HTML
-
竹叶状灰岩是一种特殊的碳酸盐内碎屑砾岩,以其侧切面似竹叶而得名,国外多称之为扁平砾石砾岩(flat-pebble conglomerate)而更形象地描述了砾屑的三维形态。竹叶状灰岩是寒武系全球普遍发育的一种碳酸盐岩相,因其在特定地层中发育,被认为可能指示了寒武纪温室气候下独特的古海洋和古生态环境[1⁃2]。同时,竹叶状灰岩通常被认为是风暴沉积,由风暴浪打碎已固结的条带灰岩,经过搬运改造沉积而成[3⁃4]。而风暴沉积在恢复古气候和古地理演变、古板块位置等方面都具有重要指示意义。尽管如此,对风暴作用过程的认识,现代海洋观察和相关实验室模拟研究均较为匮乏,因此对很多竹叶状灰岩的成因,尤其是竖直或倾斜排列的(如倒“小”字、菊花状等)扁平砾屑的沉积过程,一直是沉积学的争论热点[1,5⁃9]。近年来,也有很多国内外相关研究表明,一些竹叶状灰岩可能是在早期成岩过程中由软沉积物变形而成[10⁃17],并不能直接反映风暴气候及海底强水动力环境。因此,十分有必要对竹叶状灰岩的沉积过程进行精细剖析。
竹叶状灰岩层位几何形态多种多样,多以侧向相对连续沉积为特征,但也有不同形态的透镜体状、河道状、丘状、不规则状等。在鲁西莱芜九龙山剖面寒武系芙蓉统炒米店组中部发育了一层颇为壮观的丘形竹叶状灰岩,近年来引起多位学者的关注,并对其成因进行了不同角度的探讨[18⁃21]。因其得到广泛关注,且成因解释各不相同,又缺乏相关的沉积学证据,或会引起学界同仁的误读。作为对上述研究的补充,本文对该丘形竹叶状灰岩开展了详细系统的观察和描述,并对其成因提出新的见解。在传统沉积学研究中,对任何沉积现象的成因解释须基于翔实的野外和镜下沉积学特征,希望本文能起到抛砖引玉之作用,引起沉积学同仁的关注。
-
华北台地是典型的陆表海碳酸盐岩台地,形成于华北板块(又称为中朝板块)稳定克拉通之上[7]。华北台地寒武系主要是一套以碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩交互沉积为特征的稳定沉积序列(图1)。鲁西地区发育的多个寒武系剖面是华北台地寒武系标准剖面(如馒头山剖面、唐王寨剖面、九龙山剖面等)。现将鲁西地区寒武系岩石地层由下至上简要介绍如下:李官组(厚约40 m)主要在临沂和淄博地区发育,上覆于前寒武纪花岗片麻岩或变质沉积岩之上,主要含交错层理石英砂岩和纹理状泥岩[22]。朱砂洞组(厚15~40 m)主要以纹理状泥状白云岩、叠层石、及灰绿色泥岩等为特征[23]。馒头组(厚220~250 m)以砖红色—紫红色泥岩、丘状交错层理砂岩及少量鲕粒灰岩等为特征[23]。张夏组(厚约180 m)以巨厚层鲕粒灰岩、凝块石、树形石为特征,在莱芜、沂南等地,张夏组中部发育盘车沟页岩段[24]。崮山组(厚50~105 m)主要以紫红色和黄绿色页岩夹薄板状、瘤状灰岩和竹叶状灰岩为特征[14]。炒米店组(厚190~260 m)主要以多种碳酸盐岩相为特征,包括条带灰岩、薄板状灰岩、生屑粒泥—泥粒和颗粒灰岩、鲕粒灰岩、微生物岩及多层竹叶状灰岩[14,25]。上覆三山子组白云岩的原生沉积岩相与炒米店组类似,但其在鲁西地区有较大的穿时性[25],这也导致其下的炒米店组的厚度有一定变化。
-
本研究关注的丘形竹叶状灰岩层发育在九龙山剖面炒米店组中部层位(图1),属于寒武系芙蓉统江山阶,即原长山阶中上部(图1)。笔者针对该层在九龙山剖面的6个露头点进行追踪研究(图2),在九龙山剖面的南侧距离800多米的三个露头点(露头1~3)以及北侧的两个露头(露头4~5),均发现在鲕粒灰岩层中发育形态不尽相同的丘形或不规则状竹叶状灰岩,但再向东侧追踪到露头6,在该鲕粒灰岩中没有发现竹叶状灰岩丘。
-
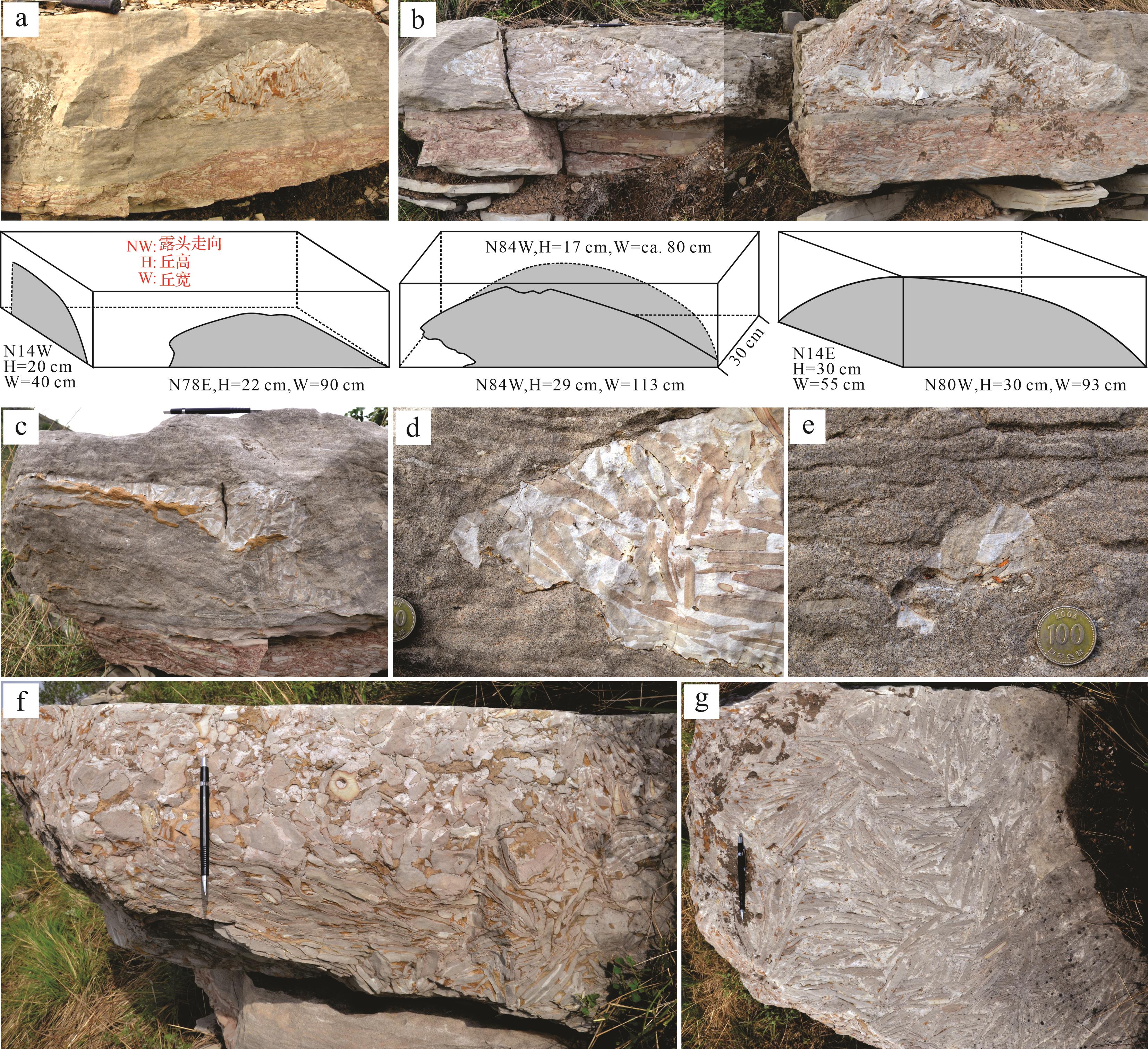
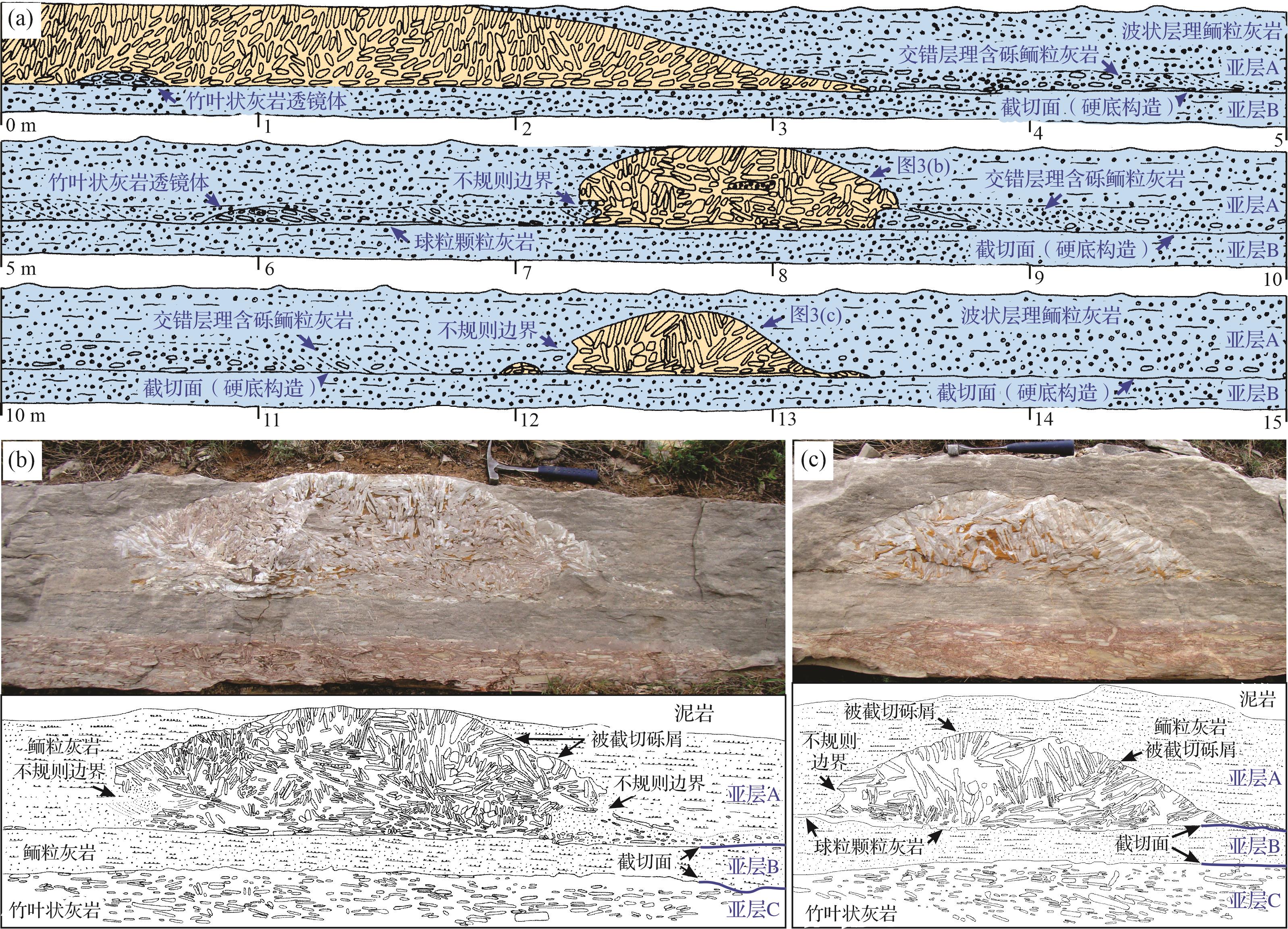
竹叶状灰岩丘发育在一层横向产出稳定的碳酸盐岩相中,该岩层之下为薄板状泥状灰岩夹页岩,之上为钙质泥岩夹薄板状—瘤状泥状灰岩(图1)。该岩层主要含上部具波状层理的鲕粒灰岩(亚层A和B)及下部具交错层理或叠瓦状构造的竹叶状灰岩(亚层C),三个亚层均由清晰的截切面分隔(图3)。鲕粒灰岩A和B亚层之间发育清晰、突变、平缓的界面(图4a),该界面截切之下的鲕粒,横向可追踪上千米,是典型的硬底构造[26],竹叶状灰岩丘发育在该硬底构造之上(图3、图4b)。

Figure 3. Sketch and photograph of the flat⁃pebble conglomerate mounds and associated facies in outcrop 1 of the Jiulongshan section
鲕粒灰岩中偶夹一层2~4 cm厚、横向不连续的球粒颗粒灰岩,且具清晰的上下界面(图4c,d)。鲕粒灰岩主要含有同心鲕、少量椭圆形鲕粒、球粒及生物碎屑,亮晶方解石胶结。硬底构造之上的鲕粒灰岩A亚层下部含有少量扁平状砾屑,具板状交错层理,或呈叠瓦状或平伏状排列(图3、图4a,c)。两层鲕粒灰岩普遍发育波状层理,其层面见对称浪成波痕构造(图4d,e),偶见板状—槽状交错层理。鲕粒灰岩B亚层横向(向东)厚度变薄,但其上的硬底构造依然清晰可见。
该岩层下部的C亚层是具交错层理的竹叶状灰岩,砾屑主要为细至粗砾大小(granule⁃cobble)的泥状灰岩和球粒颗粒灰岩(图4g)。杂基主要含有球粒颗粒和生物碎屑等,一般为亮晶方解石胶结。砾屑大多具有红色氧化圈、分选较差、磨圆较好,见一端呈棱角状的破碎砾屑。少量较大的砾屑无红色氧化圈,且磨圆较差。砾屑多呈平伏状或叠瓦状,上部见板状交错层理(图3b)。竹叶状灰岩底界清晰突变,明显侵蚀下伏薄板状、具纹理的泥状灰岩;顶面亦清晰突变,该竹叶状灰岩内的砾屑和杂基被截切,其上覆为波状层理鲕粒灰岩B亚层。偶见该竹叶状灰岩由几厘米厚的一薄层含砾球粒颗粒灰岩覆盖,该颗粒灰岩也被截切,截切面偶被缝合线改造,上覆为鲕粒灰岩(图4g)。
竹叶状灰岩席或透镜体也出现在鲕粒灰岩B亚层顶部的硬底构造之上(图3、图4h,i),厚度仅为几厘米,略具平缓起伏状,有时见底部呈下凸状,类似于浅水道;砾屑主要为具红色氧化圈的泥状灰岩和少量球粒颗粒灰岩、鲕粒灰岩、和生屑颗粒灰岩,磨圆较好,但有些砾屑破碎呈棱角状;杂基多为球粒颗粒灰岩;砾屑多呈叠瓦状排列。此类竹叶状灰岩席或单独出现在鲕粒灰岩中(图4h),其顶部砾屑和杂基被截切;或位于竹叶状灰岩丘底部且二者界面可识别(图4i)。
2.1. 产出层位
2.2. 共生岩相
-
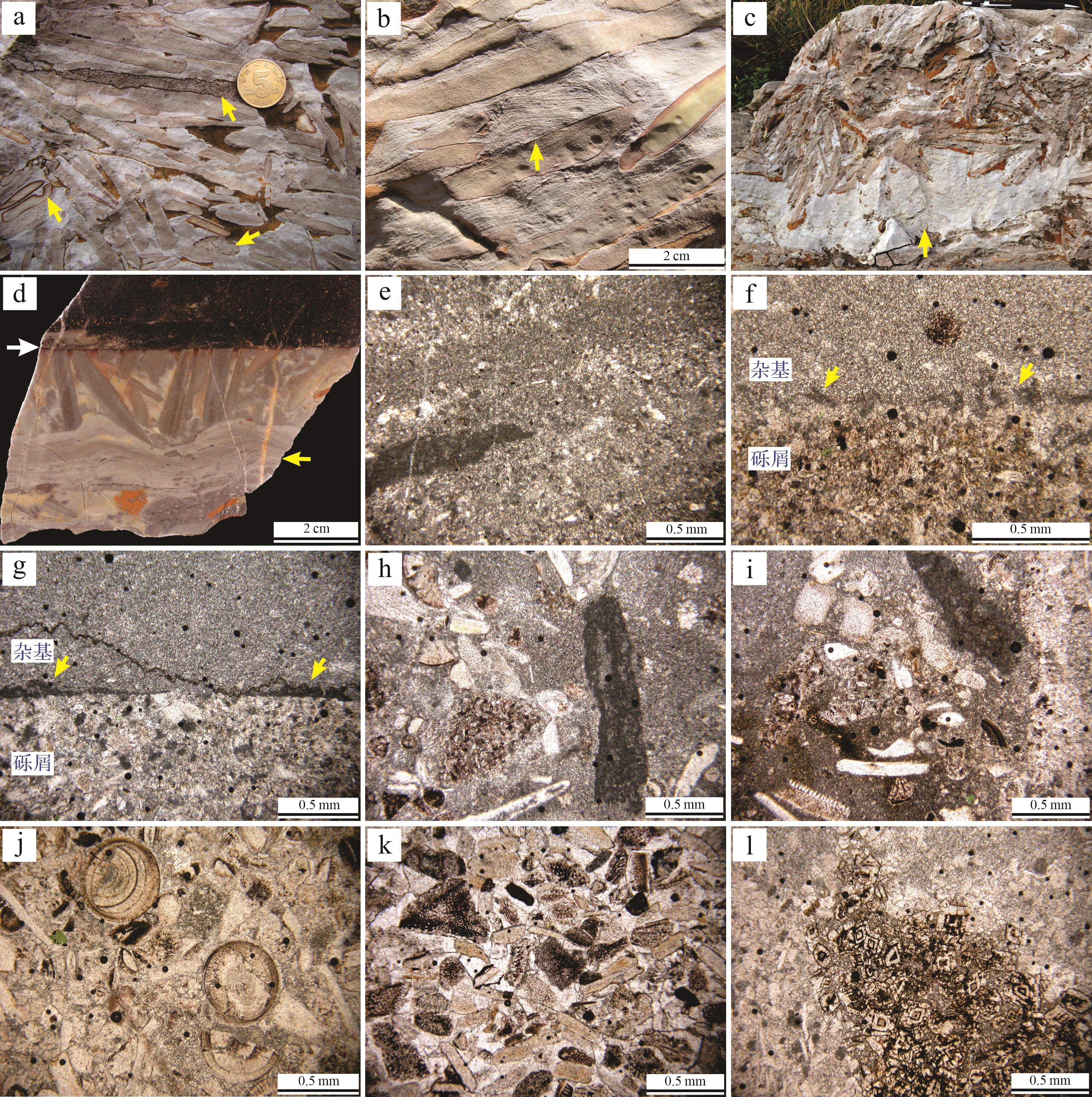
在野外露头剖面上,竹叶状灰岩丘多呈底平顶凸并向两侧逐渐变薄的丘形(图3),在不同方向的露头均可见丘形(图5a,b),表明其三维形态为圆形或椭圆形丘的可能性较大(图5a,b)。但通过一个侧面的观察,也见不规则状(图5c)。虽然如果垂向露头并非绝对平面可导致圆形丘侧切面形态不规则,但也很可能反映该竹叶状灰岩的三维形态就是不规则的。竹叶状灰岩丘两侧下部多呈清晰突变的不规则状边缘(图5d),见竹叶状灰岩团块脱离岩丘(图5d,e)。所观察到的竹叶状灰岩丘厚度多小于鲕粒灰岩的厚度,但也见其与鲕粒灰岩层顶面一致,丘厚度可达33 cm。在竹叶状灰岩丘与鲕粒灰岩层厚度一致时,竹叶状灰岩丘顶部则多呈平缓或极平坦状(图5f,g)。
-
丘形竹叶状灰岩主要含中至粗砾砾屑,砾屑主要岩性为具纹理状球粒颗粒灰岩,次棱角—次磨圆状(图6a~c)。见少量具红色氧化圈的均质泥状灰岩和生物碎屑颗粒灰岩砾屑,磨圆较好(图6a),偶见含海绿石鲕粒灰岩砾屑(图6a)。砾屑多呈扁平状,见弯曲起伏状。竹叶状灰岩主要为砾屑支撑、砾屑杂乱状排列、无定向结构。竹叶状灰岩丘底部见较为完整的薄板状球粒颗粒灰岩和平伏的砾屑,而其上部多为倾斜和竖直排列的砾屑,且上部的砾屑和杂基均被截切(图6d),顶部竖直砾屑360°均有排列(图5g)。
杂基主要含有白色、具纹理状或凝块状微生物岩(多为泥晶—微晶方解石),以及褐色白云岩(图6a~d)。见叠层石发育在砾屑之上,呈小型隆起构造,几至几十厘米宽、几厘米高(图6b~d);镜下可见交替出现的泥晶(钙化微生物?)和亮晶方解石的纹层,沿纹理也见明显的泥晶化的钙化微生物团块(图6e)。砾屑上侧常见原地发育的葛万菌(Girvanella)和似肾形菌(Renalcis)等钙化蓝细菌(图6f,g)。杂基也含钙化葛万菌碎屑和团块(图6h,i),见破碎鲕粒和多期次鲕粒(图6j),生物碎屑包括三叶虫、棘皮类、腕足类、钙藻等,以及球粒、海绿石等颗粒(图6k)。杂基局部被白云岩化,形成自形白云石晶体(图6l)。
3.1. 几何形态
3.2. 砾屑和杂基
-
我国学者对竹叶状灰岩的研究可追溯到20世纪20年代[27],之后很多学者对竹叶状灰岩的成因展开讨论[4,6,9,13,17,28⁃33],其成因大多被解释为风暴沉积。竹叶状灰岩一般呈现不同形态的层位几何形态和砾屑的排列状态等特征,因此也被解释为风暴流不同程度搬运和改造之后在不同沉积环境下的沉积(如原地和异地沉积)。鲁西寒武系炒米店组鲕粒灰岩中发育的丘形竹叶状灰岩,因见其在一些露头中有较为规则的丘状形态,其成因解释引起诸多讨论[18⁃21]。
非常遗憾地指出,van Loon et al.[18⁃19]没有经过系统细致观察,认为这些竹叶状灰岩丘均含有相同的成分和组构,而且这些竹叶状灰岩丘具有“头部和尾部”,以及“底部的剪切带”等特征,但据本文上述特征可以看出,其实均不然。而作者据此将这些竹叶状灰岩丘解释为滑移(sliding)而成。但如果是滑移,那么这些丘形竹叶状灰岩是怎么被破碎而成的?若如作者所述,可能是风暴破碎而成,又为何未在地层中广泛出现?因为没有直接的地质证据,只能推测,可能是由于极强风暴引起竹叶状灰岩岩块的滑移(及随后的不断破碎),但风暴引起的什么沉积过程和水动力条件将之破碎?云云,不得而知。
而在其后的研究中[21],van Loon作为通讯作者在其2012年的文章基础上,又增加了一些新的野外照片,以佐证其相关论点,但对一些岩性的描述是完全错误的。如将寒武系典型的条带灰岩,即浅灰色泥状灰岩(lime mudstone)和黄色泥灰岩(marlstone)互层,分别描述为鲕粒灰岩和泥状灰岩(文献[21]中图14);将一些竹叶状灰岩杂基中的白云岩描述为鲕粒灰岩(文献[21]中图15)。另外,作者在该文中提出新的观点,否定了之前的猜测,认为风暴不可能打碎一个横向连续的岩层,也无法让其移动并滑移[21]。作者又提出海啸可触发上述现象的推论,但海啸同样会引起其他沉积现象,而他们却没有发现这类证据(也没有进一步解释)。最终,该文作者提出最可能引起竹叶状灰岩层破碎并滑移的机制是地震作用,且地震作用是由同沉积断层引起;其推测的同沉积断层是由于不均一的沉积速率和载荷导致,这一论断也没有任何地质证据或参考文献佐证,而且作者在后文中又提及(华北)陆表海并非以显著的水深变化为特征。既是如此,又何来不均一的沉积速率和载荷导致同沉积断层?貌似自相矛盾。更何况整个鲁西地区炒米店组(及其之上的三山子组)原生沉积岩相类型和厚度并没有较大变化[14,25,34]。
另一方面,笔者与研究生导师根据前期工作认为这些竹叶状灰岩丘并非丘形,也可能像是底平顶凸的“隧道”形状[20],并将之解释为液化的含竹叶状砾屑的流体,在外力触发下注入到鲕粒灰岩中。虽然注入岩(injectite)的确经常发育在碎屑岩体系中,并形成多种几何形态,如碎屑岩墙、岩床、沙火山等[35⁃36],但文中所描述的竹叶状灰岩若是由含砾屑的液化流注入鲕粒灰岩,又为何没有突出于该鲕粒灰岩层之上,即便其之上的泥岩比鲕粒更难以固结,也没有发现任何挤入泥岩的现象。相反的是,竹叶状灰岩的顶面最多与鲕粒灰岩层同高(图3),并以平滑的硬底构造为特征。
因此,本文认为这些竹叶状灰岩丘并非是由碎屑岩墙的挤入形成的[20],也非风暴、海啸或地震引起的竹叶状灰岩层的破碎及滑移而成[18⁃19,21],应该是在初始沉积过程中堆积、改造形成。具体沉积过程详细阐述如下。
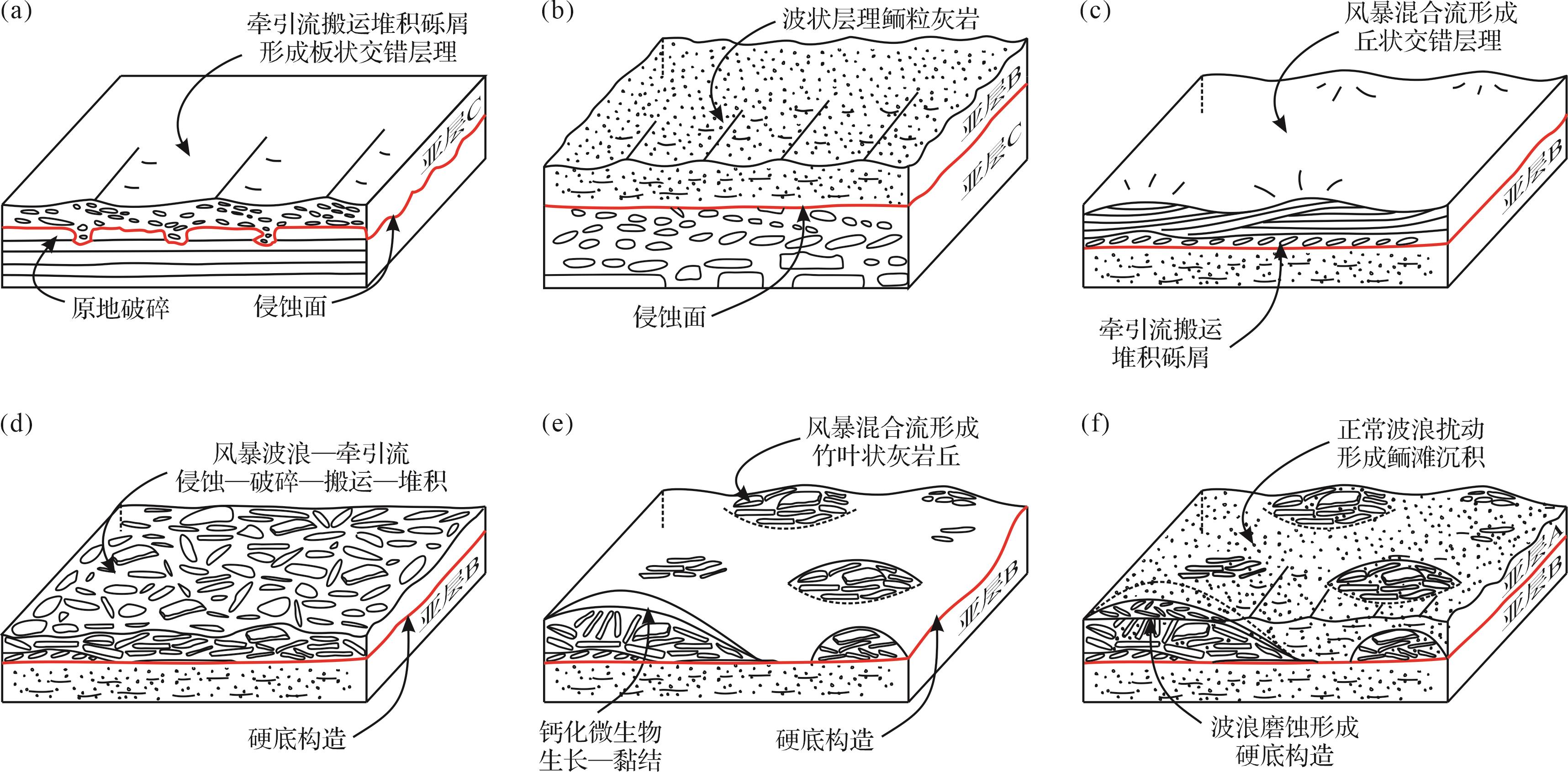
亚层C竹叶状灰岩中的板状交错层理、叠瓦状构造等特征指示其沉积于较强的牵引流作用之下(图7a)。大多砾屑和杂基由该牵引流搬运、磨圆,甚至再次破碎,并在此沉积,而少量较大的、形状不规则的砾屑则可能是由强水流在原地侵蚀、破碎薄板状灰岩形成。破碎的和磨圆较好的砾屑均指示高能状态下砾屑之间强烈的碰撞。该竹叶状灰岩或其之上局部堆积的球粒颗粒灰岩均被截切,表明其在遭受侵蚀之前已经固结为硬底构造。波浪不断磨蚀竹叶状灰岩亚层C之上的硬底构造,同时沉积形成波状层理鲕粒灰岩(亚层B,图7b)。鲕粒灰岩亚层B在胶结后也被侵蚀,形成广阔的硬底构造。在该硬底构造面之上,风暴混合流搬运并沉积薄层的、横向不连续的竹叶状灰岩(图4h,i),并在其之上沉积一定厚度的丘状交错层理球粒颗粒灰岩(图7c)。这些薄板状球粒颗粒灰岩被风暴浪原地破碎成砾屑(图7d),并可能继续侵蚀之下的鲕粒灰岩硬底构造。在硬底构造之上,强大的风暴浪加之风暴引起的盆地回流相互干涉形成的混合流,将从上游或附近搬运而来的砾屑以及先前原地破碎的砾屑,堆积成初始的竹叶状砾屑丘或不连续的、厚度不均的砾屑层(图7e);在风暴过后,砾屑之上和之间的空隙被蓝细菌充填,并形成叠层石。叠层石的黏结阻碍了竖直砾屑被再次改造,并进一步黏结或障积下次风暴流带来的砾屑,最终逐渐形成大小不均的竹叶状砾屑丘或滩(图7e)。之后,可能由风暴引起的强水流携带少量砾屑和鲕粒,搬运并堆积形成A亚层下部的板状交错层理含砾鲕粒灰岩;在风暴之后,在以正常波浪主导的鲕滩环境中,波状层理鲕粒灰岩逐渐堆积(图7f)。在竹叶状砾屑丘或滩堆积形成之后,不断地遭受水流和波浪的冲刷改造,形成清晰的边缘,而竹叶状砾屑丘顶部可能遭受波浪长时间的磨蚀,形成平坦的硬底构造(图7f)。这之后,可能由于相对海平面上升,钙质泥岩沉积于正常浪基面之下。
由此可见,这几十厘米厚的岩层中,蕴藏着多次风暴事件引起的、跌宕起伏的沉积过程和水动力条件的变化,加之钙化微生物的参与,使得这种含竖直扁平砾屑的竹叶状灰岩丘最终堆积保存于鲕粒灰岩中。以上是对该竹叶状灰岩丘沉积成因定性的分析和讨论。风暴引起的混合流能搬运细砂级沉积物并在正常浪基面之下、风暴浪基面之上形成丘状—洼状交错层理[37⁃38]。强大的风暴引起的混合流能否搬运并堆积竹叶状砾屑,并形成砾屑丘或滩,尚需水槽实验或计算机模拟等对水动力机制进行定量研究[39]。
-
鲁西寒武系炒米店组在鲕粒灰岩中发育的竹叶状灰岩丘应该是再风暴引起的初始沉积过程中堆积、并被后期的水流和波浪改造而成,其反映了复杂的沉积过程和水动力条件。先前由风暴混合流形成的薄板状球粒颗粒灰岩再次被后来强大的风暴引起的水流或波浪破碎、搬运、并堆积成似丘状形态。在沉积之后,钙化微生物的黏结作用使得竖直状扁平砾屑得以保存,并可再次黏结或障积砾屑或其他碳酸盐颗粒,最终竹叶状灰岩丘在水流和波浪的不断侵蚀下,被同时沉积的鲕粒埋藏。
对该竹叶状灰岩丘成因的探讨,是基于对其详细野外特征的过程解释,若有不当之处,敬请学界前辈和同仁批评指正、不吝赐教。因篇幅有限,未能展示该层的所有野外和镜下特征,如有同仁对此感兴趣或有异议,抑或想了解更多相关特征,欢迎随时与笔者联系,也可同去野外现场讨论。













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: