area[J]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. [30] 彭靖淞,刘树根,赵霞飞,等. 川西中三叠统天井山组风暴沉积的发现及古地理意义[J]. 岩性油气藏,2009,21(1):83-88,111. Peng Jingsong, Liu Shugen, Zhao Xiafei, et al. Discovery of tempestite in Middle Triassic Tianjingshan Formation in western Sichuan and its paleogeographic significance[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2009, 21(1): 83-88, 111. [31] 曾德勇,时志强,张华,等. 广元上寺剖面下三叠统飞仙关组风暴岩:巨型季风体制下的极端气候事件?[J]. 沉积学报,2011,29(3):440-448. Zeng Deyong, Shi Zhiqiang, Zhang Hua, et al. Tempestite of Early Triassic Feixianguan Formation in Shangsi section, Guanyuan: Are they extreme climatic event under Megamonsoon system?[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(3): 440-448. [32] 李华启,姜在兴,邢焕清,等. 四川盆地西部上三叠统须家河组二段风暴岩沉积特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2003,24(1):81-86. Li Huaqi, Jiang Zaixing, Xing Huanqing, et al. Characte-ristics of storm deposits in Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(1): 81-86. [33] 赵聪,刘树根,宋金民,等. 川西汉旺地区雷口坡组四段风暴岩特征及地质意义[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(1):94-103. Zhao Cong, Liu Shugen, Song Jinmin, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and geological significance of tempestites in the fourth member of the Leikoupo formation at the Hanwang section, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(1): 94-103. [34] 郭正吾. 四川盆地形成与演化[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1996. Guo Zhengwu. The formation and development of Sichuan Basin[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1996. [35] 刘伟,洪海涛,徐安娜,等. 四川盆地奥陶系岩相古地理与勘探潜力[J]. 海相油气地质,2017,22(4):1-10. Liu Wei, Hong Haitao, Xu Anna, et al. Lithofacies paleogeography and exploration potential of Ordovician in Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2017, 22(4): 1-10. [36] 陈洪德,郭彤楼. 中上扬子叠合盆地沉积充填过程与物质分布规律[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2012. Chen Hongde, Guo Tonglou. Sedimentary filling process and material distribution in Middle and Upper Yangtze superimposed basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. [37] 贾承造,李本亮,张兴阳,等. 中国海相盆地的形成与演化[J]. 科学通报,2007,52(增刊1):1-8. Jia Chengzao, Li Benliang, Zhang Xingyang, et al. Formation and evolution of the Chinese marine basins[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(Suppl.1): 1-8. [38] 宋金民,杨迪,李朋威,等. 中国碳酸盐风暴岩发育特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质,2012,26(3):589-600. Song Jinmin, Yang Di, Li Pengwei, et al. Development characteristics and geological significance of carbonate tempestites in China[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(3): 589-600. [39] 周进高,赵宗举,邓红婴. 淮南地区风暴岩特征及其沉积环境[J]. 石油勘探与开发,1999,26(5):73-76. Zhou Jin’gao, Zhao Zongju, Deng Hongying. Upper Proterozoic Lower Paleozoic tempestites characters and their environmental significance to Huainan region of Anhui[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1999, 26(5): 73-76. [40] Jin J S, Harper D A T, Cocks L R M, et al. Precisely locating the Ordovician equator in Laurentia[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(2): 107-110. [41] 刘育燕,杨巍然,森永速男,等. 华北、秦岭及扬子陆块的若干古地磁研究结果[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报,1993,18(5):635-641. Liu Yuyan, Yang Weiran, Hayao M, et al. Some paleomagnetic results on North China, Qinling and Yangtze blocks[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1993, 18(5): 635-641. [42] 吴汉宁,朱日祥,白立新,等. 扬子地块显生宙古地磁视极移曲线及地块运动特征[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,1998,28(增刊1):69-78. Wu Hanning, Zhu Rixiang, Bai Lixin, et al. Revised apparent polar wander path of the Yangtze Block and its tectonic implications[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 1998, 28(Suppl.1): 69-78. [43] Marsaglia K M, Klein G D. The paleogeography of Paleozoic and Mesozoic storm depositional systems[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(2): 117-142. [44] Aumann H H, Ruzmaikin A, Teixeira J. Frequency of severe storms and global warming[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(19): L19805. -





 下载:
下载: