-
四川盆地是我国西部重要的含油富气盆地,自1964年发现威远气田以来,已陆续在埃迪卡拉系至侏罗系多套含油气层系探获油气资源[1]。近年来,安岳气田的发现使四川盆地下组合(埃迪卡拉系—寒武系)再次成为油气勘探的热点领域[2]。
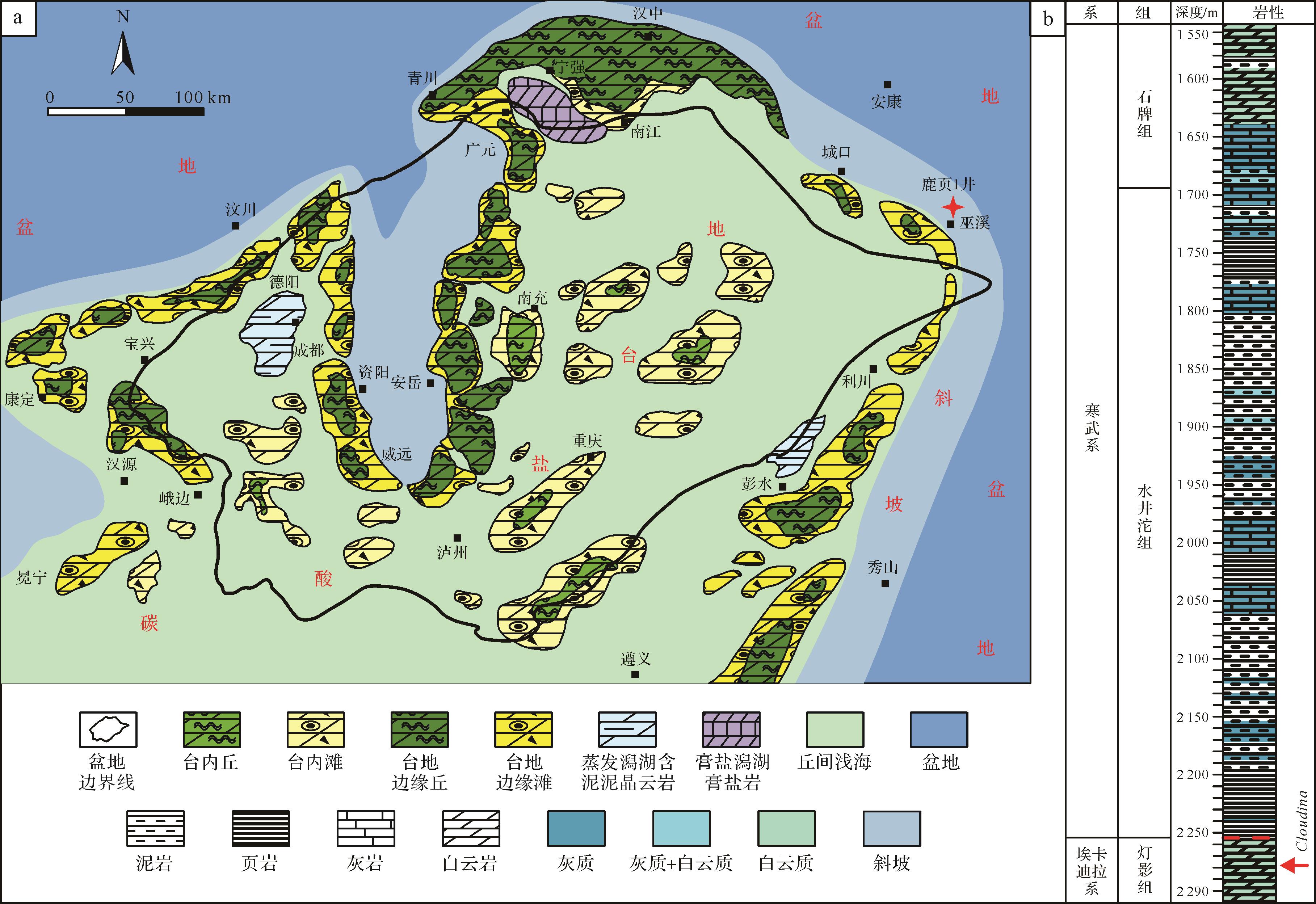
四川盆地埃迪卡拉系油气藏资源主要分布在灯影组内部。四川盆地灯影组自下而上发育四个典型的岩性段。其中,灯一段、灯二段、灯四段为典型的台地碳酸盐岩建造,以白云岩为主,灯三段以碎屑岩为主[2]。油气藏主要集中在孔隙发达的灯二段和灯四段。灯四段沉积时期受到灯影期末构造抬升引起的岩溶作用影响[2⁃5],其储集空间以角砾间溶孔、大规模溶孔溶洞为主[3],与灯影组古岩溶地貌密切相关[6]。而灯二段和灯四段均发育了大量格架孔、粒内孔、粒间孔以及“葡萄花边”构造残留孔洞,这些孔隙主要受丘滩复合体和表生期岩溶作用的共同控制形成[3],属于蓝细菌丘滩白云岩裂缝—孔洞型储层[4],因此灯二段和灯四段的储层潜力又与蓝细菌丘滩结构的分布和规模密切相关。
克劳德管(Cloudina)是一种在埃迪卡拉纪末期全球广布的套管状化石[7⁃12]。部分学者认为,Cloudina是最早具备矿化骨骼建造能力的后生生物之一,在纳米比亚地区可见由Cloudina参与构建的生物礁结构,它们可能代表了已知最古老的后生动物—微生物礁[10⁃11,13⁃14]。尽管学界对于Cloudina的矿化及建礁能力仍存在不同意见,有学者基于这些早期矿化生物富集层的沉积学研究,认为这类生物骨架在全球碳酸盐岩中的出现可能意味着显生宙型底质在埃迪卡拉纪末期的出现。这些骨屑颗粒集合体,尤其以生物滩形式在南美的巴西和乌拉圭、北美的加拿大和非洲的纳米比亚等地的出现,为喜好硬底的底栖生物类型提供了丰富的栖息地[15⁃17]。在显生宙,后生生物礁—滩结构是油气勘探的重要关注对象[18⁃19],大量的后生生物架构及骨屑结构能够为油气提供丰富的储集孔隙。但到目前为止,对埃迪卡拉系储集孔隙的研究仍以蓝细菌相关的丘滩结构为主要对象,而对后生生物Cloudina礁或Cloudina富集层的油气储层潜力还缺乏评估。
近年来,人们陆续在陕南及峡东与灯三段至灯四段相当的地层中发现丰富的Cloudina化石,并探讨了它们的生物属性、地层分布、生物矿化及保存特征等问题[7⁃12]。在油气勘探过程中,本研究首次在川东北地区巫溪地区钻井岩心中灯影组顶部发现了丰富的Cloudina化石。本文将初步探讨Cloudina富集层作为灯影组可能的储集孔隙提供者在油气勘探中的潜在意义。
-
中国主要包含了华南、华北和塔里木三个古老克拉通[20]。其中华南克拉通是东亚最大的克拉通之一,其北部以秦岭—大别—苏鲁造山带与华北克拉通相隔,西南部以哀牢山—松马构造带与印支地块相隔,西北部以龙门山断裂带与松潘—甘孜地块相隔,东南部为古太平洋[20]。华南克拉通可进一步分为扬子地块和华夏地块,二者在约1 140 Ma就已经发生了部分的聚合[21],并被江南造山带所隔断[20]。研究区巫溪地区位于扬子地块北缘,在四川盆地东北部和秦岭造山带之间,属于南大巴山前陆褶皱冲断带东段,其北部为城口—房县断裂,主要构造格架为近东西向的背斜和向斜构造[22]。区内沉积地层处于川东、川北与鄂西三峡地层系统的过渡地带,前人将其划归于扬子地层区,上扬子地层分区,四川盆地小区[23](图1)。研究区最古老的地层是雪球地球事件[24⁃26]中沉积的南沱组冰碛岩,主要分布在巫溪康家坪地区,未见其底界出露。全球性冰川消融之后,扬子地区接受了广泛快速的海侵[26],并在区域上形成了陡山沱组沉积,岩性以黑色页岩、泥岩为主,夹白云岩和砂岩,可以与峡东剖面进行对比[27⁃28]。陡山沱组沉积后期,先前形成的台内盆地被逐步填充[26],并在灯影组沉积时形成了广泛的碳酸盐岩台地[1,29]。当时巫溪地区处于台地边缘—斜坡过渡相带[29⁃30],因此区内灯影组岩性在横向上较为多变,以中厚层—块状白云岩为主,部分地区和层段见鲕粒白云岩和砂屑白云岩,代表了间歇性的高能环境[30]。
-
研究样品取自川东北巫溪地区的鹿页1井2 269.64 m附近,接近灯影组顶部(图2)。手标本拍照使用Nikon D3200结合SAGA高清三目体式变倍显微镜,在成都理工大学沉积地质研究院完成;薄片单偏光及正交偏光拍照在成都理工大学地球科学学院使用Nikon偏光显微镜LV100POL完成;化石及孔隙的扫描电镜拍照和能谱测试以及阴极发光拍照在成都地质调查中心使用HITACHIS-3000N和Nikon AX10完成,束电压15 kV,束电流400 μA。所有样品均采用相同测试条件以进行对比,检测标准依据SY/T 5916-2013岩石矿物阴极发光鉴定方法。

图 2 四川盆地东北部鹿页1井地层柱状图及岩心照片
Figure 2. Stratigraphic column at well Luye 1 in the northeastern Sichuan Basin, and core photographs
Micro-CT测试在天津三英精密仪器股份有限公司使用nanoVoxel-5000系列CT设备完成。选取的样品分为不同大小两种,包括直径约1.5 mm的圆柱体3枚,以及长宽约5.0 mm、高约2.5 mm的立方柱体1枚,用以对白云岩基质和含化石层进行不同分辨率的micro-CT扫描。对于小块的基质样品,可以使用高达0.53 μm分辨率的micro-CT分析得到微米级的孔隙形态和更加精确的孔隙率数据。但由于基质不均一,单个样品并不具有代表性,不同的小块样品micro-CT的样本偏差可能较大。因此,为得到较为全面客观的数据,需要选取多个样品进行分析。大块的含化石样品能够提供管状化石的三维形态、空间分布特征,得到的孔隙数据也更全面并具有代表性,但由于扫描精度不足,分辨率仅有8.3 μm,难以识别微米级、亚微米级的孔隙。因此,本研究使用3枚来自基质的小块样品进行高分辨率分析,结合1枚含化石的样品提供宏观形貌,在不同尺度上评估研究材料的孔隙形态和孔隙率。Micro-CT数据使用AVIZO数据处理软件进行处理。首先通过对原始micro-CT数据进行裁剪切割,以去除样品边缘对孔隙识别过程的干扰;后续使用人工方法对CT灰度图进行阈值分割,进而识别孔隙与不同类型的矿物组分,最终对孔隙和不同矿物的空间分布特征进行重建,并通过软件内置程序计算孔隙度。含化石层的岩心样品和薄片在完成相关分析后均存放于成都理工大学沉积地质研究院。
-
研究样品为生物碎屑微晶白云岩。岩心手标本呈浅灰色,块状构造,未见纹层发育(图2a~d)。大量数毫米至数厘米长的深灰色管状生物碎屑长轴平行于层面方向堆积,未见明显定向性和粒序特征。生物化石占岩石总体积20%~30%,化石之间以基质支撑为主,少数呈颗粒支撑(图2b~d)。管状化石在镜下可见薄的管壁,偶见偏心套锥状构造(图3g),据此认为该管状化石应当属于Cloudina[7⁃11,31]。

图 3 鹿页1井Cloudina的薄片镜下照片
Figure 3. Thin⁃section photomicrographs showing Cloudina fossils
in well Luye 1 镜下可见化石富集层基质以微晶白云石为主。微晶白云石晶体表面比较污浊,保留了部分平直的晶面,没有见到雾心亮边结构(图3a~l),以暗红色阴极发光为特征(图4a~j)。化石和基质中分布有较大的白云石晶粒,晶粒往往干净透明,边界平直,在管状化石中与内壁的界线较为清楚(图3g~l),并具有亮红色的阴极发光特征(图4d,g,h)。较大的白云石晶粒往往被石英所交代,石英未见内部结构,有时呈原始白云石矿物的假象,保留了格子状的解理缝和三角形的溶孔,常与焦沥青、重结晶白云石伴生(图3i~j),无阴极发光(图4c~h)。化石的原始管壁结构受到溶蚀作用破坏,已不可见,薄片中化石管壁的位置由大小不一的白云石晶粒所充填(图3j~l)。部分壳体和管内空间可被焦沥青充填,焦沥青也无阴极发光特征,呈均一的黑色(图3h~l、图4a~f)。

图 4 鹿页1井灯影组白云岩薄片镜下照片和阴极发光特征
Figure 4. Photomicrographs and cathodoluminescence images of Dengying Formation dolomite in well Luye 1
基质中可见泥晶白云石和有机质富集形成的微生物组构(图3a~f),其形态可分为凝块状、絮状和团粒状三种。凝块状组构的发育较为局限,往往只有数毫米至厘米级大小。它们在薄片中既不成层分布,也不组成格架,而是呈分散状分布(图3a~c)。絮状组构较为常见,一般呈长0.5 mm至数毫米的不规则絮状,有时呈卷曲状。它们可能代表凝块状组构发育的早期阶段(图3d,e)。团粒状组构在薄片中较少见。它们的直径一般不超过0.2 mm,分布没有明显的规律性,偶见聚集(图3f)。这些微生物组构在阴极发光下呈亮红色(图4i,j)。
-
基于扫描电镜观察和micro-CT数据,发现样品中的孔隙类型主要有粒间孔、沥青孔、晶内溶孔、晶间溶孔与生物孔(图5)。

图 5 Cloudina及其基质的扫描电镜(SEM)和能谱分析(EDS)
Figure 5. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images and energy dispersive spectra (EDS) of Cloudina and matrix
粒间孔常见于一些白云石晶粒的边缘,呈等厚环边状围绕着中心的晶粒分布,并为沥青所充填,其宽度基本小于10 μm。局部的黏土矿物集合体中也可见丝缕状、网格状的孔隙,这些孔隙的直径往往只有数微米(图5a,b)。沥青孔指沥青内部的孔隙,它们主要呈圆形或不规则状,分布也没有明显规律,宽度从数微米至数十微米不等(图5c,d)。晶内溶孔是碳酸盐晶体内部遭受溶蚀而形成的孔隙。它们顺碳酸盐矿物解理面发育,多呈数微米宽的三角状,有时也可见保存在碳酸盐矿物假象的石英晶体中(图5e,f)。晶间溶孔分布在粗晶的石英和白云石颗粒之间,它们的形状受周围晶体边界的控制,往往呈港湾状或参差状,宽度变化较大,有的可达1 mm。这些孔隙现也多被沥青填充(图5g)。生物孔主要来自Cloudina管状化石的空腔。材料中Cloudina的管体截面呈圆形,直径可达1~2 mm。此外,Cloudina化石管壁多遭受溶蚀,这些被溶蚀的部分也形成了孔隙,并可为沥青所填充(图5g~j)。
Micro-CT数据显示,基质中的孔隙形态呈分散状(图6a~c),主要分布在密度较低的矿物内部和裂隙中(图6b)。这类矿物占比较小,呈不规则状,结合对基质的观察结果(图3a~l),推测其为重结晶的白云石。因此这些分散状孔隙可能代表白云石的粒间孔、晶内溶孔和晶间溶孔。基质中的孔隙大小介于1~3 μm,大多数孔隙小于2 μm,基质的整体孔隙度介于0.1%~0.4%(图6a~c)。从大块样品与小块样品在同一分辨率下的对比可见,小块样品在高分辨率扫描下能够识别出更多精细的孔隙(图6d,e)。化石富集层赋存的孔隙主要受到管状化石形态的控制,多沿化石长轴分布,呈连通的长条状,有时弯曲(图7a~c)。从micro-CT图像切片来看,富化石层中存在三种不同灰度的物质组分。其中最暗灰度的部分代表沥青和孔隙,中等灰度的是粗晶石英或白云石,最亮的部分代表微晶白云岩基质(图7a)。在灰度图中计算不同的灰度分布区间(图8a,c),得出三者分别占总体积的2%,12%和86%(图8b),其中孔隙占比约0.7%。孔隙可能来自管状化石残余的生物孔、与石英和白云石晶粒相关的粒间孔、晶内溶孔和晶间溶孔以及与沥青相关的沥青孔。由于在不同分辨率下能够识别的孔隙大小有所差异,化石富集层的孔隙度应比通过灰度图计算出的体积更高。

图 6 鹿页1井灯影组白云岩基质的micro⁃CT图像与孔隙特征
Figure 6. Micro⁃CT images and pore characteristics of Dengying Formation dolomite matrix in well Luye 1
-
研究材料中识别出的成岩作用类型主要有胶结作用、重结晶作用、硅化作用、溶蚀作用,还有与碳氢流体演化有关的沥青充填作用。综合分析推测,这些生物碎屑微晶白云岩在不同阶段内经历了差异性的成岩作用,并不断对孔隙类型和孔隙度造成改变(图9)。

图 9 鹿页1井灯影组白云岩成岩作用和孔隙演化序列
Figure 9. Diagenesis and pore evolution sequence of Dengying Formation dolomite in well Luye 1
薄片下呈暗红色阴极发光(图4a~j)的部分可能代表最早期形成的碳酸盐胶结物。此外,微生物组构中可见顺纹层发育的亮红色阴极发光,可能代表不同纹层中与有机质相关的自生泥晶的含量差异[32],其中的富有机质纹层多呈亮红色发光(图4i,j)。粗晶白云石充填物在阴极发光下显示出中等强度的亮红色(图4a~h),和其他碳酸盐矿物(图4c)或与热液溶蚀相关的孔隙周边(图3a,c~h)存在的较明亮胶结物类似,可能来自较晚期次的胶结作用。明亮的亮红色阴极发光白云石晶粒(图4d,g,h),主要分布在溶蚀的孔隙内部并与焦沥青、重结晶白云石伴生(图3g~l、图4b~h)。这些矿物可能来自最末期的成岩阶段。
-
在讨论Cloudina化石在油气储层中的潜在贡献前,首先需要考虑这些生物的时空分布及其能够形成储层的潜在规模。一般认为,Cloudina的最早出现时间大概在551~548 Ma,消失于埃迪卡拉纪末期,与华南地区灯影组的沉积年龄大致相当。华南地区Cloudina的出现时间相对较晚,大量黄铁矿化和磷酸盐化保存的Cloudina化石最早被报道于陕南地区的灯影组高家山段,其层位相当于四川盆地的灯三段[7⁃9]。此外,在峡东地区的灯影组石板滩段也有Cloudina化石的报道,层位可能与四川盆地的灯三段一致。之前的研究普遍认为埃迪卡拉纪末期Cloudina的消失可能同时伴随着其他埃迪卡拉生物的灭绝[33⁃34],然而,近年来在埃迪卡拉—寒武系界线附近(约540~535 Ma),全世界范围内均发现了丰富的Cloudina化石。在部分地区,Cloudina与一些寒武纪最早期的小壳化石混生,这一现象在一定程度上改变了之前对埃迪卡拉纪末期生物大绝灭事件强度的认识,也暗示了寒武纪大爆发的“深根”或许能够下延至埃迪卡拉纪末期[9,35]。
在空间分布上,陕南[7⁃9]、神农架[36]和峡东地区[31]灯影组均有较为丰富的Cloudina发现。本研究表明,Cloudina在扬子地台上的分布可能比原先认识到的更加广泛。整体来看,在545~540 Ma,已知Cloudina富集层的分布靠近扬子地台的边缘,而扬子地台内部的报道相对较少。在当前研究阶段,这样的地理分布特征很可能是由研究程度、采样偏差以及化石保存条件差异造成的[12, 31, 37]。Cloudina在埃迪卡拉纪末期扬子地台的实际分布情况,还有待进一步研究。
-
埃迪卡拉纪—寒武纪转折期是碳酸盐工厂的关键转折期之一,在该时期,生物碳酸盐沉积的主要生产者由前寒武纪长期占据主导地位的微生物逐步向后生生物转变。在这个过程中,也伴随着主要造礁生物的转变。生物礁是一种由生物建造的具有正向构造的地形。在前寒武纪,生物礁均为微生物所构成。步入显生宙后,后生生物礁(如古杯礁)逐步崛起,取代微生物成为碳酸盐工厂的重要生产机构,同时也是油气储层发育的重要场所。
目前学界关于Cloudina是否具有造礁能力仍然存在争议。反对者的主要依据是[38]:(1)Cloudina的外壳可能并非矿化的,而是主要由几丁质组成,因此缺乏主动构建生物礁的能力;(2)通过统计和3D重建工作发现,纳米比亚的Cloudina富集层主要由生物碎屑构成,而不是此前所认为的生物构建的结果,具定向排列特征的Cloudina化石不超过3%;(3)此前认为的疑似生物胶结特征实际上更可能是成岩作用的结果。不过,后续的研究表明,Cloudina是具备成礁能力的[13⁃14]。例如,钙同位素数据证实存在生物构建和在管体外分泌矿物质进行胶结加固的特征,再次表达了对Cloudina具备建礁能力这一观点的支持[39]。
无论如何,这类由Cloudina构成的生物骨架可能代表了显生宙型后生生物硬底在全球埃迪卡拉纪末期的出现,这是除底质革命和农业革命之外,又一个重要的生物演化事件[14]。尽管Cloudina富集层的几何构造相对简单,但能够提供丰富的生物碎屑,这个过程深刻影响了当时海洋沉积物的底质条件。一方面,作为寒武纪大爆发可能的前提条件之一,埃迪卡拉纪末期生物骨架富集的底质条件为后续的生命辐射事件铺设了舞台[17,39⁃40];另一方面,丰富的生物骨架颗粒也为沉积物提供了丰富的储集空间,从这一点上看,它们与显生宙的生物颗粒没有任何本质的区别[41]。
另外,Cloudina与微生物有着十分密切的关系。基于硬体部分的形态学和生态学研究复原了Cloudina作为固着底栖和滤食性动物的特征[7⁃8,42⁃44],其管体底端可能以嵌入方式固着于微生物席基底上[7⁃8,10,44⁃47]。同时,微生物席可能还为Cloudina提供了营养来源。因此,Cloudina对微生物层有强烈的依赖性。在陕南[8,48]、巴拉圭[15]和纳米比亚[10,14,39]等地,常见Cloudina与微生物席或叠层石礁的密切共生。来自巴拉圭和纳米比亚的研究结果表明,Cloudina骨架在沉积物中的过度富集可能对微生物层的生长起到抑制性的作用[39]。巴拉圭地区能够识别两种不同的骨架富集状态[41],类型1表现为密集堆积的异地搬运颗粒碎屑,类型2为近原地埋藏的松散堆积的骨架集合体。
从灯四期古地理格局上看(图1),鹿页1井所在的巫溪地区处于台地边缘—斜坡相带[29⁃30],岩心中并未见到明显的斜坡环境滑塌构造标志,而是以块状的微晶白云岩为主,伴随生物碎屑富集层,因此推测鹿页1井灯影组顶部沉积于台地边缘环境。镜下可见Cloudina富集层基质以微晶白云石为主,其中含有丰富的凝块状、絮状微生物组构,往往代表了能量较低的水体环境[49]。由于这些微生物组构零星发育,并不能形成规模,因此推测Cloudina富集层可能处于丘基微相。这一微相多形成于海平面扰动背景下的低能向高能转换的正地形环境,微生物较为缺乏但处在逐步繁盛的阶段。凝块状微生物组构大多为分散状,可推测沉积过程的水体能量有一定的波动变化,但总体处于较低水平。本研究中也可见Cloudina与微生物组构相邻保存,尽管大部分管状化石保存相对完整,但由于缺乏确切的原地埋藏证据,因此其与微生物之间的共生关系并没有得到直接体现,尚且不能对Cloudina-微生物礁的生态模式提供支持。除此之外,本文中的骨架颗粒更接近巴拉圭地区中类型2的骨架集合体,峡东地区灯影组顶部Cloudina富集层则似乎与类型1更加接近[31,41]。
-
从阴极发光揭示的成岩序列来看,灯影组顶部Cloudina富集层的孔隙类型和孔隙度随着成岩作用改造不断变化(图9)。在同生成岩阶段,孔隙类型主要为碳酸盐矿物颗粒之间的晶间孔和Cloudina管状结构形成的生物孔(图3j~l、图4a,b)。在早成岩阶段,粗晶白云石胶结物对溶孔和管状化石内部的生物孔进行充填,该阶段的孔隙类型主要为残存的生物孔和生物格架溶蚀孔(图3g~l)、碳酸盐矿物之间的粒间孔(图5a)以及溶蚀作用下形成的晶间溶孔和晶内溶孔(图5e,f)。晚期胶结作用的分布和发育程度可能受到了热液流体的控制,这一阶段主要的孔隙类型没有变化,但孔隙度相对变低。中—晚成岩阶段,酸性的碳氢热液流体对岩石造成溶蚀作用和进一步重结晶作用。这一阶段也没有孔隙类型的变化,但由于重结晶与沥青(图3k~l、图4c~f)充填作用,导致整体孔隙度降低。
从micro-CT揭示的基质中的孔隙分布结果来看,细小的孔隙均匀地分布在微晶白云岩内部(图6a,b),偶尔呈裂隙状分布(图6b),连通性较差。它们主要来自白云石尤其是重结晶白云石的粒间孔、晶内溶孔和晶间溶孔,代表了不含管状化石时岩石孔隙度的背景值。而含化石层的micro-CT结果显示,管状化石是重要的孔隙提供者(图7b,c),残余的生物孔能够提供部分孔隙空间。管内白云石和石英晶粒也成为较小的孔隙赋存场所,这些晶粒提供的孔隙类型同样为粒间孔、晶内溶孔和晶间溶孔。除了管状化石的内部空间,化石管壁在成岩阶段溶解后留下的空间也能作为孔隙度来源和流体运移通道。结合前文所述,化石富集层的孔隙、沥青(约2%)以及粗晶石英和白云石胶结物(约12%)占整体约14%。从图像上看(图8c),这些孔隙和充填物主要分布在管状化石的内部,少量分布在基质中。因此,其中的相当一部分与管状化石所占岩石的体积重合。据此推测,在同生成岩阶段,管状化石内的生物孔提供的孔隙率可能超过10%(图9),随着成岩过程中对孔隙的不断破坏,管状化石大部分受到充填,最终在化石富集层中保留了至少0.7%左右的孔隙度(图9)。结果显示,即便管状化石内部经历了多期次成岩作用改造,包括碳质充填,相对于不含化石的白云岩基质0.1%~0.4%的孔隙度,Cloudina富集层中至少0.7%的孔隙度仍然要高得多。此外,由于micro-CT分析精度存在差异,化石富集层真实的孔隙度应当比分析得到的孔隙度更高。这说明管状化石Cloudina的富集对储层孔隙具有积极影响。
四川盆地灯二段和灯四段的储集孔隙与微生物岩和溶蚀构造密切相关[50⁃54],有利储层的空间分布受到古隆起控制。其中川中古隆起的规模最大,对灯影组储层发育尤为重要[52]。川中古隆起灯影组发育大量藻丘和颗粒滩[50],又受到桐湾运动的影响[1,5⁃6,53],形成了大规模有利于油气储集的层段[50,52]。从川中地区的灯四段储层成岩演化来看,岩石经历了从(准)同生阶段、早成岩阶段到中晚成岩阶段的多个期次,并受到了来自大气淡水、热液等多种来源的溶蚀,同时伴随不同阶段胶结物的充填作用[55]。随着成岩作用的不断叠加改造,岩石整体孔隙度逐渐呈波状降低[55]。川东北鹿页1井灯影组页岩接受了相似的成岩作用期次改造,包括区域上普遍识别的桐湾运动形成的不整合(图1,2),但二者在最终的储集空间上存在一定差异。主要原因在于,来自鹿页1井的样品受成岩改造幅度较小,没有经历较强的溶蚀作用,相反,不同阶段的胶结作用填充了大部分孔隙,最终岩石孔隙空间仅不足1%。总之,针对川东北地区埃迪卡拉系顶部后生生物Cloudina富集层的油气储层潜力提供了一些理论依据。受材料所限,此次所取得的认识是否适用于四川盆地其他地区灯影组油气勘探工作仍有待考察。如前文所述,这些最早的生物骨架颗粒的时空分布、富集程度是决定其油气储层潜力的关键因素之一。从此次的发现来看,在扬子地台中,Cloudina及其富集层可能存在更为广泛的时空分布[7⁃9,31,36]。因此,Cloudina对孔隙度的贡献或许是未来埃迪卡拉系储层研究值得考虑的一个方向。
-
在显生宙,后生生物礁或者生物层是油气勘探的重点区域,而前寒武系油气储层则以微生物或无机成因的碳酸盐岩为主。在埃迪卡拉纪末期,随着动物获得分泌矿化骨骼的能力,其对碳酸盐岩沉积体系乃至油气成藏的影响就已经开始显现。Cloudina在埃迪卡拉纪末期分布广泛,这些管状化石建造的大量碳酸盐骨骼不仅影响了当时的海洋碳循环、改造了沉积物底质,还对碳酸盐工厂和油气储层的面貌产生了深远的影响。
川东北灯影组克劳德管富集层及其储集特征分析
doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2024.049
cstr: 32268.14.cjxb.62-1038.2024.049A Cloudina-rich Bed from the Dengying Formation, Northeastern Sichuan Basin, and Its Reservoir Characteristics
-
摘要:
目的 近年来,继安岳气田的发现和绵阳—长宁裂陷的提出,四川盆地埃迪卡拉系—下寒武统得到了重点关注。这些油气藏的储集层主要发育在灯二段和灯四段的微生物岩和富岩溶孔隙白云岩中。通过讨论埃迪卡拉纪末期首次出现的动物骨骼化石克劳德管(Cloudina)对当时白云岩储层的潜在影响,可拓展区域油气勘探开发思路。 方法 基于四川盆地东部鹿页1井岩心资料,通过偏光显微镜、阴极发光、扫描电子显微镜观察和micro-CT分析,对灯四段顶部的岩矿特征、孔隙类型、成岩类型、成岩序列、孔隙演化进行了初步研究。 结果 川东巫溪地区灯影组顶部生物碎屑微晶白云岩中存在较丰富的管状动物化石,依据其形态特征可鉴定为Cloudina,其基质中存在大量微生物组构。识别出的孔隙类型有管状化石壳体构成的生物孔,以及基质中的粒间孔、沥青孔、晶间溶孔和晶内溶孔;识别出的主要成岩作用有多期的溶蚀作用、胶结作用以及充填作用。从重建的孔隙形态与分布来看,管状化石对生物碎屑微晶白云岩的孔隙度贡献显著,化石富集层的孔隙度至少为0.7%,而基质孔隙度仅为0.1%~0.4%。 结论 富集成层的Cloudina是灯四段局部层位中除微生物礁丘以外的另一个重要孔隙来源。这说明埃迪卡拉纪末期动物矿化骨骼的出现不仅是生物演化上的创新,也为油气储层的类型带来了深刻的改变。
Abstract:Objective The discovery of the Anyue gas field and the Mianyang-Changning intratonic sag has attracted considerable attention to the strata near the Ediacaran-Cambrian boundary in the Sichuan Basin. The reservoirs of these oil and gas fields occur mainly in the microbial and karst porous rich dolomite of the second and the fourth member of Dengying Formation. This study discusses the impact of Cloudina skeletal remains, one of the earliest metazoan mineral skeletons, on the terminal Ediacaran carbonate reservoirs, in order to expand regional oil and gas exploration strategies. Methods Drilling core material from the topmost Dengying Formation of the well Luye 1, northeastern Sichuan Basin, was examined for sedimentology, diagenesis, pore types, and porosity evolution, using a combination of methods including optical microscopy, cathodoluminescence, scanning electron microscopy, and micro-CT analysis. Results and Discussions Abundant tubular animal fossils, diagnosed as Cloudina, were aggregated in a layer of bioclastic micrite dolomite. These fossils are preserved in a micritic to microsparitic matrix, with their body axes oriented along the bedding plane. Micritic clots and filaments of probably microbial origin were found all around. The recognized pore types include biogenic pores formed by tubular fossils, intergranular pores, inter- and intracrystalline dissolution pores, and bitumen pores. The main diagenetic processes include dissolution, cementation, and filling at different periods. The high-resolution micro-CT scan shows that the porosity of the studied material is conspicuously affected by the presence/absence of the Cloudina skeleton. Only 0.1% to 0.4% of the porosity can be attributed to the dolomitic matrix, while the contribution of the tubular fossils is more than 0.7%. Conclusion Cloudina aggregates can contribute a considerable amount of porosity to the terminal Ediacaran dolomite, in addition to the microbial fabrics. The presence of mineralized animal skeletons at the end of the Ediacaran not only marks a big step in biological evolution but has also profoundly changed the types of oil and gas reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- northeastern Sichuan region /
- Ediacaran Period /
- Cloudina /
- pores /
- reservoir characteristics
-
-
[1] 邹才能,杜金虎,徐春春,等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2014,41(3):278-293. Zou Caineng, Du Jinhu, Xu Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. [2] 李智武,冉波,肖斌,等. 四川盆地北缘震旦纪—早寒武世隆—坳格局及其油气勘探意义[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(1):59-85. Li Zhiwu, Ran Bo, Xiao Bin, et al. Sinian to Early Cambrian uplift-depression framework along the northern margin of the Sichuan Basin, central China and its implications for hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 59-85. [3] 姚根顺,郝毅,周进高,等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组储层储集空间的形成与演化[J]. 天然气工业,2014,34(3):31-37. Yao Genshun, Hao Yi, Zhou Jingao, et al. Formation and evolution of reservoir spaces in the Sinian Dengying Fm of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 31-37. [4] 周进高,姚根顺,杨光,等. 四川盆地安岳大气田震旦系—寒武系储层的发育机制[J]. 天然气工业,2015,35(1):36-44. Zhou Jingao, Yao Genshun, Yang Guang, et al. Genesis mechanism of the Sinian-Cambrian reservoirs in the Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(1): 36-44. [5] 杨雨,黄先平,张健,等. 四川盆地寒武系沉积前震旦系顶界岩溶地貌特征及其地质意义[J]. 天然气工业,2014,34(3):38-43. Yang Yu, Huang Xianping, Zhang Jian, et al. Features and geologic significances of the top Sinian karst landform before the Cambrian deposition in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 38-43. [6] 刘宏,罗思聪,谭秀成,等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组古岩溶地貌恢复及意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2015,42(3):283-293. Liu Hong, Luo Sicong, Tan Xiucheng, et al. Restoration of paleokarst geomorphology of Sinian Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin and its significance, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(3): 283-293. [7] Cai Y P, Hua H, Zhang X L. Tube construction and life mode of the Late Ediacaran tubular fossil Gaojiashania cyclus from the Gaojiashan Lagerstätte[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 224: 255-267. [8] Cai Y P, Hua H, Schiffbauer J D, et al. Tube growth patterns and microbial mat-related lifestyles in the Ediacaran fossil Cloudina, Gaojiashan Lagerstätte, South China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(3): 1008-1018. [9] Cai Y P, Xiao S H, Li G X, et al. Diverse biomineralizing animals in the terminal Ediacaran Period herald the Cambrian explosion[J]. Geology, 2019, 47(4): 380-384. [10] Penny A M, Wood R, Curtis A, et al. Ediacaran metazoan reefs from the Nama Group, Namibia[J]. Science, 2014, 344(6191): 1504-1506. [11] Wood R, Curtis A. Extensive metazoan reefs from the Ediacaran Nama Group, Namibia: The rise of benthic suspension feeding[J]. Geobiology, 2015, 13(2): 112-122. [12] Cai Y P, Hua H, Xiao S H, et al. Biostratinomy of the Late Ediacaran pyritized Gaojiashan Lagerstätte from southern Shaanxi, South China: Importance of event deposits[J]. Palaios, 2010, 25(8): 487-506. [13] Wood R. Exploring the drivers of early biomineralization[J]. Emerging Topics in Life Sciences, 2018, 2(2): 201-212. [14] Shore A J, Wood R A, Butler I B, et al. Ediacaran metazoan reveals lophotrochozoan affinity and deepens root of Cambrian Explosion[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(1): eabf2933. [15] Warren L V, Quaglio F, Simões M G, et al. Cloudina-Corumbella-Namacalathus association from the Itapucumi Group, Paraguay: Increasing ecosystem complexity and tiering at the end of the Ediacaran[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 298: 79-87. [16] Wood R A. Paleoecology of the earliest skeletal metazoan communities: Implications for early biomineralization[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 106(1/2): 184-190. [17] Warren L V, Quaglio F, Riccomini C, et al. The puzzle assembled: Ediacaran guide fossil Coludina reveals an old proto-Gondwana seaway[J]. Geology, 2014, 42(5): 391-394. [18] 赵文智,沈安江,周进高,等. 礁滩储集层类型、特征、成因及勘探意义:以塔里木和四川盆地为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2014,41(3):257-267. Zhao Wenzhi, Shen Anjiang, Zhou Jingao, et al. Types, characteristics, origin and exploration significance of reef-shoal reservoirs: A case study of Tarim Basin, NW China and Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 257-267. [19] 卫平生,刘全新,张景廉,等. 再论生物礁与大油气田的关系[J]. 石油学报,2006,27(2):38-42. Wei Pingsheng, Liu Quanxin, Zhang Jinglian, et al. Re-discussion of relationship between reef and giant oil-gas fields[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(2): 38-42. [20] Zhao G C, Cawood P A. Precambrian geology of China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 222-223: 13-54. [21] Greentree M R, Li Z X, Li X H, et al. Late Mesoproterozoic to earliest Neoproterozoic basin record of the Sibao orogenesis in western South China and relationship to the assembly of Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 151(1/2): 79-100. [22] 胡健民,施炜,渠洪杰,等. 秦岭造山带大巴山弧形构造带中生代构造变形[J]. 地学前缘,2009,16(3):49-68. Hu Jianmin, Shi Wei, Qu Hongjie, et al. Mesozoic deformation of Dabashan curvilinear structural belt of Qinling orogen[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(3): 49-68. [23] 刘鸿允. 中国震旦系[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1991:1-388. Liu Hongyun. The Sinian system in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1991: 1-388. [24] Hoffman P F, Abbot D S, Ashkenazy Y, et al. Snowball Earth climate dynamics and Cryogenian geology-geobiology[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(11): e1600983. [25] Hoffman P F, Schrag D P. The snowball Earth hypothesis: Testing the limits of global change[J]. Terra Nova, 2002, 14(3): 129-155. [26] Jiang G Q, Shi X Y, Zhang S H, et al. Stratigraphy and paleogeography of the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation (ca. 635-551 Ma) in South China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19(4): 831-849. [27] 邓胜徽,樊茹,李鑫,等. 四川盆地及周缘地区震旦(埃迪卡拉)系划分与对比[J]. 地层学杂志,2015,39(3):239-254. Deng Shenghui, Fan Ru, Li Xin, et al. Subdivision and correlation of the Sinian (Ediacaran) System in the Sichuan Basin and its adjacent area[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2015, 39(3): 239-254. [28] 周传明,欧阳晴,王伟,等. 中国埃迪卡拉纪岩石地层划分和对比[J]. 地层学杂志,2021,45(3):211-222. Zhou Chuanming, Ouyang Qing, Wang Wei, et al. Lithostratigraphic subdivision and correlation of the Ediacaran in China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2021, 45(3): 211-222. [29] Zhou J G, Zhang J Y, Deng H Y, et al. Lithofacies paleogeography and sedimentary model of Sinian Dengying Fm in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2017, 4(3): 217-224. [30] 赵东方,胡广,张文济,等. 渝北巫溪鱼鳞剖面灯影组鲕粒沉积特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评,2018,64(1):191-202. Zhao Dongfang, Hu Guang, Zhang Wenji, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of ooids of Sinian (Ediacaran) Dengying Formation on the Yulin section in Wuxi, Chongqing, and geological implications[J]. Geological Review, 2018, 64(1): 191-202. [31] Zhang L, Chang S, Chen C, et al. Coludina aggregates from the uppermost Dengying Formation, Three Gorges area, South China, and stratigraphical implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 2022, 370: 106552. [32] Braithwaite C J R. Cathodoluminescence in Quaternary carbonate deposits[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 337: 29-35. [33] Droser M L, Gehling J G. The advent of animals: The view from the Ediacaran[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(16): 4865-4870. [34] Grotzinger J P, Bowring S A, Saylor B Z, et al. Biostratigraphic and geochronologic constraints on early animal evolution[J]. Science, 1995, 270(5236): 598-604. [35] Zhu M Y, Zhuravlev A Y, Wood R A, et al. A deep root for the Cambrian explosion: Implications of new bio-and chemostrati-graphy from the Siberian Platform[J]. Geology, 2017, 45(5): 459-462. [36] 杨犇,尚晓冬, Steiner M,等. 湖北神农架地区埃迪卡拉纪管状化石及其地层意义[J]. 地层学杂志,2020,44(4):448-454. Yang Ben, Shang Xiaodong, Steiner M, et al. Ediacaran tubular fossils from the Shennongjia area, Hubei province and their stratigraphic significance[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2020, 44(4): 448-454. [37] Yang B, Warren L V, Steiner M, et al. Taxonomic revision of Ediacaran tubular fossils: Cloudina, Sinotubulites and Conotubus[J]. Journal of Paleontology, 2022, 96(2): 256-273. [38] Mehra A, Maloof A. Multiscale approach reveals that Cloudina aggregates are detritus and not in situ reef constructions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(11): E2519-E2527. [39] Curtis A, Wood R, Bowyer F, et al. Modelling Ediacaran metazoan-microbial reef growth[J]. Sedimentology, 2021, 68(5): 1877-1892. [40] Hannisdal B, Peters S E. Phanerozoic Earth system evolution and marine biodiversity[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6059): 1121-1124. [41] Warren L V, Simões M G, Fairchild T R, et al. Origin and impact of the oldest metazoan bioclastic sediments[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(4): 507-510. [42] Grant S W. Shell structure and distribution of Cloudina, a potential index fossil for the terminal Proterozoic[J]. American Journal of Science, 1990, 290-A: 261-294. [43] Cai Y P, Schiffbauer J D, Hua H, et al. Morphology and paleoecology of the Late Ediacaran tubular fossil Conotubus hemiannulatus from the Gaojiashan Lagerstätte of southern Shaanxi province, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2011, 191(1/2): 46-57. [44] Warren L V, Fairchild T R, Gaucher C, et al. Corumbella and in situ Cloudina in association with thrombolites in the Ediacaran Itapucumi Group, Paraguay[J]. Terra Nova, 2011, 23(6): 382-389. [45] Hua H, Chen Z, Yuan X L, et al. Skeletogenesis and asexual reproduction in the earliest biomineralizing animal Cloudina[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(4): 277-280. [46] Germs G J B. New shelly fossils from Nama Group, south West Africa[J]. American Journal of Science, 1972, 272(8): 752-761. [47] Becker-Kerber B, Pacheco M L A F, Rudnitzki I D, et al. Ecological interactions in Cloudina from the Ediacaran of Brazil: Implications for the rise of animal biomineralization[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 5482. [48] Vinn O, Zatoń M. Inconsistencies in proposed annelid affinities of early biomineralized organism Cloudina (Ediacaran): Structural and ontogenetic evidences[J]. Carnets de Géologie, 2012, 2012/03 (CG2012_A2003): 39-47. [49] 郭玉鑫. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组沉积微相与微组构分析[D]. 北京:中国石油大学(北京),2021. Guo Yuxin. Sedimentary microfacies and microfabrics of the Sinian Dengying Formation in the Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2021. [50] 梁锋,谭兵,王立恩,等. 川中古隆起蓬莱气区上震旦统灯影组二段白云岩储集层特征及优质储层形成主控因素[J/OL]. 天然气地球科学:1-20 [2024-05-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20240429.1619.002.html. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20240429.1619.002.html Liang Feng, Tan Bing, Wang Li'en, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of dolomite reservoir in the Second member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation, Penglai gas area, central Sichuan paleo-uplift [J/OL]. Natural Gas Geoscience: 1-20 [2024-05-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20240429.1619.002.html. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20240429.1619.002.html [51] 丁一,刘树根,文龙,等. 中上扬子地区震旦纪灯影组沉积期碳酸盐岩台地古地理格局及有利储集相带分布规律[J].沉积学报,2024,42(3):928-943. Ding Yi, Liu Shugen, Wen Long, et al. Paleogeographic pattern of the carbonate platform in the Middle-Upper Yangtze area during the deposition of the Ediacaran Dengying Formation and distribution pattern of the reservoir facies[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2024,42(3):928-943. [52] 罗冰,杨跃明,罗文军,等. 川中古隆起灯影组储层发育控制因素及展布[J]. 石油学报,2015,36(4):416-426. Luo Bing, Yang Yueming, Luo Wenjun, et al. Controlling factors and distribution of reservoir development in Dengying Formation of paleo uplift in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(4): 416-426. [53] 汪泽成,姜华,王铜山,等. 四川盆地桐湾期古地貌特征及成藏意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2014,41(3):305-312. Wang Zecheng, Jiang Hua, Wang Tongshan, et al. Paleo-geomorphology formed during Tongwan tectonization in Sichuan Basin and its significance for hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 305-312. [54] 刘树根,宋金民,罗平,等. 四川盆地深层微生物碳酸盐岩储层特征及其油气勘探前景[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,43(2):129-152. Liu Shugen, Song Jinmin, Luo Ping, et al. Characteristics of microbial carbonate reservoir andits hydrocarbon exploring outlook in the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science &. Technology Edition), 2016, 43(2): 129-152. [55] 王炳森,袁海锋,王涛,等. 川中蓬莱地区震旦系灯影组四段储层成岩作用、孔隙演化及油气充注[J/OL]. 沉积学报,doi:10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2024.012. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2024.012 Wang Bingsen, Yuan Haifeng, Wang Tao, et al. Reservoir diagenesis, pore evolution and oil and gas charging in the Fourth member of the Sinian Dengying Formation in the Penglai area, central Sichuan [J/OL]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2024.012. -





 下载:
下载: