HTML
-
浊流是含陆源碎屑水体沿水下斜坡或峡谷流动的高密度底流,是由流体中的悬浮沉积物所引起的密度差造成的,具牛顿流体特性,其悬浮颗粒的主要支撑机制为湍流,为重力流的一种特殊形式[1⁃5]。浊流常存在于海洋和湖泊中,其流变性受含砂量、流速、颗粒支撑机制以及黏性等因素的影响[6⁃12],可搬运陆源沉积物到深水区中,是将沉积物向深水区输送的重要机制及营力之一[13]。浊流形成的浊积岩层能成为良好的油气储层已成为国内外石油地质学界及产业界的共识[14⁃20]。
在20世纪50年代,Kuenen et al.[21]在基于一系列水槽实验和长期野外露头观察的基础上发表了《浊流是递变层理的成因》一文,该项工作突破了传统机械沉积的认识,标志着浊流理论的正式成立,开辟了浊流沉积的新篇章。Bouma[22]于1962年根据法国Annot砂岩里多条剖面的总结建立了经典的浊积岩垂向序列,并分析了其在垂向上的岩性特征及沉积构造。然而在浊流实验中,还未能复刻一个完整的鲍马序列,故不能涵盖所有浊积岩类型[2,23];lowe[3⁃4]对鲍马序列进行了补充,依据流体流变学特征认为浊流属于流体态流。在基于浊积岩系统研究的基础上,国内外学者在基于水槽实验手段又对浊流的流速、浓度、泥砂含量、传输过程及流体演化等进行了探讨[24⁃25]。Keulegan[26]通过对密度流的研究获取了部分浊流头部的参数;Hampton[27]从理论和试验角度详细讨论了由块体流到浊流的演变,并发现该演化是在块体流的头部发生的;Garcia[28⁃29]通过水槽研究斜坡附近浊流的运移规律,在实验中观察到了明显的水跃现象,并提出了在浊流中沉积物的分布模型;Barahmand et al. [30]通过水槽实验对四种不同粗糙程度的底床进行了水跃实验,结果表明随着坡度的增大,浊流沿着跃变区和超临界区的环境水卷吸量也会随之增加。上述实验多集中于富砂、黏性的的重力流沉积物,Baker et al.[10⁃11]对比了不同黏土类型及浓度条件下沉积物重力流的流动特性,研究发现随着悬沙浓度的增加,水流类型由低密度浊流、高密度浊流和泥流转变为滑流,并定量探究了浊流的流动特性、头部速度、跳动距离以及沉积几何形态。
可见,前人对浊流流体转变、沉积过程、形成机理有了较为丰富的研究,且实验结果表明不同泥砂比、悬浮泥砂浓度对浊流的动力学及流体特性影响较大。综上,前人研究主要体现在环境流体力学方面,而应用到地质学方面的深水重力流沉积过程模拟研究还相对较少,特别是针对浊流作用下细粒沉积物运动规律及沉积特征的研究较为匮乏,亟须进一步深入探究。为正确认识浊流作用下细粒沉积物运移过程规律,深入探讨流体流速、沉积物搬运距离及展布受控因素,基于环形水槽沉积模拟实验进行研究,提出关于湖相细粒浊积岩的新认识。相关研究有助于掌握细粒浊流沉积物运移规律,可能为细粒非常规油气勘探与开发提供新的思路。
-
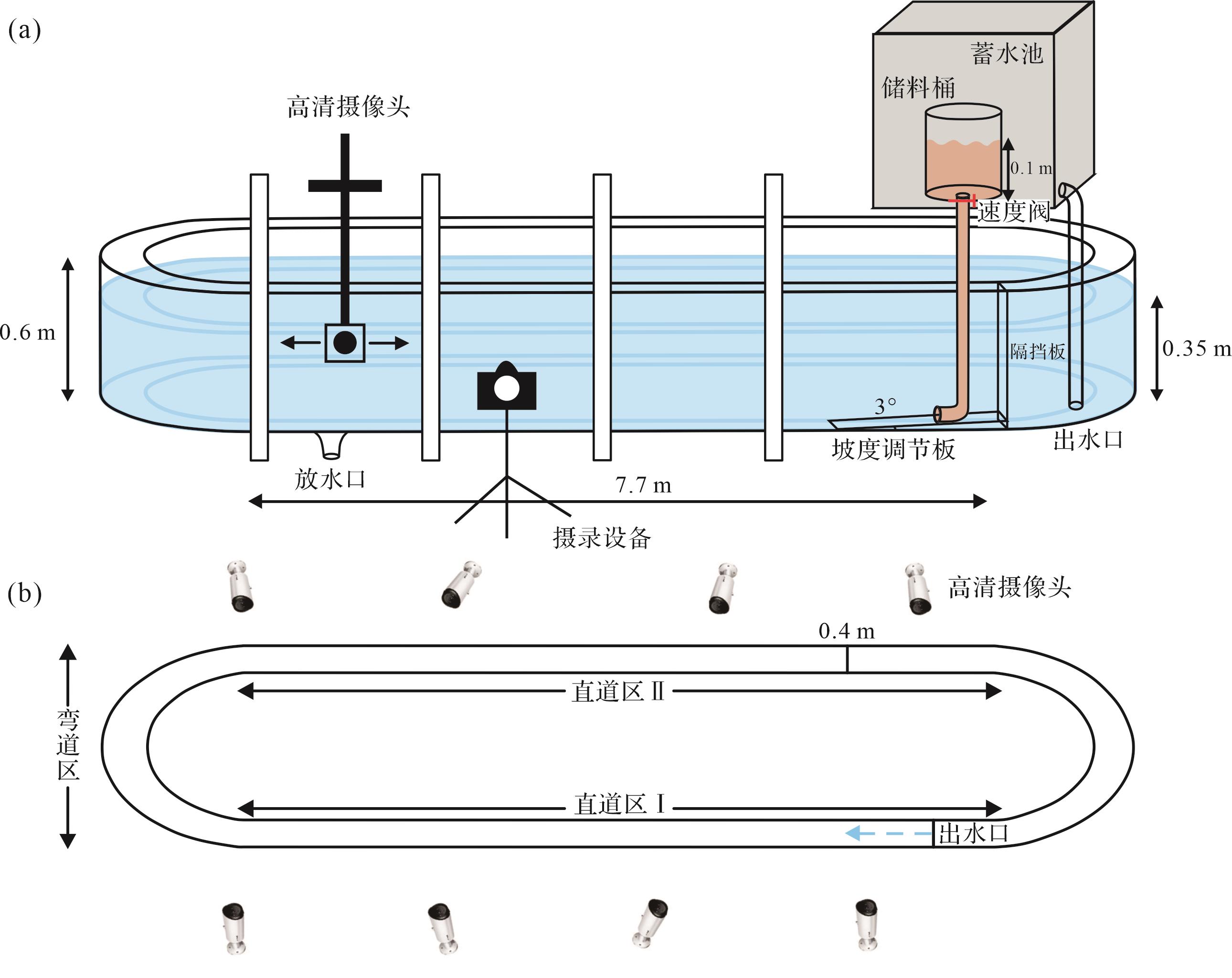
本次沉积物理模拟实验在长江大学武汉校区环形水槽模拟实验室中完成,环形水槽装置由两个直线段和两个环形段组成(图1a),其中两个直线段长各7.7 m,两半环段长各5.8 m,深0.6 m,宽0.4 m,整个环形水槽总长27 m。沉积模拟装置包括定量供水装置、储料桶、速度控制阀、循环抽水泵、图像摄录设备、坡度调节板、隔挡板等。蓄水池用于定量供水,在储料桶里对沉积物进行均匀搅拌并通过控制速度阀释放沉积物至水槽中;图像摄录设备可用于实验中全程拍照和录像(图1b),以便于后期的详细观察与研究,实验系统具有条件可控、全程监控、实时检测的优势。
-
本次实验基于前人研究[6⁃12],选取初始流速、沉积物浓度、砂泥比三组条件为实验参数(表1),开展水槽沉积模拟实验研究,该组参数能较为详尽地描述浊流的头部形态、流速、沉积形态,以探究浊流的动力学机制及流体特性,共设定为三组九轮对比实验(表1)。
实验轮次 坡度/(°) 水深/m 储料池水/m 细砂∶粉砂∶泥 初始流速/(V m/s) 沉积物浓度/C% 实验组1-1 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶12 0.15 5 实验组1-2 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶12 0.30 5 实验组1-3 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶12 0.60 5 实验组2-1 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶12 0.15 20 实验组2-2 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶12 0.15 10 实验组2-3 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶12 0.15 5 实验组3-1 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶6 0.15 5 实验组3-2 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶12 0.15 5 实验组3-3 3° 0.35 0.2 1∶2∶18 0.15 5 Table 1. Design Table for experimental periods and hydrodynamic parameters of circular flume
实验组一:主要通过模拟流速(低流速0.15 m/s、中等流速0.30 m/s、较高流速0.60 m/s)变化条件下细粒物质的搬运与沉积过程,保持其他条件不变,对比不同初始流速下细粒沉积物的搬运距离及沉积物空间分布的差异;实验组二:以实验组一为依据,其他条件不变,选取最为合适的流速,通过模拟沉积物浓度(5%、10%、20%)变化条件下细粒物质的搬运与沉积过程,对比不同沉积物浓度下细粒沉积物的扩散方式及速度、搬运距离、沉积物空间分布特征;实验组三:以实验组一、二为依据,保持其他条件不变,选取最合适的初始流速及沉积物浓度通过模拟砂泥比(1∶2∶6、1∶2∶12、1∶2∶18)变化条件下细粒物质的搬运与沉积过程,对比不同沉积物含量下细粒沉积物的流体流速、搬运距离、沉积物空间分布等特征。
-
在实验过程中,从沉积物开始释放至流动过程中,采用摄录设备从水槽侧面、顶部及底部三个方向摄录,及时记录实验现象,并对流动过程中的重要实验现象进行拍摄;使用多普勒流速仪对流体流速进行实时监测,每间隔1 m进行一次头部流速测量;待细粒沉积物在流体携带下搬运至完全沉积,采用水下测量的方式,每间隔1 m测量其沉积物厚度并进行取样,使用BT-9300ST激光粒度分析仪对样品进行粒度分析,取D10、D50、D90等有代表性的数值进行表格化处理,并对不同参数的粒度曲线结果进行对比分析。
1.1. 模拟设备与观测手段
1.2. 实验方案
1.3. 实验观测记录
-
实验发现,每轮模拟实验中流体流动过程和现象具有一定相似性。因此,现以实验组3-2为例详细描述实验过程中的现象及规律,整个搬运过程可大致分为三个阶段。
-
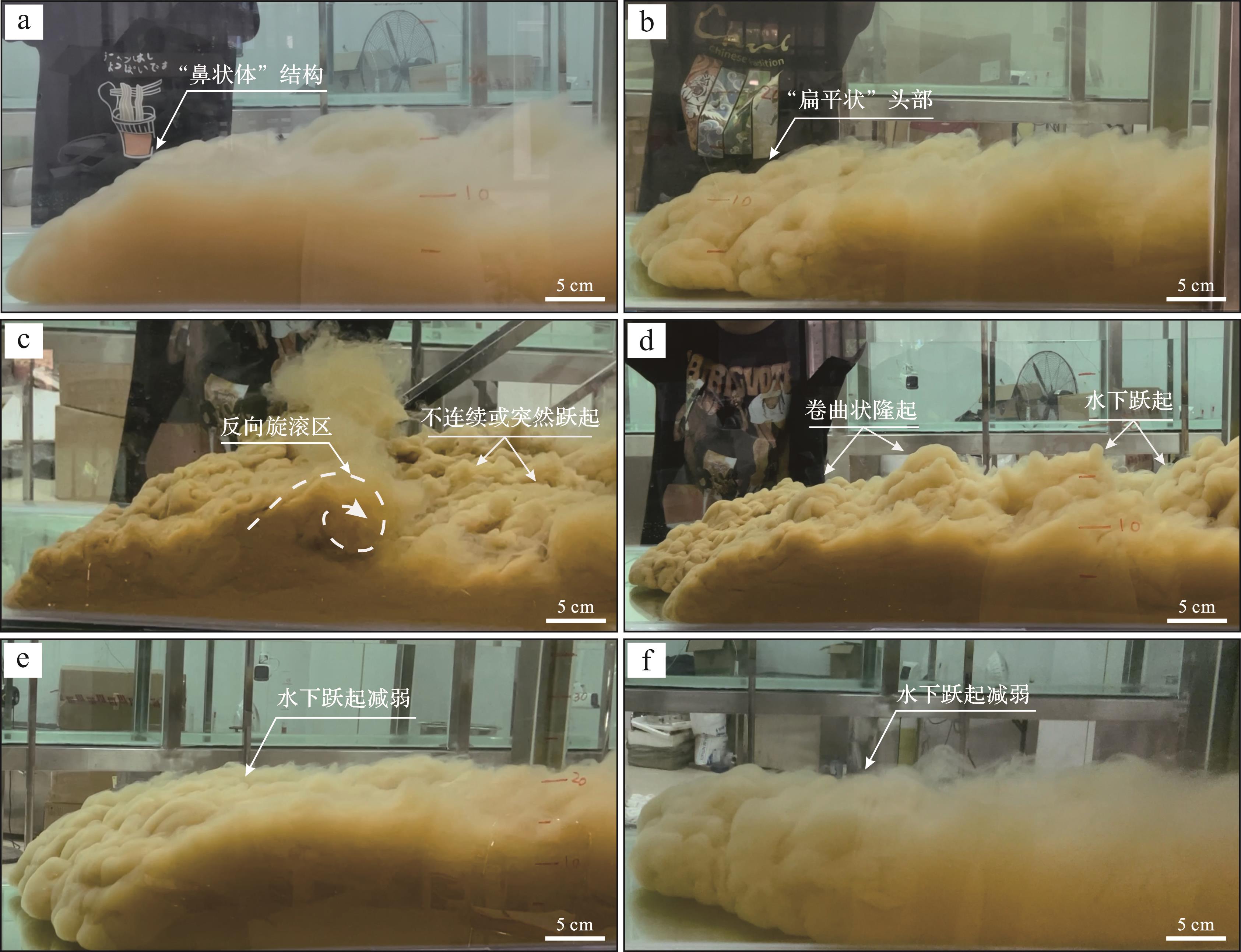
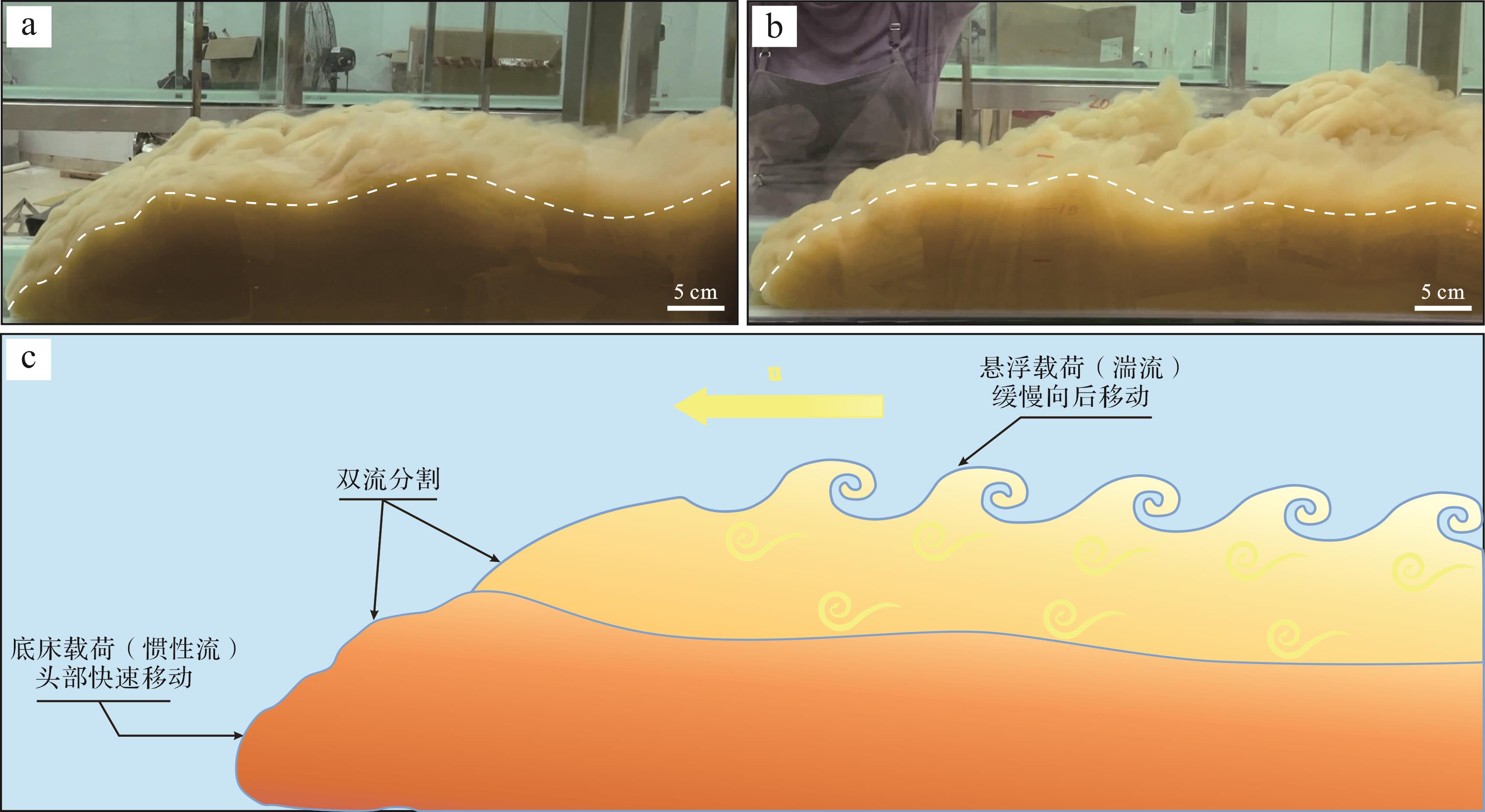
实验开始时,将速度控制阀打开,浊流携带砂泥混合物以一定的初速度突然被释放出。刚开始时,可以观察到水槽内浊流与环境流体之间发生剧烈的交互作用,流体紊乱程度较高,流体头部及体部沿着水槽向前移动,在平行水流方向上流体头部呈鼻状体结构(图2a)或尖的扁平形(图2b),这种形状以及流体头部的厚度随浊流向前搬运会不断发生细微变化;在靠近物源区,浊流流体能量较大,水槽中水下水跃现象极为发育,在浊流上部由于水跃作用强烈扰动,会出现反旋回的旋滚,将环境流体(水或空气)卷入并相互作用,形成一个反向旋滚区(图2c);而在流体表面可见多个隆起(图2c,d),隆起表现为不连续或突然跃起,不断消失又不断出现,呈现出多期次交替出现的现象。

Figure 2. Photos of the morphological characteristics of turbidity current head and water⁃jump phenomenon
水下水跃又称为水力跃迁,在紊流呈极端情况时出现,为超临界流向亚临界流过渡时产生[31]。在发生水跃时,可见浊流流速降低,流体部分动能被紊流所消散,转化为位能以致流体液面明显增高,并将环境流体(水或空气)卷入与浊流流体混合,使得沉积物及流体浓度也随之下降,甚至还可能引起流体类型的改变[32];在实验中,当流体厚度或深度突然增高时为水下水跃开始的标志,为“水跃起点”;当反向旋滚区逐渐变得平缓时,称为“水跃终点”。
当所用实验样为纯泥时,其在流体搬运中所需的能量较小,流动速度缓慢,引起的水下水跃现象不明显;可能是缺少了砂泥之间的相互作用力,导致流体前进驱动力也随之减少,水下水跃现象也逐渐减弱(图2e,f)。
悬浮沉积物继续随浊流向前搬运过程中,可见浊流头部厚度较大,头部近底层处浓度及密度最大,而体部浓度及密度较小(图3a,b)。在搬运过程中,流体依靠悬浮沉积物的湍流支撑及流体与环境流体之间的密度差获得不断前进的驱动力[10],高密度的浊流头部引导其密度、浓度及厚度均较小的本体向前移动,以快速的惯性流搬运沉积物;而在浊流上部,由于湍流扩散,且与上层水体的交换导致其体内卷吸进入更多的环境水,使流速减小,随之密度也逐渐减小,快速运动的惯性流逐渐转变为缓慢运动的湍流(图3c),泥沙浓度显著减小,呈现出流体头部较厚,体部较薄的特点。Muttiet et al.[33]应用Sander的理念将这种现象称为“双流分割”,实验中所出现的浊流由快速运动的惯性流(粒状)和缓慢运动的湍流两部分组成。
-
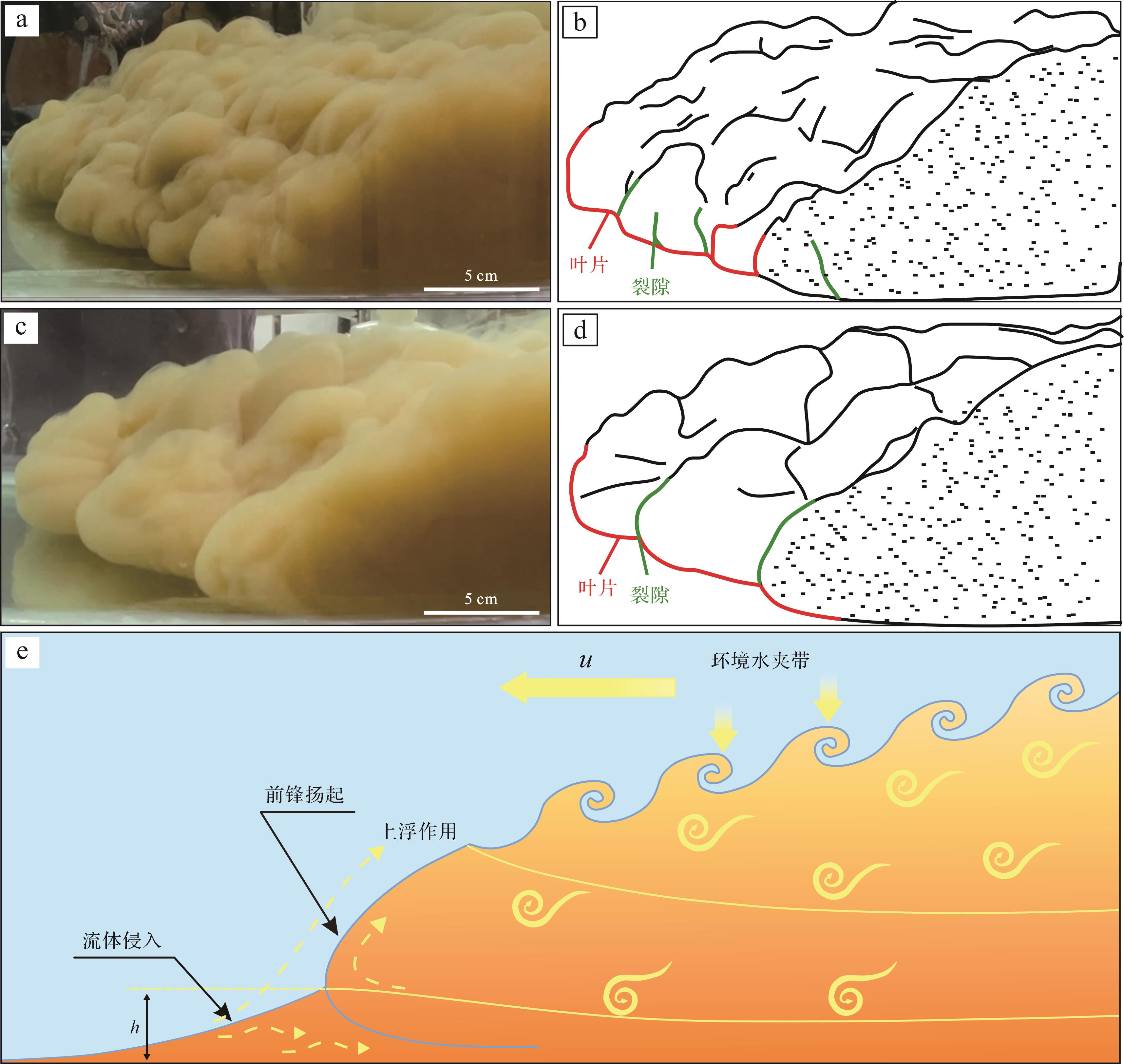
浊流流体沿水槽直道区继续向前流动直至进入弯道区,流体头部与环境流体之间发生着复杂的混合作用,从正视角度观察浊流头部特征,可见头部之间分裂成多个叶片状,主要可分为裂隙和叶片两种结构[34](图4a~d)。在直道区时裂隙和叶片已存在,尺寸较小,数量较多,在弯道区时尺寸较大,但数量较少。
根据实验观察,裂隙不会消失,一般与其附近的裂隙互相吸收。在运动过程中,叶片的宽度迅速地膨胀或收缩,当叶片达到最大尺寸,两个叶片之间就会形成新的裂隙。对裂隙和叶片的观察表明,在稳定的流体中,它们的出现和消失都十分迅速,随着搬运距离增加,流体能量逐渐降低,搬运能力下降,所产生的裂隙和叶片数量也随之减少。两种结构是由于环境流体密度与流体前锋密度之间差异导致重力不稳定而产生的。流动过程中,浊流头部涡流从底床裹挟悬浮沉积物,在流体前进过程中流体前锋底部受到水槽底部摩擦力的影响,其最底部的流线朝着流体尾部方向延伸,流体会向上扬起一些距离,由此在流体前锋的下部,产生一个环境流体的小循环(图4e)。此时环境流体进入这一密度小于流体前锋密度的区域,造成重力不稳定的现象。这部分流体上升和向前移动的过程中,逐渐形成裂隙与叶片。
-
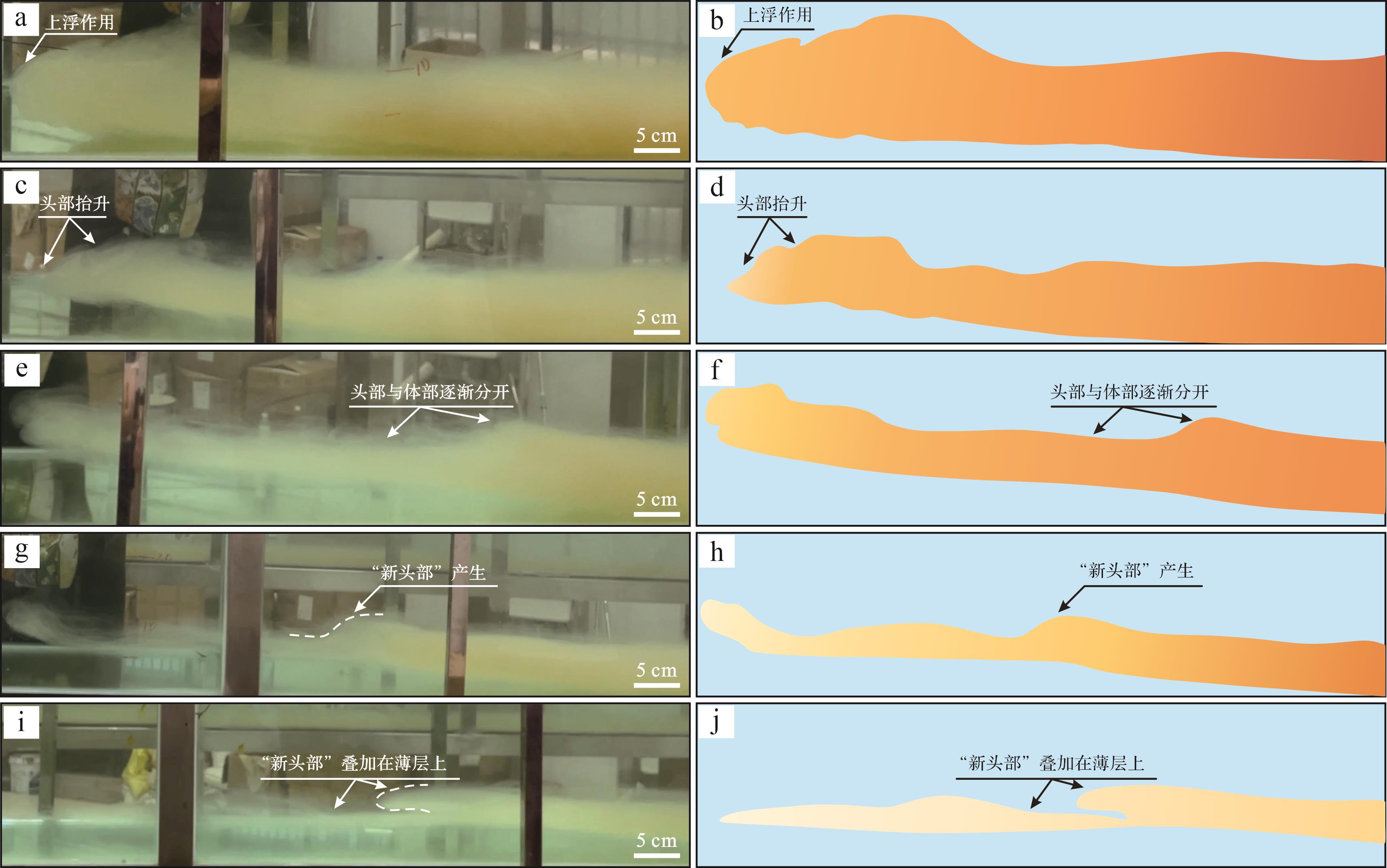
当浊流经过弯道区至第二个直道区时,流体紧贴基底底部移动,在移动一定距离后,可随时间变化逐渐观察到流体头部抬升、头部与体部逐渐分离、在本体前端逐渐形成“新头部”并继续向前运动的现象(图5),期间可大致分为四个阶段。

Figure 5. Time evolution diagram of turbidity currents from “lofting” to “new head” phenomena under experimental conditions
(1)头部抬升阶段:在移动一定距离后,观察到环境流体侵入浊流头部与基底接触部位之间,水流因沉积而失去部分砂质悬浮荷载时,淡水会引起浮力反转(抬升),流体头部逐渐开始抬升并与底床之间分离开来且距离缓慢增大,减少了流体头部与底床的剪切拖拽及摩擦力。随着流体不断被周围水体稀释变薄,流体头部浓度逐渐减小,由舌状逐渐变化成云雾状脱离水槽底床向上抬升并继续快速向前搬运,这种现象即“上浮作用”[35⁃38](图5a,d);(2)头部与体部分离阶段:在上浮作用下,流体前部的底床阻力显著降低,快速向前搬运,细粒沉积物由于流动分离作用和湍流分散压力在底床产生强烈的“云状拖曳”现象。流体头部与水体稀释,与体部产生速度与密度差,头部与体部逐渐分离,其中头部速度相对较快,浓度低,颜色较浅,呈隆起状;而体部速度较慢,但浓度高于头部,颜色较深,呈平缓状(图5e,f);(3)“新头部”形成阶段:由于头部速度较体部更快,二者逐渐拉开距离,直至头部完全脱离身体,头部继续向前搬运;而后在本体前端会缓慢地形成一个“新的头部”(图5g,h);(4)“新头部”继续运动阶段:“新头部”同样具有上扬的特点,在脱离本体后,被水体不断稀释、变形,密度降低,叠覆在薄层之上(图5i,j),缓慢地向前移动,漂浮在离散水层上快速移动的头部与附着在床层上并以较慢速度移动的体部之间由于前进速度差异导致逐渐分离,二者仅由薄层砂相连。在流体经过“上浮”、头部加速等作用后,流体头部不断裂解,发生沉积,新的流体头部又开始形成,浓度较高,呈舌状缓慢向前搬运,随着已与本体分离的头部继续往前搬运直至消散。
2.1. 第一阶段(直道区Ⅰ)
2.2. 第二阶段(弯道区)
2.3. 第三阶段(直道区Ⅱ)
-
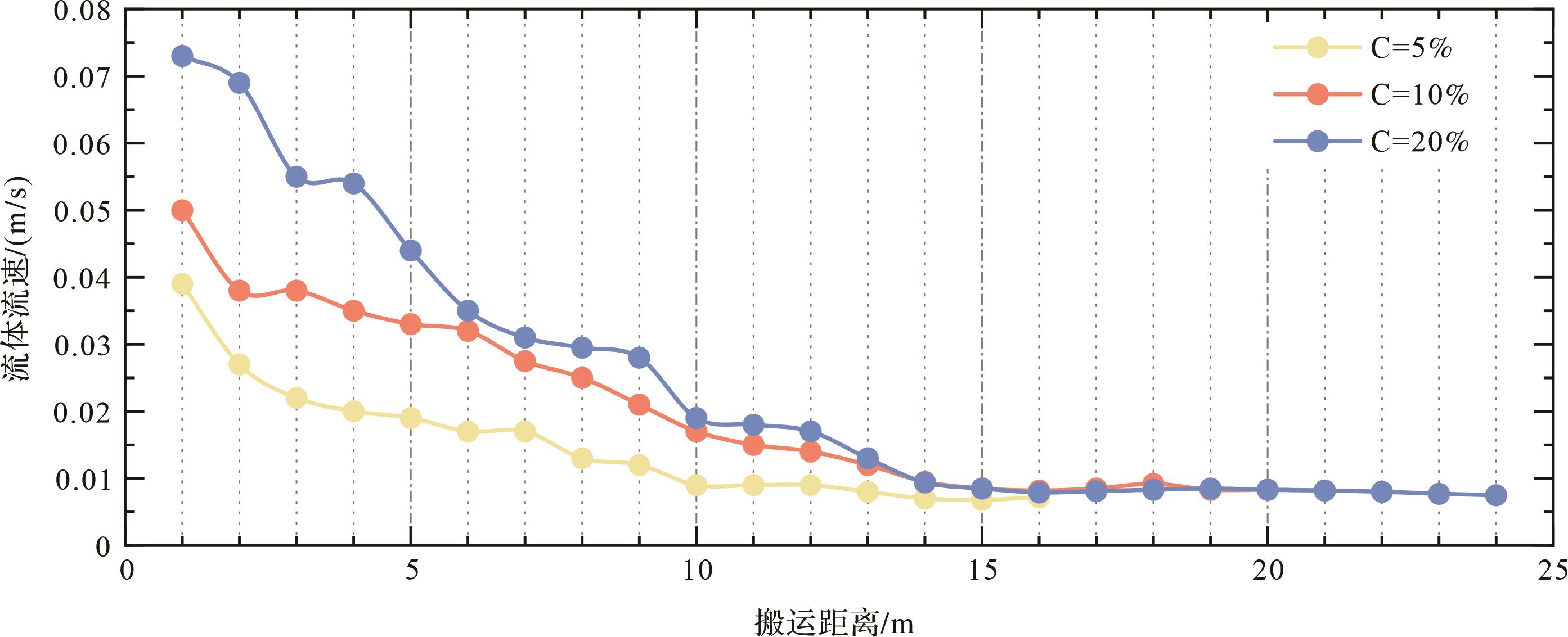
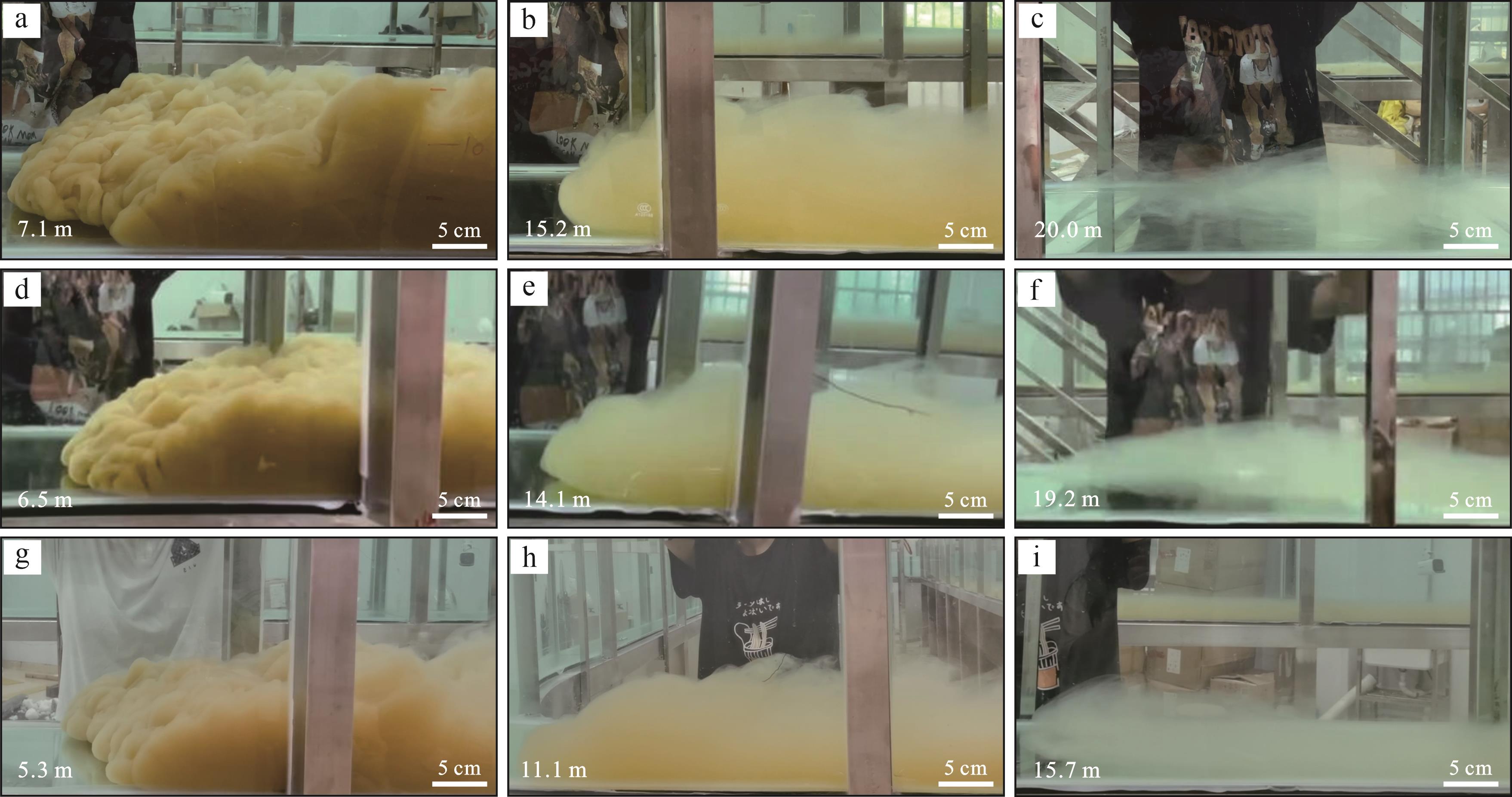
通过不同沉积物浓度水槽模拟对比实验,发现浊流移动速度及细粒沉积物搬运距离受沉积物浓度的影响较为明显,实验结果显示:(1)沉积物浓度越大,流体的流速越大,两者呈明显的正相关(图6)。由于浊流最大密度主要集中在头部,主要依靠其与周围水体的密度差获得不断前进的驱动力,当沉积物浓度较大时,与环境水的密度差越大,获得的驱动力越强,流速越大。(2)从搬运距离上来看,浓度为20%的沉积物分别在3 min、10 min、20 min时搬运至7.1 m、15.2 m、20.0 m(图7a~c);浓度为10%的沉积物分别在3 min、10 min、20 min时搬运至6.5 m、14.1 m、19.2 m(图7d~f);浓度为5%的沉积物分别在3 min、10 min、20 min时搬运至5.3 m、11.1 m、15.7 m(图7g~i)。可见流体浓度越大,其流速越大,沉积物搬运的距离也越远;流体浓度较大时,所获得的驱动力也更强,随之搬运更远(图6)。
-
不同初始流速下,细粒沉积物分布特征也各异,根据其差异可将其分为三个阶段:0~2 m段、2~7 m段、7 m直至搬运结束段。
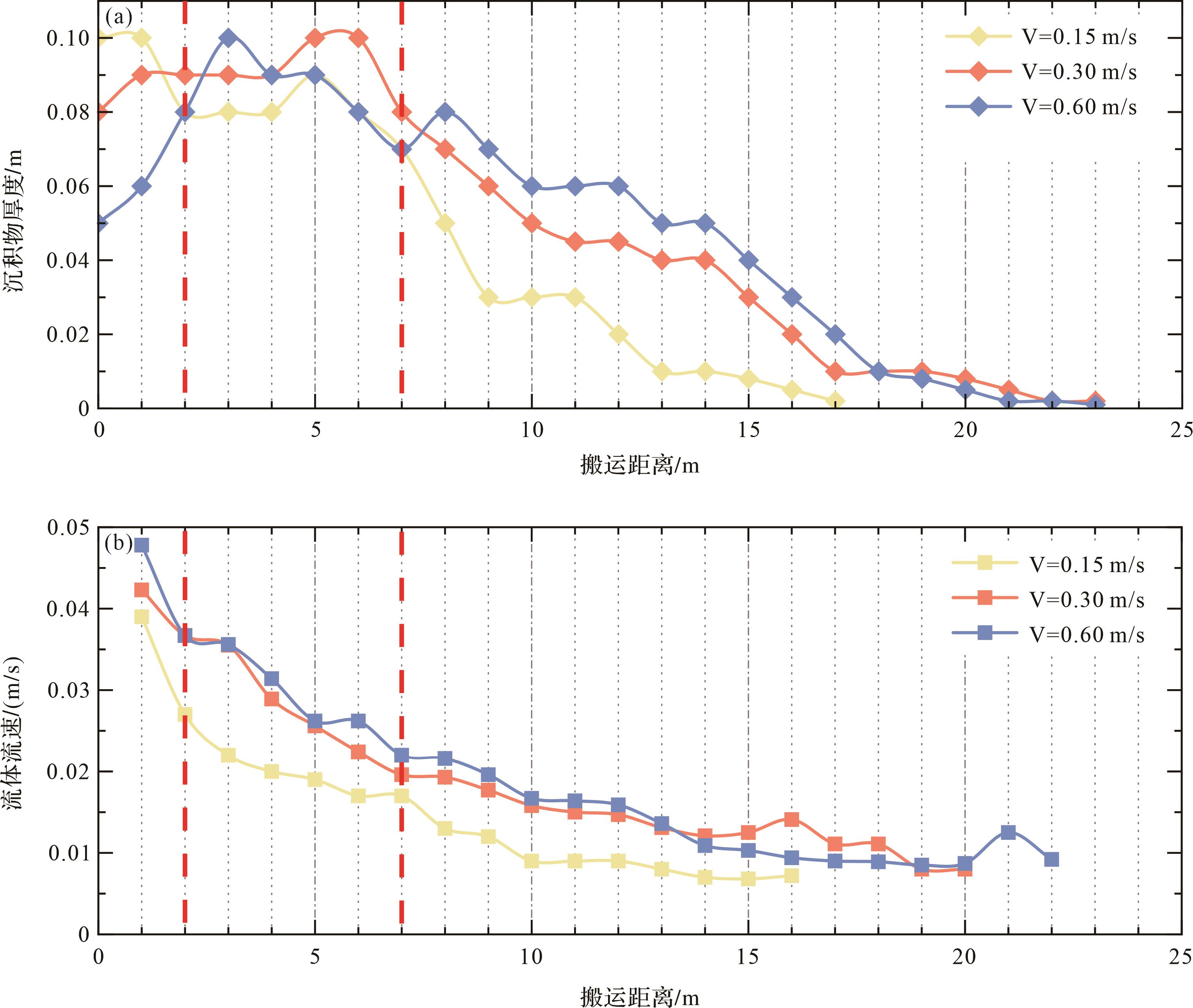
(1) 在0~2 m阶段,沉积物厚度与初始流速关系最密切。根据不同初始流速下沉积物厚度与搬运距离折线图得知,随着流体初始流速的增大,在该阶段沉积物沉积厚度减小,二者在一定程度上呈现负相关(图8a)。浊流在搬运过程中,其湍流强度随流速增大而增大,紊乱程度越高,携带沉积物的能力也随之越强,沉积物悬浮于浊流内部进行搬运,沉积物所沉积厚度即更薄。

Figure 8. (a) Line chart of sediment thickness and transportation distance during fluid release at different initial velocities; (b) line chart of fluid movement speed and handling distance under different initial velocity releases
(2) 在2~7 m阶段,此段为流体刚搬运不久,靠近物源区,流体紊乱程度较大,也是水下水跃最为活跃的阶段。水下水跃现象作为耗能的有效方式之一,在该阶段水跃现象频繁发生,通过对不同初始流速下流速与搬运距离折线图进行分析,发现在该阶段发生水跃现象时,出现在在在在在在在在浊流流体流速减小幅度突然增大以及沉积物厚度变厚的情况(图8a,b)。由于水下水跃发生时使得流体表面表现为不连续或突然跃起,沉积物在发生水跃或邻近部位会有强烈的沉积物堆积,在空间上分布亦不均匀,使得在该阶段沉积物厚度波动较大,沉积物分布特征也发生变化,最后稳定后沉积厚度增大。
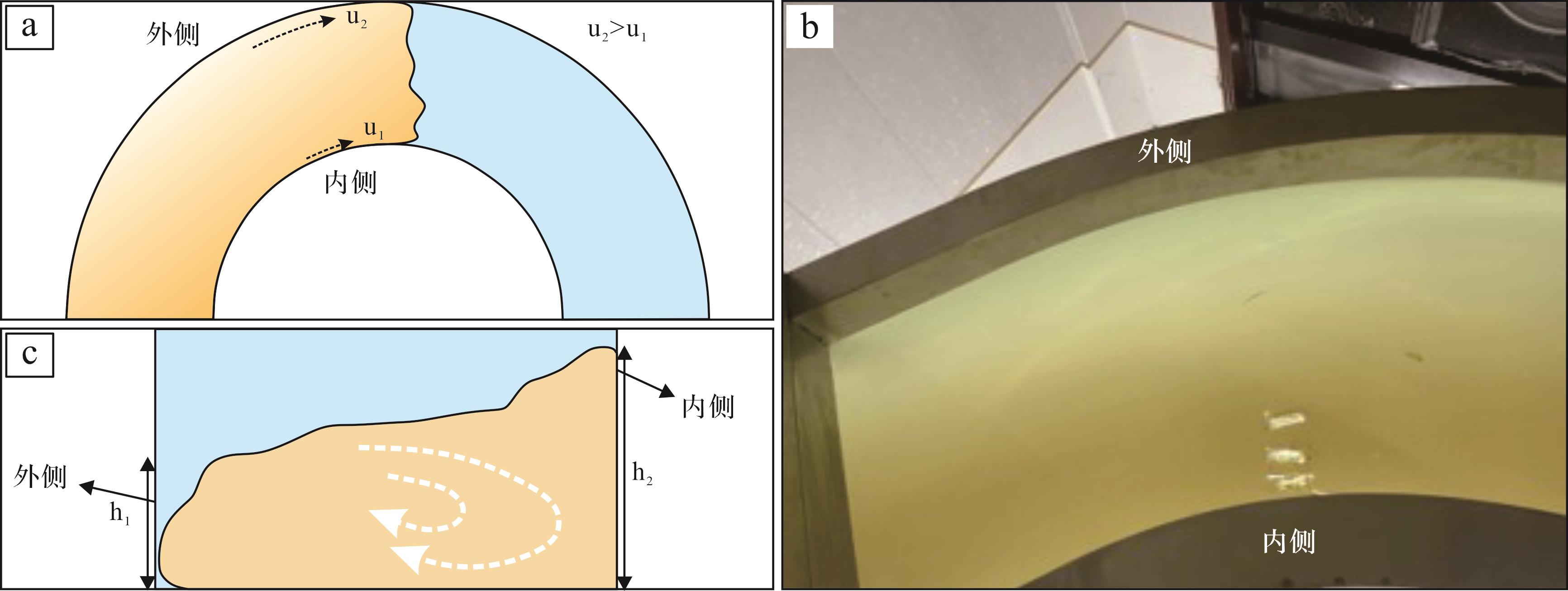
(3) 在7 m后直至搬运结束阶段,待浊流流体逐渐进入弯道区时,此时可观察到水槽外侧流体较内侧流体流速更快,高度更高(图9a);但沉积完全后,测得内侧沉积物沉积厚度较外侧更厚(图9b,c)。这可能是在进入弯道区后浊流受重力及离心力作用,水流主流线向水槽外侧偏移,浊流表层水流向水槽外侧偏移,外侧水流流速较快,多以侵蚀作用为主;而底部水流逐渐流向水槽内侧,且受水槽底部摩擦力影响,底流流速降低,搬运能力下降,细粒沉积物在内侧卸载并堆积下来,致使内侧沉积物沉积厚度更大(图9b)。
随着搬运距离的增加,流体底部边界层内流体质点受到黏性力的作用,流动速度逐渐降低;在7 m之后,平均速度呈缓慢下降趋势,与水下水跃现象减弱有关(图8b)。上浮作用的产生减弱了流体与底床之间的这种黏性力,使流体流动过程中头部微微抬起,从而环境流体进入头部下方,起到润滑基底的作用,流体流速会有短暂的加快,由此证明底部边界层内流体质点受到的黏性力是流体耗能的一种方式。
-
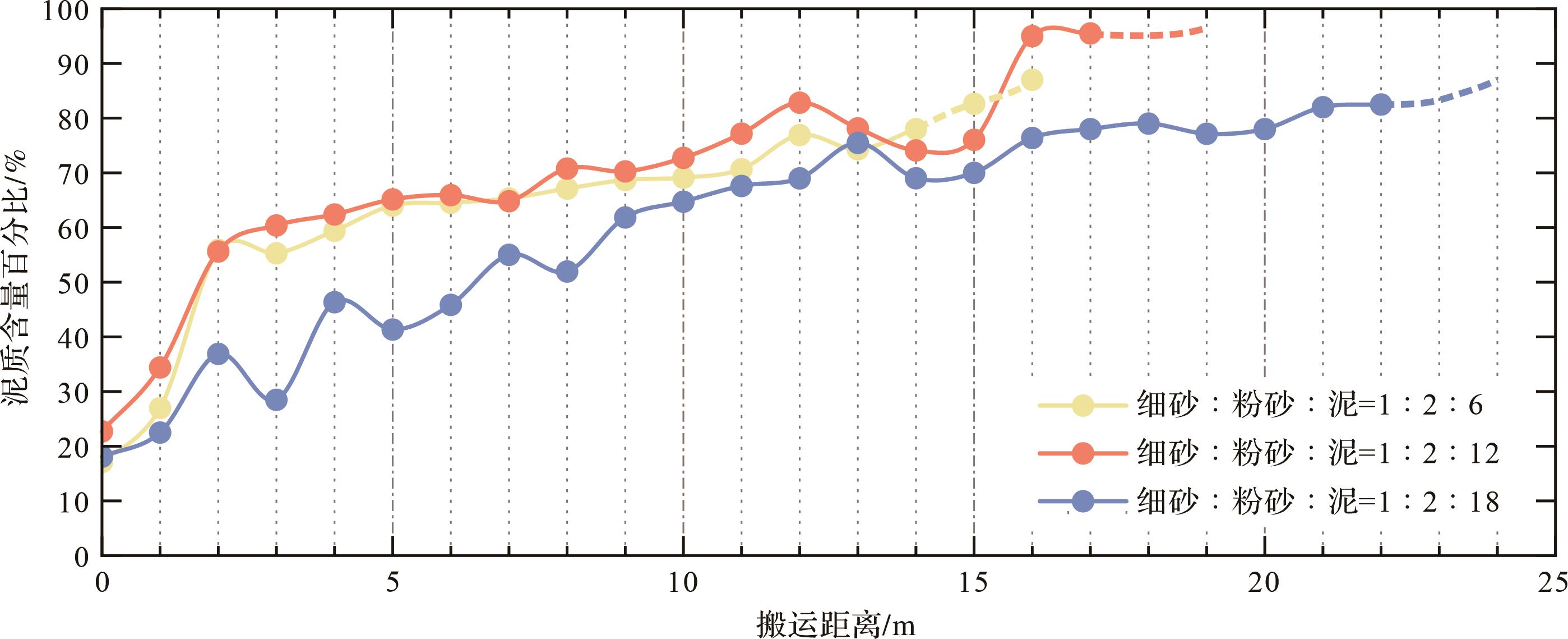
在实验结束后,待沉积物完全沉积至槽底,通过粒度分析得到下图所示结果(图10),显示沉积物的颗粒大小含量随搬运距离增加呈减小趋势;且通过对比分析三组砂泥比实验,泥质含量最多的一组较其余两组搬运距离更远(图10),表明在粗颗粒泥沙中增加适量泥质颗粒可有效提高浊流的运移能力。因此,细粒沉积物粒径的大小及含量会影响流体长距离搬运及浊流水动力学特性。
-
在实验过程中可见到流体头部上扬速度突然增快的特征,且由于头部速度较本体更快,会出现“头尾分离”的现象,砂体在水槽中能实现一定距离的“跳跃”,砂体之间不连续,仅由薄层的砂相连,直至最终发育为“分散型”的砂体(图11a)。

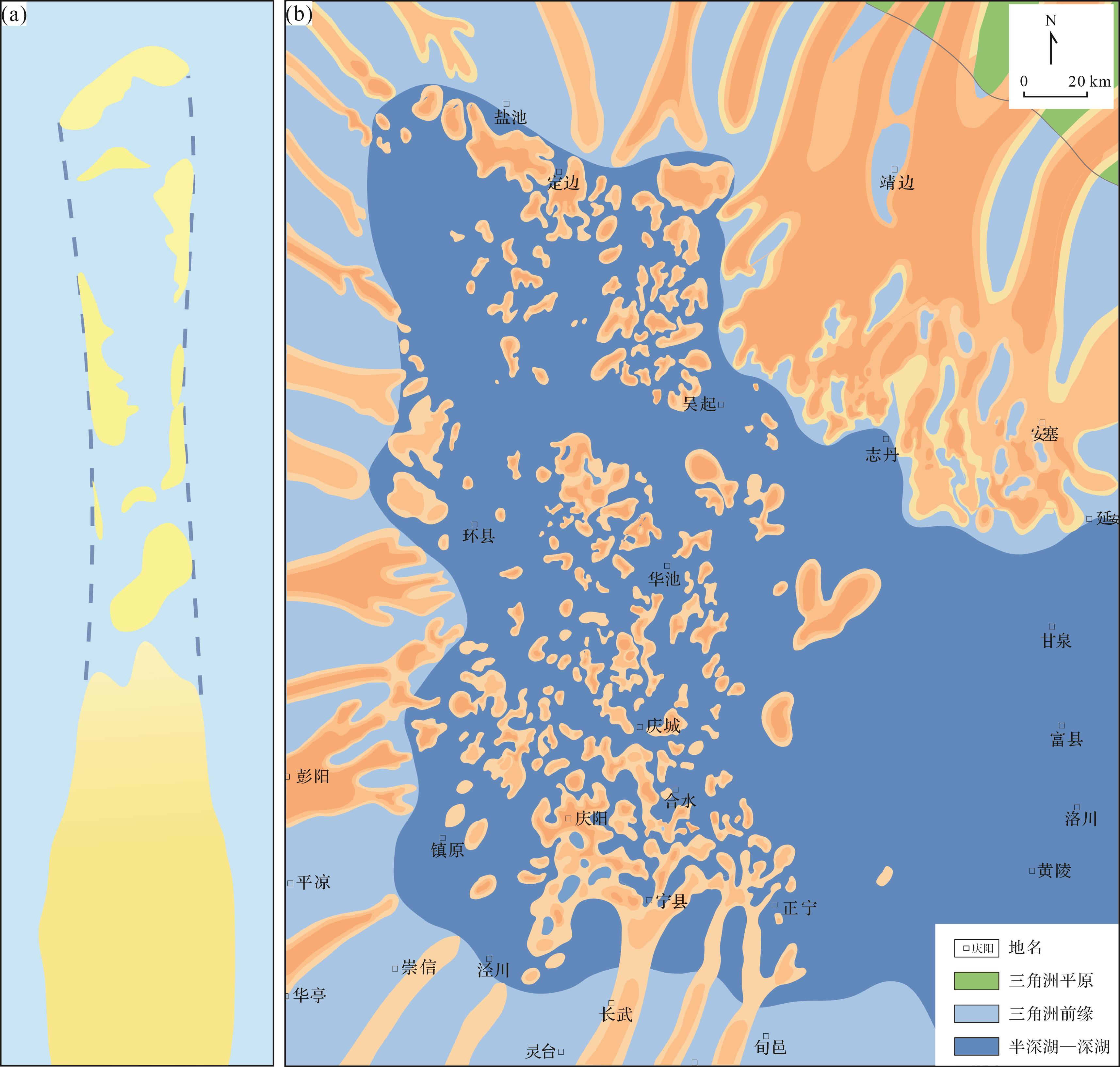
Figure 11. (a) Schematic diagram of the formation of dispersed sand bodies; (b) plane distribution of the deep⁃water gravity flow deposition in the Chang 73 member of the Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin
在该实验条件下流体头部与基底之间的上浮作用及浊流流体性质可能是形成“分散型”砂体的原因。浊流靠流体的湍流来支撑碎屑颗粒,使之呈悬浮状态;且浊流为紊流,在运移过程中,紊流的流体质点做杂乱无章的无规则运动,容易形成分散、孤立的砂体。在运移过程中,流体底部由于水体侵入且水体携带的部分砂质悬浮载荷沉积,与砂质沉积有关的相对重量损失会产生流动浮力反转而发生上浮作用使得头部抬升,有效地减少与基底之间的黏性力,使得浊流能快速流动。头部与体部由于速度差异,往往易与体部发生分离,流体也会发生裂解,分散的头部继续向前搬运一段距离后便开始沉积,而后面的体部又开始形成新的头部,不断发生裂解,从而促进了多个分散型砂体的形成,且在搬运末端所形成的分散型砂体浓度较小,厚度较薄,但展布范围较大(图11a)。前人在碎屑流水道的沉积模拟实验中也发现了相类似的规律[39]。
-
油气勘探实践表明,砂体是油气储集的重要场所,研究砂体展布对油气勘探有着显著的意义[40⁃41]。在鄂尔多斯盆地西南部延长组长7段,发育在三角洲前缘坡折带以下至深湖区的重力流砂体呈聚拢型条带状或叠加透镜状,该区域隶属于非常规油气资源,现已经实现规模勘探开发[42⁃43];在远端发育的重力流砂体与半深湖—深湖泥页岩紧密共生,呈朵叶状和舌状展布,且大多砂体在平面呈分散型和孤立型,仅少数呈片状连接在一起(图11b)[19,44]。经前人勘探预测表明,远端分散型重力流沉积砂体可有效地提高单井产能并可作为长73小层页岩油勘探的“甜点”及深水油气勘探的重点目标[42]。本次实验中所观察到的“新头部”现象解释了重力流沉积前端分散型砂体主要成因,为进一步探讨重力流砂体展布规律奠定了基础,相关研究也为细粒非常规油气勘探开发提供了新的思路。
由于实验设备条件有限,本次浊流模拟实验属于探索性研究,针对水下浊流搬运过程中出现的复杂实验现象,无法在浊流的各个现象所发生的区域大小、形状、连续时间以及弗劳德数进行定量描述;在后期实验中,将加强引进新的技术和设备(如多普勒流速仪、三维激光扫描仪),并将数值与物理沉积模拟相结合,从而为细粒重力流流体转换、混合事件层的沉积模拟及完整的数学模型的建立奠定基础。
3.1. 浓度差控制流体的移动速度与搬运距离
3.2. 初始流速、水下水跃、上浮作用共同控制着流体流速及沉积物分布
3.3. 泥质含量影响沉积物搬运距离
3.4. “新头部”现象是重力流体系前端分散型砂体主要成因
3.5. 油气地质意义及未来展望
-
(1) 基于环形水槽沉积模拟实验,分别通过控制沉积物浓度、流体初始速度、砂泥比等条件,模拟了浊流作用下细粒沉积物搬运的过程及细粒沉积物的分布与沉积特征。浊流流动过程中流体发生了一系列变化,出现了水下水跃、双流分割、裂隙和叶片、上浮作用、头部抬升、“新头部”等现象。
(2) 通过对实验现象观察和分析,以及对流体流动速度、细粒沉积物完全沉积后的厚度以及泥质含量进行测量,结果显示流体与环境流体的浓度差与流体的移动速度和搬运距离成正比;初始阶段流体初速度与沉积物沉积厚度成反比;泥质含量越多,沉积物的搬运距离越远。在流体搬运过程中水下水跃会减小流体流速,而上浮作用能减小流体与基底间的黏性力,使得流体头部加速。
(3) 在实验中,由于头部速度较体部更快,二者逐渐拉开距离,直至头部完全脱离身体,头部继续向前搬运;而后在本体前端会缓慢地形成一个“新的头部”,“新头部”现象使得砂体之间不连续,并在不同位置分散展布形成分散型砂体。结合鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长73亚段重力流沉积体系前端形成的分散型砂体,本次实验能够较好地解释其成因。













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: