HTML
-
古新世—始新世是地质历史中全球显著增温的时期[1],对于当前全球气候变化研究具有一定借鉴意义[2]。美国犹他州西南部广泛分布了一套以红色为主、灰白次之的地层,其地质年代可追溯到古新世—始新世这一时期[3⁃5],是研究该时期气候环境变化的优质材料。已有地质考察结果显示,该地层主要为湖相石灰岩[6],含部分碎屑岩石[7],结合石灰岩中含有介形类、腹足类化石以及藻类碎屑[8⁃9],地质学家认为在这一时期该地区发育了巨大的湖泊[3⁃9]。而我们对其中的Bryce峡谷国家公园进行野外实地考察发现,Claron组大部分地层以粉砂粒级为主,部分层位(尤其是底部褐红色层)发育连续的、均质红色古土壤,表现出风尘沉积的特征[10]。过去,多数学者认为该地层为河湖相沉积地层,但是地层中大部分层位呈现出风尘沉积的特征,与湖泊沉积特征相差甚远。于是探讨地层中是否存在风尘沉积,可以帮助理解以下两点问题:发育均质红色古土壤的地层,若为湖泊沉积应为什么类型的湖泊?若非湖泊沉积,应属于什么沉积类型?几十年中国黄土“风成”、“水成”之争表明,对古老地层沉积环境的认识是一个相当复杂的过程,对年代更为久远的Claron组的认识也应该是一个逐步推进的过程。鉴别地层中的风尘沉积有助于更深层次地认识其沉积环境,提取该时期所对应的更详细的沉积环境和古气候信息。
沉积物粒度特征提供了关于沉积学起源的信息[11⁃12],被广泛用于黄土沉积物的物源[13]、古气候研究[14⁃15],并取得了显著成果。沉积物频率分布曲线是粒度分布的直观体现,不同沉积动力具有显著的分选差异,形成具备自身特性的形态特征[16]。自然界中大部分沉积物是受一种或多种搬运方式和搬运动力综合作用的,具有多组分、多模态的粒度分布特征[17],对粒度分布进行简单统计分析难以反映多元沉积物的复杂性[18]。因此,应用端元分析进行粒度分解后,不同粒度端元代表不同的搬运、沉积机制和源区,可以提取被我们忽略的更多细节信息。近年来,应用不同平台如Excel、Visual Basic、Matlab以及R语言进行粒度频率分布曲线分解的模型逐渐成熟。参数法和非参数法是目前粒度分解最主要的两种方法,二者的显著区别体现在前者认为当搬运介质和搬运方式一定,且搬运动力比较稳定时,沉积物呈现由单因子控制的单组分分布[19⁃20];而后者认为不同物源、搬运动力和搬运方式的组合,应该具有不同的分选特征,所以将每个端元本身视为由不同混合和分选过程所影响的初始模态进行分析[21]。因此,非参数法是基于一组数据进行分析,相比之下更具有统计学意义和物理意义。在这一前提下,相继出现了一系列非参数算法,例如DRS-unmixer[22],EMMAgeo[23],AnalySize[24]和BEMMA[25]。van Hateren et al.[26]对这一系列端元分析模型进行评估的结果表明,使用AnalySize进行拟合的粒度端元结果更精确、可靠。因此,本文以Bryce峡谷Claron组为研究对象,考虑到地层沉积物组成的复杂性,采用AnalySize[24]非参数粒度端元分析进行粒度分布组分分解,同时分析不同端元的沉积学指示意义并且识别地层中的风尘沉积组分,进而对地层沉积环境进行更系统地探讨。
-
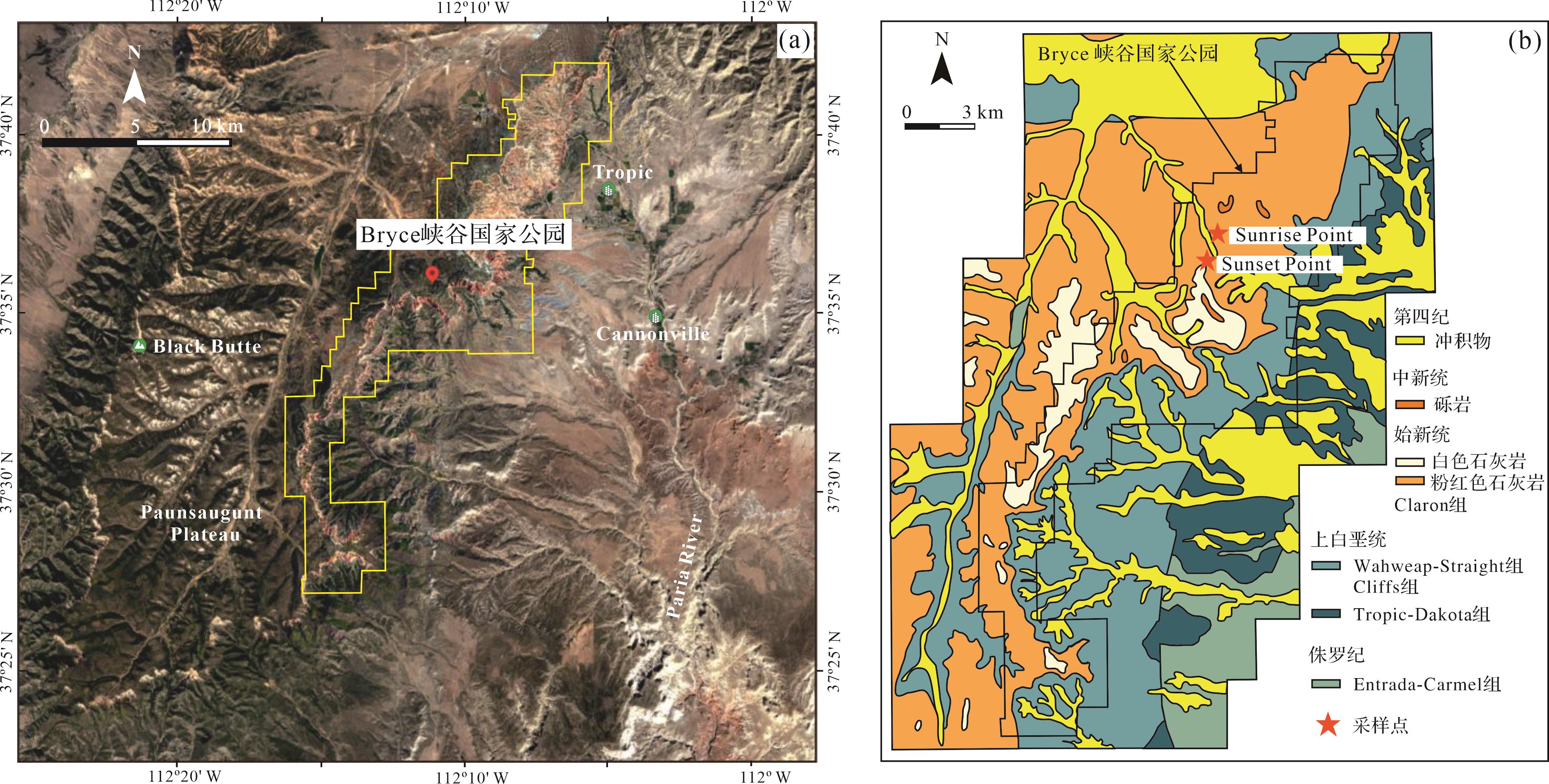
Bryce峡谷国家公园位于美国犹他州庞沙冈特(Paunsaugunt)高原东部(图1a)。该区域现代气候类型为大陆性气候,气候年际变化大,雨季集中在7—8月,年降雨量介于380~460 mm。古近纪(约70~50 Ma前)拉拉米造山运动曾影响整个北美洲,此间落基山脉隆起[27],伴随着白垩纪海陆逐渐缩小至最终关闭[28],并且发育了许多山间破碎前陆盆地[29]。距今63~40 Ma前(古新世—始新世),沉积物堆积于前陆盆地中,形成五颜六色的Claron组[27]。该地层由较柔软的岩石组成,故容易受侵蚀作用影响,沉积后遭受科罗拉多河支流帕里亚河(Paria)溯源侵蚀,在庞沙冈特(Paunsaugunt)高原东部悬崖上雕刻出一系列独立的奇形岩石(Hoodoos),这些岩石整齐排列形成类似岩石环形剧场的地貌景观(图2a),构成了如今的Bryce峡谷国家公园。Claron组是峡谷内出露最广的地层,与下伏于上白垩统Wahweap组地层不整合接触[30],地质学者基于颜色将其划分为上部白色石灰岩和下部粉红色石灰岩[31](图1b)。粉红色石灰岩呈现深—浅不同的红色变化,其间夹杂灰白色薄层(图2a),沉积厚度为152~213 m;白色石灰岩主要分布在Sunset点以南,厚度约91 m[6]。

Figure 1. Overview map of study area(a) satellite image of study area (from Google Earth); (b) geological map of study area (modified from Sprinkel et al.[30])
-
已有研究认为该地层为河湖相沉积地层,野外考察发现地层红色层中存在连续发育的古土壤,古土壤质地比较均一,置于指间有粉砂感,滴盐酸后残留肉眼可见的粉砂颗粒,疑似风尘沉积。为了更细致地了解地层的沉积环境,选择峡谷内的Sunrise点(37°37′42″ N,112°09′46″ W)及其以南的Sunset点(37°37′21″ N,112°09′57″ W)进行考察和采样(图1)。样品主要按照土壤发生层次和不同颜色层进行采集。采样首先从Sunrise顶部的灰白色层开始,所采样品均按自上而下编号。灰白色层厚约18 m,其中可见浅褐色层(图2b),采集样品B1~B5。往下可见3~4 m连续发育的红色古土壤层(图2c),其间钙结核不规则发育但总体上成层分布形成钙积层(Bk)。钙积层之上通常发育黏化层(Bt),呈均匀黏土质地且发育黏粒胶膜,钙积层与盐酸剧烈反应后残余大量粉砂颗粒,而黏化层与盐酸基本不反应。于是在该层采集样品B6~B9。继续向下可见红色层中发育彩色花斑状网纹和植物根迹(图2d),以及上述黏化层和钙积层,于是采集样品B10~B25,其中B22来自红色层中夹杂的灰白色薄层。在接近地层底部发现了一层厚度大于1 m的褐红色古土壤层(图2e),该层上部为黏化层,发育灰白色斑点和浅色淋溶带(图2f),下部为颜色稍浅的钙积层,在该层采集样品B26~B29。B30~B34来自其下部红色稍浅的层。Sunset点主要针对谷底褐红色层进行采样,样品编号BS1~BS18,采样位置与Sunrise点褐红色层大致平行。相较于Sunrise点,Sunset点的褐红色层浅色网纹更为发育。两个采样点共采集样品52块,根据采样时岩性和古土壤发育层次,将岩性柱与古土壤发生层的关系呈现在图2中;同时与孟塞尔比色卡进行比对获得样品的色调、明度和色度。采样层位更详细的信息见图2。
-
样品进行自然风干后称取0.3~2 g原样(根据样品的遮光度,灰白色样品~2 g,褐红色样品0.3~0.5 g)放至烧杯中。先加入10 mL浓度为15%的过氧化氢,放至加热板上加热直至完全去除样品中的有机质。再加入10 mL浓度为10%的稀盐酸去除样品中的碳酸盐。最后将样品静置12 h,抽取上层液,重复这一步骤直至样品呈中性即可上机测量。粒度测试使用英国Marvern公司的Mastersizer2000激光粒度仪,测量范围为0.02~2 000 μm,重复测试误差低于1%。粒度分布端元分析在Matlab中通过AnalySize程序进行,对该地层样品的粒度数据执行非参数化端元分析。端元粒度分布统计分析使用GRADISTAT 4.0[32]。石英颗粒表面结构特征主要使用扫描电子显微镜进行观察,石英颗粒提取采用焦硫酸钾—氟硅酸浸泡法[33],前处理步骤参考文献[34],提取的石英颗粒用导电碳胶带固定并镀金后置于扫描电子显微镜下观察。
1.1. 研究区概况
1.2. 样品采集
1.3. 实验方法
-
在使用AnalySize进行非参数化端元分析时,线性相关性(R2)越高,角度偏差越小,非参数化粒度端元与粒度分布曲线的拟合程度越好[35]。拟合结果(图3)显示,当端元数为4时,R2为0.976(大于0.9),但是角度偏差远大于5;当端元数为5时,R2已经达到0.986,但角度偏差仍大于5;当端元数为6时,R2为0.994,角度偏差为3.37(小于5),此时端元相关性为0.311。本着端元最少、拟合效果最佳的原则,这里将端元数确定为6个。在进行端元分析时,不同的算法可能产生不同的结果,为了使端元分析结果更加可靠,本文同时运用基于神经网络的端元分析模型(Neural Network Based End-Member Modeling Analysis, NNEMMA)进行验证[36],发现二者的拟合结果基本一致(图4)。

Figure 4. Comparison of fitted results for end members based on non⁃parametric AnalySize and NNEMMA algorithms
端元分析结果如图5所示,端元粒度参数信息见表1。端元1呈正偏态、单峰分布,众数粒径位于0.75 μm(图5a);端元2呈单峰对称分布,众数粒径位于2.38 μm(图5b);端元3呈双峰对称分布、尖峰形态,第一众数粒径位于5.33 μm,第二众数粒径位于33.63 μm,沉积物分选一般(图5c);端元4呈单峰非对称分布,众数粒径位于11.93 μm(图5d);端元5呈三峰分布,峰高从高到低分别位于21.22 μm、4.23 μm和0.85 μm,且在100~200 μm呈现粗尾(图5e);端元6呈双峰、负偏态,第一众数粒径位于42.34 μm,第二众数粒径位于8.45 μm(图5f)。
端元数 端元模态/μm 平均粒径(Mz)/μm 分选系数/d 偏度/Sk 峰态/Kg 端元1 0.75 1.31 2.48 0.26 1.06 端元2 2.38 2.01 1.88 -0.06 0.95 端元3 5.33; 33.63 5.07 2.4 0.06 1.69 端元4 11.93 8.38 2.29 -0.38 1.50 端元5 21.22; 4.23; 0.85 8.79 3.69 -0.46 0.82 端元6 42.34; 8.45 17.53 3.71 -0.41 0.89 注: 端元模态/μm分别按第一众数粒径、第二众数粒径、第三众数粒径进行排列。 -
Claron组的石英颗粒从棱角状到次圆状,表面多发育蝶形坑、撞击坑、圆麻点和阶梯状断口(图6)。许多石英颗粒表面平坦光滑,为SiO2在表面形成沉淀[37];而且在蝶形坑和撞击坑中多见圆形鼓包凸起(图6a),呈葡萄状,为葡萄状SiO2沉淀[37]。呈锯齿状、高度参差不齐且与颗粒表面之间存在一定夹角的翻卷解理薄片[38]在地层中十分常见,边缘有SiO2溶蚀沉淀加厚(图6a,b)。
2.1. 基于端元模型的粒度分布
2.2. 石英颗粒表面结构特征
-
已有研究认为Claron组为河湖相沉积地层[6⁃9],但是野外考察结果表明地层中红色层具备显著的风尘沉积特征,与河湖相沉积存在较大差异。首先,从沉积物颜色来看,河湖相为水下沉积,与缺氧的还原环境相对应,灰黑色是其现代沉积物中最常见的颜色,而Bryce峡谷Claron组绝大部分地层呈红色,且红色的深—浅和灰白色随着地层层理/层次变化而整体发生变化,说明该地层的红色和灰白色是与地层层理/层次近于同期形成的原生颜色[39]。红色与赤铁矿密切相关[40],地层呈原生红色表明红色层是在地表氧化环境中形成和保存的。其次,沉积构造也是区分不同类型沉积物比较直观的特征之一[41]。河湖相沉积与风尘沉积在沉积构造上存在显著差别,前者为水下沉积(subaqueous),具备典型的层理或层面构造[41];后者为气下沉积(subaerial),沉积物以粉砂粒级为主,具备良好的分选性,沉积层理不明显[42]。Claron组宏观展示出极好的水平层状,或许是地质学家认定为水中沉积的层理,但是仔细观察发现,剖面中岩性、粒度和其他结构特征并未呈现显著变化,而是通过红颜色的深—浅和灰白色变化来体现层理/层次变化,不同颜色层之间呈现颜色逐渐过渡的特征,显著区别于上下层截然变化的层理。尽管宏观上可见灰白色层、粉红色层和褐红色层交替的层次变化,但是剖面上无明显的层理发育,也未见泥裂、波痕等流水作用留下的痕迹;沉积物质地均一、以粉砂和黏粒为主,垂直节理发育且富含碳酸盐,剖面内可见钙结核成层分布,沉积特征与典型风成黄土、风成红土十分类似[10,42]。另外,地层红色层具备显著的加积特征,即沉积与风化成土过程几乎同时进行,这是风尘沉积物特有的特征[43]。主要体现在两个方面:一是地层中的古土壤在形成时同时具有向两个方向分异的特征,向下土壤水携带沉积物中的碳酸盐至一定深度淀积,向上则有母质缓慢加入,导致钙结核的沉积上限随着土体的上涨而上涨[10](图2c);二是地层红颜色随着层理/层次整体发生变化,且沉积物质地均一、颜色均匀,成土程度基本一致。从更大范围来看,研究区Sunrise点和Sunset点两个采样点相距约1 km,但是两个点红色层的颗粒粗细相近、地层结构相似、沉积速率基本一致、古土壤发育程度大致相当,这一特征也只有风尘沉积才能具备[10]。
-
石英颗粒具备硬度大、化学稳定性高的特点,在表生环境中所受到的各种物理和化学作用都将不同程度地在其表面留下痕迹[37],因此石英颗粒表面结构特征常被用于理解沉积物的来源和后期改造过程[44]。Claron组红色样品的石英颗粒表面分布着大小不一的撞击坑和蝶形坑,这在我国典型风成黄土石英颗粒表面十分常见[44]。蝶形坑为磨圆度较好的颗粒相互碰撞的结果,是风成环境特有的标志,一般形成于强风暴中[45]。圆麻点在风成黄土—古土壤中的古土壤发育层位更为常见,是风化成土过程中化学溶蚀的产物[44]。该地层圆麻点较少发育,只在部分石英颗粒表面可以观察到;但是表征更强化学溶蚀作用的翻卷解理薄片在地层褐红色样品中十分常见,与褐红色层古土壤发育强的特征十分吻合。SiO2在石英颗粒表面形成沉淀的现象在地层中比较常见,在部分样品撞击坑或蝶形坑的表面,还可以发现大小不一的鼓包,这可能是由于强烈的撞击导致石英颗粒表面结构不稳定,更易遭受化学溶蚀作用,在表生风化的过程中SiO2在表面形成沉淀[37]。强烈的溶蚀作用往往和显著的沉淀作用相伴随,尤其在风成环境中[46⁃47],季节性的干湿变化显著,但孔隙水时常处于不饱和状态,溶蚀的SiO2不易被水带走,多在颗粒表面沉淀[48]。此外,地层中阶梯状断口发育,往往和挤压或猛烈撞击有关,通常出现在高能的水下环境中[45]。具备典型风尘沉积特征的层位发育的阶梯状断口也可能与其原始母质进入风成环境的时间较短有关[49]。因此,地层红色层的石英颗粒表面结构特征进一步为风尘沉积提供了证据。
-
频率曲线是粒度分布的直观显示,不同沉积环境的粒度分布明显不同。例如,砂粒是河流搬运最常见的粒级[50],通常作为众数粒径在频率分布曲线上出现;而典型风尘沉积通常以粉砂粒级为众数粒径[50]。但是自然界的沉积并不总是受一种搬运动力作用,不同条件下沉积物可能受多种动力影响,使得粒度频率曲线呈现不同形态。Bryce峡谷Claron组的粒度频率分布曲线呈现出多峰分布的特征(图5),但是所有样品均没有砂粒级作为众数粒径,只有部分样品在100 μm附近呈现粗尾,地层中也不含砾石,与河流搬运沉积物差异显著,而河流所携带的物质是湖泊沉积的重要来源。在这种情况下,很难通过粒度频率曲线的形态来鉴别其沉积过程。为了更详尽地了解地层中的沉积物组成,本文使用AnalySize进行非参数化端元分析,结合NNEMMA算法进行验证,确保分析结果更加可靠。两个算法最终拟合出6个端元,分别指示不同的沉积过程。
端元1呈正偏态、单峰分布,众数粒径位于0.75 μm(图5a、表1),该粒级应该属于成土过程中形成的黏粒[42]。成土作用可以从两个方面改变沉积物的粒径,一是不稳定矿物(云母等)在表生风化过程中产生粒度较小的黏土矿物;二是形成新的黏土矿物,但这种在地表环境下形成的矿物通常小于2 μm,甚至小于1 μm[51]。所有样品的粒度频率分布曲线上均存在小于1 μm的峰值,尤其在底部褐红色古土壤中往往作为第一众数粒径,形成的粒度频率分布曲线与中国南方第四纪网纹红土的曲线形态十分接近[52⁃53],而且相应的石英颗粒表面也呈现强烈的淋溶成土特征。因此,端元1代表了沉积物沉积后经历风化成土作用的成土组分。端元2呈单峰对称分布(图5b),众数粒径位于2.38 μm(表1),属于沉积学中的淤泥、泥浆(Mud),平均粒径为2.01 μm,属于极细的黏粒,沉积物呈适度分选。无论是终年积水还是临时性的湖泊环境中,沉积物在静水中的沉降会增加细粒黏土的沉积,形成湖泊环境特有的1~2.5 μm组分[23,54⁃55]。另外,有研究表明冲—洪积形成的洼地也存在湖泊静水沉积这一特征[12]。该地层沉积时的古地形为盆地地形[29],易在排水不畅的地区形成积水洼地甚至湖泊。因此,端元2主要代表了积水洼地/湖泊静水沉降的细粒组分。
端元3含有两个众数粒径,第一众数粒径位于5.33 μm,第二众数粒径位于33.63 μm。与端元3拟合程度高的粒度分布曲线也多呈单峰分布,代表这些层位形成时期的搬运动力比较单一。该端元第一众数粒径出现频率为75%,表明其以细组分为主。非常细的组分既可能来自长距离风力搬运,也可能是河流短距离搬运沉积,又或者是风水共同作用的产物[56]。河流搬运沉积具备典型的流体动力分选特征,短距离搬运过程中会有大量粗颗粒组分沉积(大于63 μm)[57],但是从整个地层的粒度分布来看,缺乏河流搬运的砂粒作为众数粒径(图5)。而且从野外特征来看,地层中并无截然变化的沉积层理,也没有粉砂、细砂、砂粒明显粗细变化的结构特征(图2)。表明该地层沉积时并未发育大型、稳定的河流,显然端元3不属于河流搬运的产物。端元3的另一个众数粒径为33.63 μm,属于风尘基本粒组的范围[42]。风尘沉积各个粒级的含量比较均一,不同于河流沉积物各个粒级含量差别较大[50]。风动力学研究表明,在中等强度风暴条件下,小于10 μm的细粉砂可以被搬运至世界各地[58],它们既可能是聚集/吸附于粗颗粒上被搬运,也可能是被风单独搬运[59]。若以聚合体的形式或吸附于粗颗粒之上被搬运,则细颗粒应与粗颗粒同时变化[60],于是将端元3在各样品中的比例分别与端元4,5,6在各样品中的比例进行相关分析,结果均为负数或不相关。而且一些层位端元3的含量超过60%,表明端元3不是吸附于粗颗粒或以粗颗粒聚合体的形式被搬运,而更可能是高空气流远距离搬运的组分。
端元5呈三峰分布,三个峰分别位于21.22 μm、4.23 μm和0.85 μm(分别为第一、第二、第三众数粒径),具备典型的流体动力搬运、分选特征。前文已经排除地层形成时期存在稳定、大型河流的可能,而且该端元仅在100~200 μm呈现粗尾,表明粗粒组分并不是该地层稳定的来源,而粗粒组分突然增加,可能代表着该时期地表径流突然增强。该地层堆积于前陆盆地,可能位于距离风化岩石坡下不远处,降雨增加导致地表径流增强,携带大量碎屑物质至低洼处沉积。但是这种沉积方式不同于河流搬运,当降雨减少时,地表径流携带碎屑物质的能力也会减弱,表现为冲—洪积搬运。冲—洪积形成的沉积物也具有流体动力分选的特征,因此端元5应该属于地表径流增强时形成的冲—洪积组分。
端元4和端元6的粒度分布特征均与中国西峰黄土—古土壤十分相似(图7a)。相关研究表明,即使来自不同物源的粉尘,一旦在气流中经历充分混合,就会呈现相似的形态特征[60]。孙东怀等[61]对我国西峰、洛川典型风成黄土剖面的粒度分布特征进行总结后发现,它们总体呈双峰、负偏态非对称分布,分布范围一般为0~150 μm,众数粒径一般介于32~16 μm,向细粒端减小的过程中往往在2~4 μm出现第二个众数粒径。端元6呈双峰分布,第一众数粒径为42.34 μm,向细粒端缓慢减少的过程中出现第二个众数粒径8.45 μm。不同于端元5陡然变化的特征,端元6的颗粒组成更均匀,比较符合风尘沉积的特点[50]。与端元6拟合程度较高的粒度频率分布曲线与西峰第三纪风成红黏土比较相似(图7b),但红黏土在4~7 μm的细粒组分更高。相较于西峰黄土和红黏土的粒度组成,端元6的第一众数粒径更粗,且平均粒径17.53 μm也粗于西峰黄土的平均粒径(约9.95 μm),这表明端元6的平均动力更强。Tsoar et al.[58]的研究中指出粒径在30~63 μm这一范围的粉砂,为一般风暴下二次扬尘带来的近源物质或强风暴下的远源物质。端元6与昆仑山北麓现代沙尘暴沉积物的粒度频率分布曲线也十分相似,但是现代沙尘暴沉积物更粗(大于70 μm)[60]。因此,端元6代表一般风暴或强风暴搬运的近源或远源物质,这与石英颗粒表面的蝶形坑和撞击坑特征也十分吻合。而风暴过后形成的浮尘组分会在风力减弱或停止后沉降,沉降的颗粒往往小于20 μm[58]。端元4呈单峰分布,众数粒径为11.93 μm,在风暴过后的浮尘组分粒级范围之内,而且与端元4拟合程度高的曲线与西峰古土壤的曲线形态高度相似,但成土峰更高。因此,端元4应该属于风暴过后沉降的浮尘组分。

Figure 7. Comparative grain⁃size distribution curves for Claron Formation, Bryce Canyon, and typical eolian sediments
综合上述分析,结合各端元在不同层位的比例变化(图8a),对Claron组粒度分布进行分解的6个端元中,端元1属于成土组分,在地层各个层位均存在,平均含量约为17.98%,含量高的层位均与野外判定的黏化层相对应;端元2属于积水洼地/湖泊静水沉降的细粒组分,在地层中的平均含量约为16.73%;端元3代表高空气流远距离输送组分,在地层中的平均含量约为19.42%;端元4代表风暴过后的浮尘组分,在地层中的平均含量约为14.59%;端元5代表降雨量增大时期形成的冲—洪积组分,在地层中的平均含量约为15.49%;端元6代表风暴搬运的近源或远源组分,在地层中的平均含量约为15.77%。在上述6个端元中,端元3、4、6均指示风尘沉积(统称为风尘沉积端元),风尘沉积端元在地层中的平均含量约为49.79%,最大含量约为97.27%,加上部分成土物质也来自风尘沉积,表明地层中有一半以上的物质来自风尘沉积。
-
关于Bryce峡谷Claron组的沉积环境,目前尚未有对这一区域这一地层的细致研究,而主要是从大范围分布的Claron组来认识。例如Goldstrand[8]详细描述了麦格顿(Markagunt)高原和庞沙冈特(Paunsaugunt)高原广泛出露的Claron组沉积环境,认为地层红色部分主要是成土过程中植被发育,植物根系搅动沉积物形成氧化环境,生成大量赤铁矿所致,这里主要指的是次生的成土过程,沉积物来源则归因于洪水事件,而地层白色部分为湖相石灰岩。Taylor[7]对Red Hill等地区零星分布的Claron组进行岩性调查研究,总体上将Claron组划分为上下部碎屑岩相和中间石灰岩相,认为碎屑岩相主要是辫状河流沉积,石灰岩则指示湖泊沉积环境。Sanjuan et al.[3]在Claron组下部发现了轮藻(Peckichara torulosa)的微体化石,并基于该淡水植物化石在欧洲的古生态容限和生物地层分布,认为在始新世早期该地区发育了临时性湖泊。Sanjuan et al.[4]发现含有轮藻化石的泥岩,通常是埋藏良好的古土壤,其中含有腹足类、介形类和轮藻化石,这些层位通常具有较高含量的碳酸盐,进一步认为这可能是漫滩沉积。因此,对于各地区Claron组的形成环境目前尚未有定论,但倾向于湖泊起源这一观点[3⁃9]。
对Bryce峡谷的Claron组进行研究后,我们认同地层中的灰白色层可能属于湖泊沉积,因为众多学者在地层中发现的腹足类化石、藻类碎屑等水生特征主要分布于灰白色层。但是对于将红色层认定为湖泊沉积则存在诸多疑问:一是现代湖泊沉积物由于受到水下缺氧环境的限制,有机质分解缓慢,往往形成灰黑色甚至黑色沉积物,将今论古,而该地层下部总体呈氧化红色,似乎与缺氧的湖相沉积环境相矛盾;二是在红色层甚至整个剖面层理特征并不明显可见,甚至缺乏,而地层以粉砂粒级为主,如果发生积水,那么在积水被蒸发退去后,积水面很大概率会形成一层硬的泥质结皮,在层面上表现为泥裂,在剖面上就会形成层理,但不论在红色层还是灰白色层中,都很难见到层理或泥裂;另外,红色层具备显著的加积特征,代表着沉积物堆积与地表风化成土过程几乎同时发生,也较难从湖泊沉积的角度去理解。对该地层进行粒度端元分析的结果表明地层中一半以上的物质来自风尘沉积(图8),而且部分层位风尘沉积占据主导。于是存在两种可能的沉积过程,一是湖泊沉积,其中混入了较大比例的风尘沉积物质。但是从野外特征来看,地层总体呈红色且发育连续的均质古土壤,表明这不是终年积水的湖泊类型。二是风尘沉积和积水洼地/临时性湖泊交替沉积。
从各端元在剖面中的比例变化来看(图8a),代表不同沉积过程的各组分在各个层位均占有一定比例,但不同时期占据主导的组分不同。成土组分含量高的层位对应沉积物颜色较红(褐红色)。沉积物颜色在一定程度上能够反映气候的干湿变化,红色通常来自赤铁矿,代表干旱氧化的环境[40],因此红色古土壤发育的层位对应着地表干旱氧化的环境。灰白色代表过渡湿润的气候环境[62],沉积物渍水会导致其中的3价铁还原为2价铁,形成可溶于水的氢氧化铁随水流走,沉积物红色逐渐变淡。灰白色层端元2(积水洼地/湖泊静水沉降组分)和端元5(冲—洪积组分)的含量均比较高,表明其形成时期受水作用大,可能形成积水洼地甚至临时性湖泊。但不同于终年积水的湖泊,因为在灰白色层中仍然可以观察到浅褐色古土壤层,表明灰白色层也存在地表氧化的环境。因此灰白色层可能对应着积水洼地/临时性湖泊沉积;端元2则代表积水洼地/临时性湖泊静水沉降的细粒组分。
风尘沉积端元在各个时期均占有较大比例,表明风尘沉积是地层中稳定的物质来源。风尘沉积占据主导地位的层位通常对应古土壤发育程度高的层位。图8a中Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ为3个高度发育的复合古土壤层,其中Ⅰ对应的古土壤层如图2c所示,钙结核在剖面中高度发育。Ⅱ和Ⅲ同为位于地层下部的褐红色古土壤层,黏化层和浅色斑状网纹在该层高度发育(图2f)。这3个复合古土壤所在层位的端元比例变化均存在大致相似的情况,即上部成土组分占据主导,下部风尘沉积组分占据主导,同时有冲—洪积组分和积水洼地/临时性湖泊静水沉降组分加入。这一现象或许可以解释为:该地层形成于四周高、中间低的盆地中,盆地地形极易汇水且排水较差,加上处于风化岩石的坡下,强降水易形成洪流,携带粗粒物质在山前沉积,细粒物质被带到更远的地方沉积。相较于风尘沉积,冲—洪积的沉积速率高,能在短时间内形成大量沉积物。若降雨持续时间长,则易在低洼地区积水甚至形成临时性湖泊;若降雨持续时间短,沉积物沉积后浸水时间相对较短,随后气候比较干旱,进入漫长的成土期伴有风尘物质不断加积。因此,该地层为风尘沉积、冲—洪积和积水洼地/临时性湖泊交替沉积形成,在以冲—洪积和积水洼地/临时性湖泊沉积为主的时期,气候湿润;而风尘沉积和成土占据主导的时期,气候相对干旱。
3.1. 地层风尘沉积特征分析
3.1.1. 野外沉积特征分析
3.1.2. 石英颗粒表面结构特征分析
3.2. 不同端元的沉积学意义
3.3. Claron组风尘沉积识别对沉积环境的指示意义
-
(1) Bryce峡谷Claron组宏观上呈现深—浅不同的红色和灰白色变化,但并未相应地呈现岩性、颗粒粗细和沉积构造的变化,而且不同颜色呈现逐渐过渡特征,显著区别于突变的水成层理。地层红色层呈现出显著的加积特征,结合石英颗粒表面结构特征可知Claron组红色层以风尘沉积为主。
(2) 对Bryce峡谷Claron组进行非参数化粒度端元分析,共分解出6个具有不同沉积意义的端元。其中端元1代表成土组分;端元2代表积水洼地/临时性湖泊静水沉降的细粒组分;端元3代表高空气流远距离输送组分;端元4代表风暴过后的浮尘组分;端元5代表冲—洪积组分;端元6代表风暴搬运的近源或远源组分。其中,端元3、4、6(第一众数粒径分别为5.33 μm、11.93 μm、42.34 μm)均来自风尘沉积,统称为风尘沉积端元。风尘沉积端元在地层中的平均含量约为49.79%,表明地层中一半以上的物质来自风尘沉积。地层各个层位均含有较大比例的风尘沉积组分,表明风尘沉积是该地层稳定的物质来源。
(3) 从各端元在剖面中的比例变化来看,该地层是由风尘沉积、冲—洪积和积水洼地/临时性湖泊交替沉积形成。而代表不同沉积过程的端元与沉积物颜色、古土壤发育程度的关系表明,在冲—洪积和积水洼地/临时性湖泊沉积占据主导的时期气候湿润,而风尘沉积和成土占据主导的时期气候相对干旱。











 DownLoad:
DownLoad:






