-
渤海陆架是新生代亚洲大陆东部一系列边缘海发育的最年轻部分[1⁃2];平均水深约18 m,仅其东面与黄海相通处的狭窄水道深度超过80 m[3]。新近纪—第四纪时期,渤海盆地持续沉降[4⁃6],所堆积的数千米厚度的湖相、河流相、海相等地层,为追溯东亚大陆边缘的海陆相互作用、太平洋板块向亚洲板块俯冲和青藏高原隆升过程与效应等关键科学问题提供了重要素材[3,7⁃9]。近年来随着各项技术应用的不断突破与完善,越来越多的证据表明渤海陆架所经历的演化历程既有大区域环境过程的一致性,又具有自身区域的特殊性。根据地理位置的不同,渤海可划分为五个部分,即北部辽东湾、西部渤海湾、南部莱州湾、中部中央海盆和东部庙岛群岛(图1)。不同部分的沉积背景显著不同;其中,莱州湾地区因物源较近、物质供给丰富、沉降过程稳定等特点,过去海平面变化等地质、环境事件未能造成较大的沉积间断,因而较为连续地记录了区域环境过程的历史[10⁃11]。
近半个世纪以来,渤海地区的钻孔岩心研究已经在一定程度上揭示了区域地质构造、水文过程、资源状况[3,7,9,11]。例如,赵松龄等[10]根据数十支钻孔岩心构建了晚第四纪中国东部三次海侵的沉积学基本框架,并探讨了海侵的空间范围,这一成果得到了后续一系列研究的支撑[2,12⁃25]。尽管不同年代学方法标定的海侵时间并不完全相同[10⁃11],但框架也已应用于黄东海地区[7,26⁃35]。另一方面,长钻孔的沉积学与古环境研究[36⁃43]揭示出渤海盆地由古湖向陆架的演化导致了区域环境和生物群落重组[1⁃2,44⁃45],包括水系调整、卤水资源富集和动物迁徙等。这些研究成果,极大地推进了对渤海陆架演化及其潜在影响的认识。
然而,由于陆架沉积与环境过程的复杂性,渤海盆地获得的长序列记录仍显不足,早更新世至更早时期的地层对比也未能充分展开。针对这一现状,本文尝试在整理莱州湾现有钻孔岩心结果的基础上,构建莱州湾第四纪地层与年代的基本框架,进而对比渤海盆地其他地区的已有成果,探讨渤海陆架演化过程及其可能的环境效应。
-
莱州湾位于郯庐断裂带山东段(沂沭断裂)的东西两支之间,中新世中晚期以来整体处于稳定的沉降环境,表现为地震剖面上不整合面以上同相轴基本平行、连续稳定,地层无较大的起伏[46⁃47]。
莱州湾地区第四纪地层主要包含冲洪积、海积、湖积沉积层,由南向北、自东向西地层厚度逐渐增加,央子断裂以北、白浪河—虞河一带厚度最大,可划分为平原组、潍北组、旭口组、临沂组、沂河组等。晚第四纪三次主要海侵事件由赵松龄等[10]命名,从老到新包括沧州海侵(第三海侵层)、黄骅海侵(部分地区包括次级的渤海海侵)(第二海侵层)和献县海侵(第一海侵层)。
自西向东有小清河、弥河、白浪河、潍河、胶莱河等河流,自南向北注入莱州湾。这些河流发源于鲁中山区,蜿蜒北流,河流长度多介于100~200 km,年输沙量可达百万吨。由于降水主要集中在夏季,这些河流的径流量和输沙量也以夏季为多,占全年的一半以上[19];河水从鲁中山区直接进入山前平原地带,形成面积广大的冲洪积扇与古河道。
-
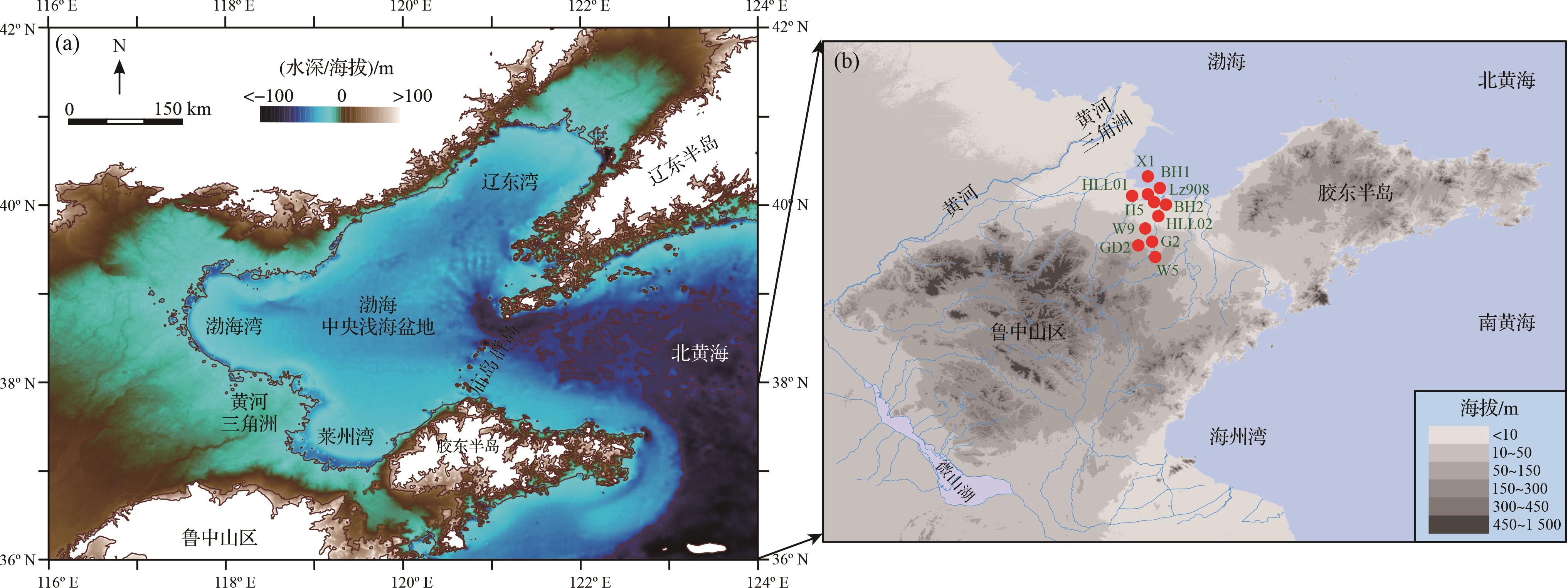
用于本项研究的11支钻孔岩心取自莱州湾及沿岸(图1),由天津地质调查中心和自然资源部第一海洋研究所完成钻进取心。其中,HLL01、HLL02、BH1、BH2、Lz908、W5、W9和GD02等8支已在此前的研究中有所涉及,G2、H5和X1孔是本研究首次报道。11支钻孔岩心的具体信息已在表1中列出。
表 1 研究钻孔信息及其发表情况
站位 经度 纬度 高程/m 进尺/m 取心率/% 文献 HLL01 119.119°E 37.107°N 2.3 452 94 文献[48] HLL02 119.137°E 37.033°N 3.4 425 90 文献[1] BH1 119.110°E 37.311°N -4.0 199 94 文献[1] BH2 119.075°E 37.182°N 3.0 228 95 文献[1] Lz908 118.972°E 37.150°N 6.0 101 75 文献[2,19] W5 119.044°E 36.707°N 31.0 64 90 文献[11] W9 119.209°E 36.819°N 10.2 95 93 文献[11] GD02 119.129°E 36.848°N 11.4 137 90 文献[11] G2 119.149°E 36.901°N 6.3 130 92 本研究 H5 119.041°E 37.094°N 3.5 150 95 本研究 X1 119.018°E 37.253°N -4.0 160 95 本研究 -
前人研究已指出,莱州湾沉积的载磁矿物主要是磁铁矿,部分样品含有少量的赤铁矿成分[49]。因此,本研究中涉及的磁性地层研究选用交变退磁和热退磁方法,对3支未定年钻孔岩心的定向样品进行系统退磁。具体的测试内容包括:(1)G2孔,交变退磁46块(上部16 m),热退磁242块;(2)H5孔,交变退磁114块(上部48 m),热退磁364块;(3)X1孔,交变退磁442块。剩磁测量在天津地质调查中心和同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室的低温超导磁力仪2G-755K(2G Enterprises,USA)上完成。测量数据,采用PuffinPlot数据处理软件[50],利用主成分分析法进行特征剩磁方向的计算。特征剩磁方向通过线性拟合方式[51]获得,每次拟合利用不少于4个连续数据点进行,且最大角偏差(MAD)小于15°。
-
综合已有钻孔岩心结果,莱州湾地区已发表的沉积类型可大致划分为三类,从下至上分别以河流—冲洪积相沉积、湖相沉积、海相沉积为主[1,11]。简述如下(图2):(1)河流—洪积相。研究区内的河流—冲洪积相沉积主要发育在第四纪地层的下部,棕黄色、棕灰色、杂色的中—粗沙(图2c),偶见砾石混杂,无明显层理发育。(2)湖相沉积。渤海地区湖相沉积在第四纪时期曾广泛发育。莱州湾地区的湖相沉积,以青灰色、棕灰色、灰褐色的含黏土质粉砂为特征(图2b),发育钙质结核,部分层位发育2~5 mm厚的微层理;产介形类,如Candoniella suzini苏金小玻璃介、Ilyocypris salebrosa粗糙土星介、Ilyocypris cornae柯氏土星介、Ilyocypris bradyi布氏土星介等(钻孔未发表资料)。湖相沉积中(图2b),青灰色、灰褐色沉积层较棕灰色沉积层更为致密、粒度更细、生物碎屑较少,可能指示较弱的动力环境。(3)海相沉积。莱州湾地区的海相沉积以海侵—海退层序为主要特征,包含灰色、青灰色、灰褐色的粉砂—细砂(图2a),发育水平层理,海侵层可见大量生物碎屑。区域内海相沉积中含有丰富的有孔虫与介形虫化石。据钻孔未发表资料,有孔虫化石主要有Ammonia卷转虫、Elphidium advenum异地希望虫、Cribrononion incertum易变筛九字虫、Cribrononion porisuturalis孔缝筛九字虫、Nonion akitaense秋田诺宁虫、Quinqueloculina sp. 块虫等潮下带到浅海种;海相介形化石有Leguminocy⁃thereis spp.豆艳花介、Campylocythereis sp.弯艳花介、Leguminocythereis hodgii.侯德豆艳花介、Cushmanidea spp.库士曼介、Perissocytheridea sumatraensis苏门答腊奇美花介、Perissocytheridea japonica日本奇美花介等;贝壳类生物化石有Arca subcrenata毛蛤、Meretrix文蛤、Aloidis laevis光滑兰蛤等。
三类典型沉积不但表观差异显著,粒度特征也存在明显不同。以研究程度较高的HLL02孔沉积物粒度特征为例(图2):海相沉积粒度分布的主峰位于50~100 μm的粗粉砂—细砂区间,缺失或较少包含0.3~30 μm的黏土—细粉砂等较细颗粒;湖相沉积具有明显的多峰特征,主要表现为10~100 μm细粉砂—细砂为主的宽峰分布,同时包含较多的黏土质组分和砂质颗粒;河流—冲洪积相沉积的粒度特征在海相与湖相之间,主峰位于50~300 μm的细砂—中砂区间,同时包含多个较显著的细颗粒组分。此外,三类沉积的粒度参数线性关系也存在显著差异(图2)。这些粒度组分和参数的特征差异,与现代沉积所观察到的现象具有较好的一致性,指示沉积物粒度特征在重建莱州湾地区古环境变化研究中的重要潜力[52⁃54]。
-
三支钻孔岩心的系统退磁结果具有相似的特征。对于交变退磁样品,在15~30 mT之前,剩磁强度降低较快,这代表低矫顽力磁性矿物(主要是磁铁矿)的信号;在70~80 mT时,样品的剩磁强度衰减至天然剩磁的5%~20%(图3),说明高矫顽力磁性矿物(赤铁矿等)在部分样品中也是重要的剩磁载体。对于热退磁样品,多数样品的剩磁强度在500℃~600 ℃已衰减至天然剩磁的不足5%,少部分样品在690 °C已完全衰减(图3)。这些退磁特征说明,20~60 mT、500 ℃~600 ℃或600 ℃~690 ℃区间的退磁数据可分离出线性较好的特征剩磁分量。根据这一特点,三支钻孔岩心最终获得了具有稳定特征剩磁的磁极性序列(图4),成功率分别为37%(G2,106/288)、42%(H5,200/478)和55%(X1,241/442)。在此基础上,本研究定义的极性段至少包含极性相同的3个相邻样品,地层厚度超过1 m。

图 3 新增三支钻孔岩心典型样品的系统退磁结果
Figure 3. Orthogonal diagrams of demagnetization results of the representative samples
研究区构造背景稳定,且三支钻孔岩心无明显沉积间断发育,本研究根据这新增三支钻孔岩心的古地磁结果,同时参考莱州湾地区已发表的磁极性序列特征[1⁃2,11,48],将已识别的磁极性区间初步(顺序)对比至国际标准地层年表(GPTS)中第四纪磁极性序列[55](图4)。具体对比方案如下:(1)正极性区间N1对比至布容正极性时(C1n);(2)正极性区间N2对比至加拉米诺正极性亚时(C1r.1n);(3)N3可能对应于Cobb Mountain正极性事件(CM);(4)N4对应至奥杜维尔正极性时(C2n);(5)正极性区间N5~N6仅记录于G2孔下部,且与基底风化壳接近,考虑到此处变化与晚上新世古地磁场的变化情况相似,可能对应于高斯正极性时(C2An)。根据这一对比方案,三支钻孔岩心各时期的沉积厚度呈现明显的向海(北)增加的趋势,与已发表的成果一致(表1)。
-
前人研究已指出,莱州湾地区第四纪地层主要包含下伏的湖相与上覆的海侵层沉积,河流—冲洪积相沉积少量发育,或发育于上新世[1⁃2,11,48]。对于上覆海侵层,地层年代学研究主要基于14C测年和古地磁漂移事件[10,21],随着释光测年技术的发展,近年来的研究成果多基于光释光年龄[25,56]。尽管不同年代学法所标定的海侵事件年龄存在较大差异且各方法的适用性也仍需更多的检验,Yi et al.[1],易亮等[11]在对比不同年代技术优劣势的基础上,认为第一海侵层发生于全新世,不同测年方法的结果基本一致;第二海侵层应始于氧同位素5期(MIS 5),MIS 3期部分地区发育海相残余沉积;第三海侵层始于MIS 7期,可持续至MIS 6期。因聚焦于整套第四纪地层的对比,上覆海侵层的特征与对比在此不再赘述。
相较于晚第四纪海侵的研究成果,中下更新统的相关研究由于受到长序列钻孔不易获取的客观制约,对比框架尚未统一认识[7,9,11]。
为揭示莱州湾地区第四纪地层的空间分布规律,本研究利用11支钻孔岩心的古地磁结果,分别以布容正极性时和松山负极性时的底界为基准进行区域地层对比研究(图5)。识别等时面是追踪盆—山沉积体系演化的重要内容[57⁃58],通过等时面深度的对比,可以再现不同沉积单元的沉降差异,在以往的沉积地层研究中具有广泛应用[59⁃63]。结果显示,松山—布容M/B界限(中更新统埋深)普遍分布于50 m左右,并向北(向海)方向逐渐增加(图5a),指示了过去1 Ma以来不同沉积单元沉降量差异较小,可能反映了较为稳定的盆—山沉积背景。这一结果与渤海其他地区的结果类似[33,36⁃37,39⁃40,42⁃43,64⁃66]。不过,山前四支钻孔岩心底部(W9孔、G2孔、GD02孔和W5孔)均发现了基岩风化壳,表明盆地南缘基底埋深较浅,古隆起尚未完全消失。
若将对比基准下移至高斯—松山Ga/M界限(更新统底界),不同地点的Ga/M埋深差异十分显著(图5b)。例如,BH1孔和BH2孔Ga/M界限埋深170 m左右;HLL01孔和HLL02孔的埋深接近,约140 m;X1孔和H5孔未见Ga/M界限,但根据上部地层的沉积速率推算,Ga/M埋深可能超过200 m。然而,山前钻孔岩心的情况则完全不同:Ga/M界限与M/B界限接近,高斯正极性时的顶部埋深40~80 m。
莱州湾钻孔岩心两个关键时间点对应的埋深差异与区域沉积背景密切相关。考虑到盆—山界限附近W9孔约36 m处的剥蚀特征,本文推测莱州湾地区向海一侧在早更新世曾经历显著的沉降过程,导致盆地向山区一侧广泛扩张。
-
在综合钻孔岩心年代对比结果的基础上,本文以河流、干湖(棕灰色、粒度稍粗的湖相沉积层)、沿海湖沼(有孔虫化石数量较少)等三个次级沉积相指示低位域沉积体系,以海相(有孔虫化石数量较多的沉积层)和湖沼相(青灰色—灰褐色、粒度较细的湖相沉积层)指示高位域(水进域)。在磁性地层结果的制约下,结合已发表的生物化石结果[8,22,67],通过11支钻孔岩心从陆向海排列,将特征相似、年代相近的沉积层相连构建等时面(近等时面),形成了莱州湾第四纪地层的初步框架[67],并识别出17个水退—水进旋回(图6)。具体划分如下:(1)全新统。包含1个海侵沉积序列,埋深10~20 m。(2)中更新统上部—上更新统。包含2个海侵—海退序列,埋深20~60 m。(3)下更新统上部—中更新统。包含7个海侵/水进—水退序列,埋深80~120 m。这些海侵/水进旋回可与深海氧同位素曲线所指示的冰期—间冰期序列对应,与渤海其他地区所报道的结果相似[36,42,64⁃65]。(4)下更新统。包含7个水进—水退序列,埋深差异较大。
根据这一划分方案,近1 Ma以来10次水进—水退旋回与地球公转轨道参数偏心率的主周期一致,表现为0.1 Ma的韵律特征;第四纪早期的7个水进—水退旋回则大致对应了约0.2 Ma的准周期特征。
早更新世晚期以来的区域相对水深定量重建显示,莱州湾地区的相对水深变化基本与全球海平面变化一致[2],均表现为0.1 Ma左右的冰期—间冰期旋回,与本文所划定的10个海侵/湖进—水退旋回一一对应。
由于地球轨道参数变化的0.2 Ma周期强度太弱,一般无法直接以主周期的形式表现在地质记录中[68],使得莱州湾地区第四纪早期的约0.2 Ma准周期的水进—水退旋回在古气候研究中并不常见[69⁃70]。尽管如此,过去全球变化研究还是报道了一些0.2 Ma为主周期的古气候记录[69,71⁃76],这些古气候研究将0.2 Ma周期解释为偏心率周期的变种[69,73⁃74]或地轴斜度周期的多种组合[70]。因此,未来在莱州湾地区开展早更新世湖相沉积演化的详细研究,有可能进一步发掘地层记录的古气候信息,为解译0.2 Ma准周期提供新证据。
-
参考莱州湾地区第四纪地层的初步框架,通过收集、整理渤海地区已有结果,同时考虑到最近一次“渤海古湖”解体与早期海侵开始于1 Ma左右[11],本文以加拉米诺正极性亚时的底部(~1 Ma)为对比基准(等时面),开展环渤海地区的地层对比分析(图7)。结果显示,中更新世以来渤海盆地内各单元沉降量的差异较小,而渤海湾北部和靠近庙岛古隆起区域的沉降量十分可观,指示了盆地东部和西北部边缘主要在过去1 Ma内实现快速扩张,晚于莱州湾南缘的扩张时间。尽管不同单元内的沉积特征存在一定差异,渤海地区在2~1 Ma湖相沉积发育相对稳定,且较少受到来自河流—冲洪积等高能沉积环境的影响,可能对应了最近一期“渤海古湖”发育[1]。
-
受区域构造活动的控制[78],西北太平洋海水被浙闽古隆起、千里岩古隆起和庙岛古隆起分别阻挡于南黄海、北黄海和渤海之外[1,31],黄—渤海地区在晚上新世—早更新世形成了类似于“三级水库”的地理格局[11]。此后,伴随三大古隆起的逐步解体,黄—渤海地区最终和东海连为一体,转换为陆架沉积环境。
综合上述沉积地层特征与年代对比结果,并结合区域已有的古环境与古地理重建[33,36⁃37,39⁃40,42⁃43,64⁃66],推测渤海盆地可能经历了如下几个主要阶段。
(1) 中新世晚期或更早,根据少数钻孔岩心结果推测,渤海地区以河流沉积体系为主(粗颗粒沉积的冲洪积相),可能没有形成持久的巨型湖泊。因湖水无法蓄积,推测渤—黄海盆地此时可能保持连通状态。
(2) 上新世晚期开始(据莱州湾地层对比推测时间为3.8~3.6 Ma),盆—山体系的差异沉降可能导致渤海盆地逐渐被孤立,造成区域河流无法排出、湖水蓄积。此时区域内虽广泛发育湖相沉积,但钻孔岩心之间的精细对比相对困难(图7);同时湖相沉积中常夹有粒度较粗的河流—冲洪积薄层,可能说明此时区域古地理以湖群为主或湖泊规模较小,各单元的湖泊发育相对独立。
(3) 第四纪早期(2.0 Ma左右),区域内大量钻孔岩心资料显示,以深灰色、青灰色细粒的深湖相为主,且不同单元内获得的环境代用指标也具有较好的可比性[36⁃38,66],指示了较为稳定的湖相沉积发育。因此,此阶段盆地内湖泊规模可能较大,且不同单元间连通性较好,可能对应了最近一期“渤海古湖”发育[1]。不过,随着堆积总量的增加,盆—山差异沉降产生的容积空间将逐步减少。
(4) 早更新世晚期(1.0 Ma左右),区域内少数钻孔岩心的沉积物已出现海侵特征,如BH08孔、TJC1孔和X1孔(图5,7)。不过,盆地内仍以棕灰色浅湖相沉积为主,夹有粒度较粗的河流—冲洪积薄层。考虑到渤海盆地此时水位高于现代海平面4~6 m[2],推测古湖开始萎缩,但庙岛群岛古隆起尚未完全解体[1]。
(5) 中更新世晚期以来(0.3 Ma左右),渤海盆地周边发生了三次重大海侵事件[10⁃11]。此时区域水位波动频繁,总体呈持续下降趋势[2,52⁃54],表明庙岛隆起的“屏障”作用明显消退。渤海盆地发展为内陆架海,水位主要受控于全球海平面变化[2,52⁃54]。
因此,渤海盆地自上新世晚期可能经历了三个主要演化阶段[11],即3.8~3.6 Ma之前,盆地以河流—冲洪积堆积为主;0.3 Ma之前为“渤海古湖”发育(图8),庙岛古隆起地势相对较高;~0.3 Ma以来古湖消亡,陆架形成。

图 8 中国北方哺乳动物、渤海地区植被群落与盆地演化
Figure 8. Mammals in northern China, vegetation communities and evolution of the Bohai Basin
渤海盆地的多阶段演化模式,既伴随着与北美五大湖区两倍面积相当的巨量湖水的聚集,又经历了古隆起的下沉和巨量湖水的外泄,是东北亚地质、地理、气候、环境格局演变的重要组成。从更大空间尺度来看,渤海盆地与庙岛古隆起作为整个黄河流域的侵蚀基准面,陆架形成的0.3 Ma左右正是三门古湖[81⁃82]、大同盆地[83⁃84]、泥河湾盆地[85⁃87]等古湖消亡的时间耦合点。那么,庙岛古隆起的解体与渤海古湖湖水的外泄,是否因显著降低流域的侵蚀基准面,加速了流域内一系列古湖的消亡?回答这一问题有可能为揭示黄土高原、黄河流域、东部陆架演化的关联性提供重要切入点。
从区域植被演替的角度来看(图8),莱州湾南岸HLL02孔的孢粉记录指示了研究区植物群落在上新世—早更新世早期呈现出蒿属、藜科及禾本科为主的草原环境[80],HLL02孔与天津G3孔的孢粉记录则共同记录了早更新世整体较为温暖湿润的森林环境[44,80]。进入中更新世,渤海地区以栎属、松属为主的针叶阔叶混交林明显萎缩,森林在当地植被中的比例持续下降[44]。区域生态系统的这些变化,虽然主要受控于全球气候变冷[44],但渤海古湖的发育,有可能通过改善或延缓区域气候环境的恶化,促成森林环境在早更新世的扩张。
此外,第四纪人类和哺乳动物对环境变化的进化响应长期以来一直存在争议[88⁃89]。虽然大量证据表明动物种群水平的变化通常不会导致新物种的起源[90],但哺乳动物的进化速度在整个更新世显著增加[91]。对比中国北方第四纪大型哺乳动物演化[79],哺乳动物可能对植被演替和渤海演化的阶段性存在一定的响应,特别是1.2~0.7 Ma期间(图8),华北地区大型哺乳动物物种总数大幅减少、动物区系快速重组可能与大区域内草地的扩张有关[44,79]。三大古隆起的下沉也可能促进了长江与邻近沿海流域之间淡水鱼类的基因交换[45],显著增加了陆架鱼类种群的多样性[92]。
-
本研究通过莱州湾地区11支钻孔岩心年代成果的集成,构建了区域第四纪地层对比的初步框架,识别出17个水进—水退的旋回,发现莱州湾第四纪时期的首次海侵时间为~1.0 Ma。通过与渤海其他地域钻孔岩心的对比研究,划分了渤海盆地由陆到海转化的主要阶段,即3.8~3.6 Ma之前,盆地以河流—冲洪积堆积为主,0.3 Ma之前为“渤海古湖”发育,庙岛古隆起相对地势较高,~0.3 Ma以来古湖消亡,陆架形成。在此基础上,初步探讨了渤海演化阶段性与华北植被演替与大型哺乳动物区系变化的潜在联系,指出渤海古湖的古环境研究可能为揭示黄土高原、黄河流域、东部陆架演化的协同性提供新的视角。然而,因缺少生物化石序列、河湖相地层环境代用指标序列等证据,此次所构建的第四纪地层初步框架与环境影响的讨论仍有很多局限性,这些初步结论尚需更多相关证据的检验。
Framework of Quaternary Stratigraphy in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, and Its Paleoenvironmental Significance
-
摘要: 目的 莱州湾位于渤海陆架的南端,是研究第四纪东北亚地理与环境重组的关键地点之一,较为连续地记录了渤海盆地陆—海转换时区域环境变化的历史。 方法 为揭示区域地层特征及其可能的环境意义,以莱州湾地区11支钻孔岩心为研究对象,详细分析了第四纪地层对比框架与沉积演化过程。 结果 (1)通过布容正极性时和松山负极性时两个等时面的对比分析,推测莱州湾地区向海一侧在早更新世经历了显著的沉降过程,导致盆地向南(山区一侧)广泛扩张;(2)基于11支钻孔岩心的地层特征对比,初步构建了区域第四纪地层框架,识别出17个水退—水进旋回,包括全新统1个、中更新统上部—上更新统2个、下更新统上部—中更新统7个、下更新统7个;(3)开展环渤海地区地层对比研究,基于加拉米诺正极性亚时的等时面对比,推测中更新世渤海盆地向东、西北缘显著扩张。 结论 初步重建了渤海盆地陆—海转换的主要过程,包括晚上新世的泛湖—湖群环境,早更新世的大湖发育(最近一期“渤海古湖”),中更新世大湖萎缩—弱海侵过程,晚更新世大海侵—陆架沉积环境等阶段。因此,莱州湾第四系的初步框架为重构盆地演化和区域古环境过程提供了新证据,也为探讨更大区域内盆地演化的协同性积累了新素材;不过由于缺少生物化石序列等证据,这些推测仍需更多的检验。Abstract: Objective Laizhou Bay is located in the southern Bohai Sea, where the Quaternary history of regional environmental changes during the transition from land to sea is continuously recorded in coastal sediments. Studying these geological records provides critical insights into the geographical and environmental reorganization of northeastern Asia during the Quaternary. Previous studies have reported a major transition from lacustrine to shelf environment in the Middle Pleistocene. Three transgression events have been dated to marine isotope stage (MIS) 7-6, MIS 5-3, and the Holocene. However, the evolution of the Bohai paleolake was not clear, since the framework of these lacustrine deposits had not yet been established. Methods To reveal the evolutional history of the Bohai paleolake/sea, analyses of the Quaternary sedimentary strata in 11 drilling cores from Laizhou Bay were carried out to establish a preliminary framework. These mainly included magnetostratigraphy, sediment grain size and stratigraphic correlation. Results (1) The magnetostratigraphy of three new cores implied newly defined magnetozones generally correlated to the Brunhes, Matuyama and Gauss chrons in the geological polarity timescale, consistent with previous studies of Laizhou Bay. (2) Three major types of Quaternary sediment were identified (fluvial-alluvial, lacustrine, and continental-shelf); the sedimentary properties and the relationships of sediment grain-size parameters are distinctive and potentially useful for paleoenvironmental inferences. (3) Stratigraphic analyses and isochronous strata correlation (Brunhes and Matuyama chrons) found that Laizhou Bay may have experienced significant subsidence in the Early Pleistocene. (4) In establishing a stratigraphic framework for Quaternary sediments in Laizhou Bay, 17 alternations between extension and shrinking of sea/lake water were identified: one in the Holocene; two in the Upper Pleistocene and latter part of the Middle Pleistocene; seven in the Middle Pleistocene; and seven in the Early Pleistocene. (5) The preliminary framework indicates predominant periodicities of 100 ka in the upper transgression-related strata and 200 ka in the lower lacustrine/fluvial strata, implying a dominant role of orbital eccentricity in these regional paleoenvironmental processes. (6) Correlations of Quaternary strata around the Bohai Basin and of isochronous strata based on the Jaramillo subchron indicated significant subsidence of the eastern and northwestern margins during the Middle Pleistocene. [Conclusions and Prospects] It is inferred that the land/sea transition of the Bohai Basin has experienced the following processes: alluvial and diluvial systems in the Early Pliocene or earlier; a lake-group environment prior to the early part of the Early Pleistocene; the latest stage of a Bohai paleolake in the Early Pleistocene; shrinking of the lake and weak transgression in the Middle Pleistocene; and shelf deposition since the Late Pleistocene. Preliminary correlation of these developmental stages of the Bohai Basin indicate the evolution of a series of paleolakes in the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River, possibly implying potential covariation. However, the main finding in the work is the lack of fossil evidence, which is worthy of further investigation.
-
Key words:
- magnetostratigraphy /
- Laizhou Bay /
- Bohai paleolake /
- continental shelf evolution /
- Quaternary
-
图 3 新增三支钻孔岩心典型样品的系统退磁结果
空心圆上的数字代表退磁的交变场强mT或热退磁温度℃;实心方块代表水平投影,空心圆代表垂直投影;NRM为天然剩磁
Figure 3. Orthogonal diagrams of demagnetization results of the representative samples
numbers on open circles = alternating fields in mT or thermal demagnetization temperature in ℃; open (solid) circles (squares) = vertical (horizontal) plane; NRM = natural remanent magnetization
图 4 新增三支钻孔岩心的古地磁结果与对比方案
N1~N6.古地磁正极性区间;MAD.最大角偏差;B.布容正极性时;M.松山负极性时;J.加拉米诺正极性亚时;CM.Cobb Mountain正极性事件;O.奥杜维尔正极性时;Ga.高斯正极性时;Gi.吉尔伯特负极性时;GPTS.国际地层极性年表[55];以下各图相同
Figure 4. Magnetostratigraphy of three cores
N1⁃N6. normal polarity chrons; MAD. maximum angular deviation; B. Brunhes chron; M. Matuyama chron; J. Jaramillo subchron; CM. Cobb Mountain excursion; O. Olduvai chron; Ga. Gauss chron; Gi. Gilbert chron; GPTS. geological polarity time scale[55]; same in following figures
图 5 莱州湾第四纪地层年代对比
(a)布容等时线;(b)高斯等时线;HLL01孔(据文献[48]);HLL02、BH1、BH2孔(据文献[1]);Lz908孔(据文献[2,19,52]);W5、W9、GD02孔(据文献[11]);G2、H5、X1孔为本研究新增
Figure 5. Chronostratigraphical correlation of Laizhou Bay in the Quaternary
core HLL01 (after reference [48]); cores HLL02, BH1, BH2 (after reference [1]); core Lz908 (after references [2,19,52]); cores W5, W9, GD02 (after reference [11]); cores G2, H5, X1 from this study
图 7 环渤海地层对比与中更新世盆地扩张(据文献[1]修改)
BH08孔(据文献[36]);MT04孔(据文献[77]);BZ2孔(据文献[66]);TJC1孔(据文献[42]);BH1孔和HLL02孔(据文献[1])
Figure 7. Lithological and magnetostratigraphical correlations around Bohai Sea and Middle Pleistocene basin evolution(modified from reference [1])
core BH08 (after reference [36]); core MT04 (after reference [77]); core BZ2 (after reference [66]); core TJC1 (after reference [42]); cores BH1 and HLL02 (after reference [1])
表 1 研究钻孔信息及其发表情况
站位 经度 纬度 高程/m 进尺/m 取心率/% 文献 HLL01 119.119°E 37.107°N 2.3 452 94 文献[48] HLL02 119.137°E 37.033°N 3.4 425 90 文献[1] BH1 119.110°E 37.311°N -4.0 199 94 文献[1] BH2 119.075°E 37.182°N 3.0 228 95 文献[1] Lz908 118.972°E 37.150°N 6.0 101 75 文献[2,19] W5 119.044°E 36.707°N 31.0 64 90 文献[11] W9 119.209°E 36.819°N 10.2 95 93 文献[11] GD02 119.129°E 36.848°N 11.4 137 90 文献[11] G2 119.149°E 36.901°N 6.3 130 92 本研究 H5 119.041°E 37.094°N 3.5 150 95 本研究 X1 119.018°E 37.253°N -4.0 160 95 本研究 -
[1] Yi L, Deng C L, Tian L Z, et al. Plio-Pleistocene evolution of Bohai Basin (East Asia): Demise of Bohai paleolake and transition to marine environment[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 29403. [2] Yi L, Deng C L, Xu X Y, et al. Paleo-megalake termination in the Quaternary: Paleomagnetic and water-level evidence from south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 319: 1-12. [3] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 渤海地质[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1985:1-232. Laboratory of Marine Geology Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Bohai geology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985: 1-232. [4] Allen M B, Macdonald D I M, Xun Z, et al. Early Cenozoic two-phase extension and Late Cenozoic thermal subsidence and inversion of the Bohai Basin, northern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1997, 14(7/8): 951-972. [5] He L J, Wang J Y. Cenozoic thermal history of the Bohai Bay Basin: Constraints from heat flow and coupled basin-mountain modeling[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 2003, 28(9/10/11): 421-429. [6] Hu S B, O'Sullivan P B, Raza A, et al. Thermal history and tectonic subsidence of the Bohai Basin, northern China: A Cenozoic rifted and local pull-apart basin[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2001, 126(3/4): 221-235. [7] 石学法,乔淑卿,杨守业,等. 亚洲大陆边缘沉积学研究进展(2011—2020)[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2021,40(2):319-336. Shi Xuefa, Qiao Shuqing, Yang Shouye, et al. Progress in sedimentology research of the Asian continental margin (2011-2020)[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(2): 319-336. [8] 刘东生. 黄土与干旱环境[M]. 合肥:安徽科学技术出版社,2009:1-537. Liu Tungsheng. Loess and arid environment[M]. Hefei: Anhui Science and Technology Press, 2009: 1-537. [9] 姚政权,刘健,万世明,等. 中国东部陆架第四纪沉积环境演化研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(5):42-57. Yao Zhengquan, Liu Jian, Wan Shiming, et al. Progress and prospects of research on the Quaternary sedimentary environment in the eastern shelf of China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(5): 42-57. [10] 赵松龄,杨光复,苍树溪,等. 关于渤海湾西岸海相地层与海岸线问题[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1978,9(1):15-25. Zhao Songling, Yang Guangfu, Cang Shuxi, et al. On the marine stratigraphy and coastlines of the western coast of the gulf of Bohai[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1978, 9(1): 15-25. [11] 易亮,姜兴钰,田立柱,等. 渤海盆地演化的年代学研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2016,36(5):1075-1087. Yi Liang, Jiang Xingyu, Tian Lizhu, et al. Geochronological study on Plio-Pleistocene evolution of Bohai Basin[J]. Quaternary Science, 2016, 36(5): 1075-1087. [12] 阎玉忠,王宏,李凤林,等. 渤海湾西岸BQ1孔揭示的沉积环境与海面波动[J]. 地质通报,2006,25(3):357-382. Yan Yuzhong, Wang Hong, Li Fenglin, et al. Sedimentary environment and sea-level fluctuations revealed by borehole BQ1 on the west coast of the Bohai Bay, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(3): 357-382. [13] 韩德亮. 莱州湾E孔中更新世末期以来的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报,2001,23(2):79-85. Han Deliang. Geochemistry of core E in the Laizhou Bay since late stage of Middle Pleistocene[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2001, 23(2): 79-85. [14] 庄振业,许卫东,刘东生,等. 渤海南部S3孔晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1999,19(2):27-35. Zhuang Zhenye, Xu Weidong, Liu Dongsheng, et al. Division and environmental evolution of Late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 27-35. [15] 张祖陆,聂晓红,刘恩峰,等. 莱州湾南岸咸水入侵区晚更新世以来的古环境演变[J]. 地理研究,2005,24(1):105-112. Zhang Zulu, Nie Xiaohong, Liu Enfeng, et al. The accumulation records of environmental evolution on the salt-water intruded area south of Laizhou Bay since Late Pleistocene[J]. Geographical Research, 2005, 24(1): 105-112. [16] 姚政权,郭正堂,陈宇坤,等. 渤海湾海陆交互相沉积的磁性地层学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2006,26(1):9-15. Yao Zhengquan, Guo Zhengtang, Chen Yukun, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of marine-terrigenous facies deposits in Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(1): 9-15. [17] 陈宇坤,李振海,邵永新,等. 天津地区第四纪年代地层剖面研究[J]. 地震地质,2008,30(2):383-399. Chen Yukun, Li Zhenhai, Shao Yongxin, et al. Study on the Quaternary chronostratigraphic section in Tianjin area[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2008, 30(2): 383-399. [18] 肖国桥,郭正堂,陈宇坤,等. 渤海湾西岸BZ1钻孔的磁性地层学研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2008,28(5):909-916. Xiao Guoqiao, Guo Zhengtang, Chen Yukun, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of BZ1 borehole in west coast of Bohai Bay, northern China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(5): 909-916. [19] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. Late Quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the south Bohai Sea, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 329-330: 101-117. [20] Wang Q, Li F L, Li Y D, et al. Shoreline changes in west-southern coastal plain of the Bohai Sea since 150 ka[M]//Qin Y, Zhao S. Late Quaternary sea-level changes. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1986: 62-71. [21] Zhao S L. Transgression and coastal changes in Bohai Sea and its vicinities since the Late Pleistocene[M]//Qin Y, Zhao S. Late Quaternary sea-level changes. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1986: 53-62. [22] 赵松龄. 陆架沙漠化[M]. 北京:海洋出版社,1996:1-212. Zhao Songling. Shelf desertification[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1996: 1-212. [23] Yang S Y, Li C X, Cai J G. Geochemical compositions of core sediments in eastern China: Implication for Late Cenozoic palaeoenvironmental changes[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 229(4): 287-302. [24] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36(4/5): 318-331. [25] Li Y, Tsukamoto S, Shang Z W, et al. Constraining the transgression history in the Bohai coast China since the Middle Pleistocene by luminescence dating[J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 416: 105980. [26] 汪品先,闵秋宝,卞云华,等. 我国东部第四纪海侵地层的初步研究[J]. 地质学报,1981(1):1-13. Wang Pinxian, Min Qiu bao, Bian Yunhua, et al. Strata of Quaternary transgressions in east China: A preliminary study[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1981(1): 1-13. [27] 汪品先,闵秋宝. 我国第四纪海侵研究中的几个基本问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1985,5(1):15-25. Wang Pinxian, Min Qiubao. Quaternary marine transgressions in China: Some basic questions[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1985, 5(1): 15-25. [28] 王张华,丘金波,冉莉华,等. 长江三角洲南部地区晚更新世年代地层和海水进退[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2004,24(4):1-8. Wang Zhanghua, Qiu Jinbo, Ran Lihua, et al. Chronostratigraphy and transgression/regression during Late Pleistocene in the southern Changjiang (Yangize) River delta plain[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 1-8. [29] 王中波,张江勇,梅西,等. 中国陆架海MIS5(74~128 ka)以来地层及其沉积环境[J]. 中国地质,2020,47(5):1370-1394. Wang Zhongbo, Zhang Jiangyong, Mei Xi, et al. The stratigraphy and depositional environments of China’s sea shelves since MIS5(74-128) ka[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1370-1394. [30] 刘健,段宗奇,梅西,等. 南黄海中部隆起晚新近纪:第四纪沉积序列的地层划分与沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(5):25-43. Liu Jian, Duan Zongqi, Mei Xi, et al. Stratigraphic classification and sedimentary evolution of the Late Neogene to Quaternary sequence on the central uplift of the south Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(5): 25-43. [31] Yi L, Ye X Y, Chen J B, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and luminescence dating on a sedimentary sequence from northern East China Sea: Constraints on evolutionary history of eastern marginal seas of China since the Early Pleistocene[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 349: 316-326. [32] Wang Z H, Xu H, Zhan Q, et al. Lithological and palynological evidence of Late Quaternary depositional environments in the subaqueous Yangtze Delta, China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73(3): 550-562. [33] Mei X, Li R H, Zhang X H, et al. Evolution of the Yellow Sea warm current and the yellow sea cold water mass since the Middle Pleistocene[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 442: 48-60. [34] Duan Z Q, Liu Q S, Shi X F, et al. Reconstruction of high-resolution magnetostratigraphy of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River delta, China[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2016, 204(2): 948-960. [35] Gao L, Li J, Hu B Q, et al. Luminescence dating of a sedimentary sequence in the eastern north Yellow Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 138: 105543. [36] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Liu Q S, et al. Paleomagnetic and astronomical dating of sediment core BH08 from the Bohai Sea, China: Implications for glacial-interglacial sedimentation[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 393: 90-101. [37] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Qiao S Q, et al. Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least ~880 ka ago[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 2827. [38] Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Liu Q S, et al. Sedimentary architecture of the Bohai Sea China over the last 1 Ma and implications for sea-level changes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 451: 10-21. [39] Xu Q M, Yang J L, Hu Y Z, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of two deep boreholes in southwestern Bohai Bay: Tectonic implications and constraints on the ages of volcanic layers[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2018, 43: 102-114. [40] Yang J L, Liang M Y, Algeo T J, et al. Upper Miocene-Quaternary magnetostratigraphy and magnetic susceptibility from the Bohai Bay Basin (eastern China) and implications for regional volcanic and basinal subsidence history[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 538: 109469. [41] Liu J X, Liu Q S, Zhang X H, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of a long Quaternary sediment core in the south Yellow Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 144: 1-15. [42] 李翔,李日辉,陈晓辉,等. 渤海西部TJC-1孔磁性地层研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2016,36(1):208-215. Li Xiang, Li Rihui, Chen Xiaohui, et al. Quaternary magnetostratigraphy recorded in the sediments of core TJC-1 in the western Bohai sea[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(1): 208-215. [43] 王忠蕾,郑洪波,梅西,等. 辽东湾北部钻孔磁性地层年代框架及地质意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2020,40(3):616-632. Wang Zhonglei, Zheng Hongbo, Mei Xi, et al. Magnetic stratigraphy of boreholes in the north of Liaodong Bay and its significance[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(3): 616-632. [44] Zhou X Y, Yang J L, Wang S Q, et al. Vegetation change and evolutionary response of large mammal fauna during the Mid-Pleistocene transition in temperate northern East Asia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 505: 287-294. [45] Li M Y, Yang X S, Ni X M, et al. The role of landscape evolution in the genetic diversification of a stream fish Sarcocheilichthys parvus from southern China[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2023, 13: 1075617. [46] 吴时国,余朝华,邹东波,等. 莱州湾地区郯庐断裂带的构造特征及其新生代演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2006,26(6):101-110. Wu Shiguo, Yu Zhaohua, Zou Dongbo, et al. Structural features and Cenozoic evolution of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(6): 101-110. [47] Yu Z H, Wu S G, Zou D B, et al. Seismic profiles across the Middle Tan-Lu Fault Zone in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, eastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 33(5/6): 383-394. [48] 姜兴钰,易亮,田立柱,等. 莱州湾南岸HLL01孔磁性地层定年[J]. 地质通报,2016,35(10):1669-1678. Jiang Xingyu, Yi Liang, Tian Lizhu, et al. Magnetostratigraphic chronology of borehole HLL01, south coast of Laizhou Bay[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(10): 1669-1678. [49] 李倩,易亮,刘素贞,等. 渤海南部莱州湾Lz908孔沉积物的岩石磁学性质[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(5):1717-1728. Li Qian, Yi Liang, Liu Suzhen, et al. Rock magnetic properties of the Lz908 borehole sediments from the southern Bohai Sea, eastern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(5): 1717-1728. [50] Lurcock P C, Wilson G S. PuffinPlot: A versatile, user-friendly program for paleomagnetic analysis[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(6): Q06Z45. [51] Kirschvink J L. The least-squares line and plane and the analysis of palaeomagnetic data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1980, 62(3): 699-718. [52] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. A reconstruction of Late Pleistocene relative sea level in the south Bohai Sea, China, based on sediment grain-size analysis[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 281: 88-100. [53] Chen Y P, Lyu W Z, Fu T F, et al. Centennial impacts of the East Asian summer monsoon on Holocene deltaic evolution of the Huanghe River, China[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(6): 2799. [54] Liu G, Han X B, Chen Y P, et al. Early-Holocene paleo-tropical cyclone activity inferred from a sedimentary sequence in south Yellow Sea, East Asia[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2022, 33(3): 789-801. [55] Gradstein F M, Ogg J G, Schmitz M D, et al. Geologic time scale 2020[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020. [56] Yi L, Lai Z P, Yu H J, et al. Chronologies of sedimentary changes in the south Bohai Sea, China: Constraints from luminescence and radiocarbon dating[J]. Boreas, 2013, 42(2): 267-284. [57] 李思田,杨士恭,林畅松. 论沉积盆地的等时地层格架和基本建造单元[J]. 沉积学报,1992,10(4):11-22. Li Sitian, Yang Shigong, Lin Changsong. On the chronostratigraphic framwork and basic building blocks of sedimentary basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1992, 10(4): 11-22. [58] 胡光明,王军,纪友亮,等. 河流相层序地层模式与地层等时对比[J]. 沉积学报,2010,28(4):745-751. Hu Guangming, Wang Jun, Ji Youliang, et al. Fluvial sequence stratigraphy mode and isochronous strata correlation[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(4): 745-751. [59] 王多云,陈应泰,刘文彬,等. 用最大熵谱分析进行等时沉积序列的相关性对比[J]. 沉积学报,1992,10(2):62-68. Wang Duoyun, Chen Yingtai, Liu Wenbin, et al. Determining relativity of isochronous sedimentary sequences with maximum entropy matrix analysis[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1992, 10(2): 62-68. [60] 刘英辉,黄导武,段冬平,等. 煤层等时格架下中深层储层地震沉积学预测[J]. 沉积学报,2018,36(5):957-968. Liu Yinghui, Huang Daowu, Duan Dongping, et al. Application of seismic sedimentology to the prediction of middle-deep sand body in coal-bearing isochronous stratigraphic framework[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(5): 957-968. [61] 郑荣才,彭军. 陕北志丹三角洲长6油层组高分辨率层序分析与等时对比[J]. 沉积学报,2002,20(1):92-100. Zheng Rongcai, Peng Jun. Analysis and isochronostratigraphic correlation of high-resolution sequence stratigraphy for chang-6 oil reservoir set in Zhidan delta, northern Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(1): 92-100. [62] 李维,朱筱敏,陈刚,等. 基于等时界面识别的浅水三角洲—河流沉积体系研究:以高邮凹陷黄珏地区古近系垛一段为例[J]. 沉积学报,2018,36(1):110-119. Li Wei, Zhu Xiaomin, Chen Gang, et al. Research based on isochronous surface about shallow-water deltas and fluvial sedimentary system: A case from Duo1 member of Paleogene in Huangjue area, Gaoyou Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(1): 110-119. [63] 李彦泽,王志坤,商琳,等. 小湖盆浅水三角洲沉积特征及其等时格架划分方案:以南堡4-3区东二段为例[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(5):1079-1086. Li Yanze, Wang Zhikun, Shang Lin, et al. Study on sedimentary characteristics of shallow‑water deltas and isochronous stratigraphic framework: An example of Ed2 of 4-3 zone of Nanpu oilfield[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(5): 1079-1086. [64] 施林峰,翟子梅,王强,等. 从天津CQJ4孔探讨中国东部海侵层的年代问题[J]. 地质论评,2009,55(3):375-384. Shi Linfeng, Zhai Zimei, Wang Qiang, et al. Geochronological study on transgression layers of the CQJ4 borehole at Dagang area in Tianjin, China[J]. Geological Review, 2009, 55(3): 375-384. [65] Liu J, Wang H, Wang F F, et al. Sedimentary evolution during the last ~ 1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 451: 84-96. [66] Yao Z Q, Guo Z T, Xiao G Q, et al. Sedimentary history of the western Bohai coastal plain since the Late Pliocene: Implications on tectonic, climatic and sea-level changes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 54-55: 192-202. [67] 田立柱, 施佩歆, 姜兴钰, 等.中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告(比例尺: 1:50000), 小清河口幅(J50E017021)、横里路幅(J50E018021)、固堤镇幅(J50E019021)、潍坊市幅(J50E020021)[R]. 中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心, 2018. Tian Lizhu, Shi Peixin, Jiang Xingyu, et al. Regional geological survey report, People's Republic of China (Scale: 1:50000), Xiaoqinghekou Panel (J50E017021), Hengli Road Panel (J50E018021), Gudi Town Panel (J50E019021), Weifang City Panel (J50E020021)[R]. Tianjin Geological Survey Center, China Geological Survey, 2018. [68] Laskar J, Robutel P, Joutel F, et al. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2004, 428(1): 261-285. [69] Hilgen F, Zeeden C, Laskar J. Paleoclimate records reveal elusive~200-kyr eccentricity cycle for the first time[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2020, 194: 103296. [70] Huang H, Gao Y, Ma C, et al. Organic carbon burial is paced by a ~173-ka obliquity cycle in the middle to high latitudes[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(28): eabf9489. [71] Beaufort L. Climatic importance of the modulation of the 100 kyr cycle inferred from 16 m.y. long Miocene records[J]. Paleoceanography, 1994, 9(6): 821-834. [72] Boulila S, Vahlenkamp M, De Vleeschouwer D, et al. Towards a robust and consistent Middle Eocene astronomical timescale[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 486: 94-107. [73] Hilgen F J, Abels H A, Kuiper K F, et al. Towards a stable astronomical time scale for the Paleocene: Aligning Shatsky rise with the Zumaia-Walvis ridge ODP site 1262 composite[J]. Newsletters on Stratigraphy, 2015, 48(1): 91-110. [74] Liebrand D, Beddow H M, Lourens L J, et al. Cyclostratigraphy and eccentricity tuning of the Early Oligocene through Early Miocene (30.1-17.1 Ma): Cibicides mundulus stable oxygen and carbon isotope records from Walvis Ridge Site 1264[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 450: 392-405. [75] Westerhold T, Bickert T, Röhl U. Middle to Late Miocene oxygen isotope stratigraphy of ODP site 1085 (SE Atlantic): New constrains on Miocene climate variability and sea-level fluctuations[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2005, 217(3/4): 205-222. [76] Yi L, Hu B Q, Zhao J T, et al. Magnetostratigraphy of abyssal deposits in the central Philippine Sea and regional sedimentary dynamics during the Quaternary[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2022, 37(5): e2021PA004365. [77] 胥勤勉,袁桂邦,秦雅飞,等. 滦河三角洲南部MT04孔磁性地层研究及其构造与气候耦合关系的探讨[J]. 第四纪研究,2014,34(3):540-552. Xu Qinmian, Yuan Guibang, Qin Yafei, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and discussion of coupling relationship between tectonic movement and climate change of MT04 borehole in southern Luanhe River delta[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(3): 540-552. [78] 郭玉贵,莫杰,郭平. 东海及邻域大地构造特征及ODP钻孔选位[J]. 海洋科学,1996(3):31-34. Guo Yugui, Mo Jie, Guo Ping. Analysis on the tectonic features of East China Sea and its adjacent area and proposal on the drilling site of ODP[J]. Marine Sciences, 1996(3): 31-34. [79] 邱占祥.中国北方“第四纪(或亚代)”环境变化与大哺乳动物演化 [J]. 古脊椎动物学报,2006,44(2):109-132. Qiu Zhanxiang. Quaternary environmental changes and evolution of large mammals in north China[J]. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2006, 44(2): 109-132. [80] 姜兴钰,王琳,郝秀东,等. 晚上新世以来莱州湾南岸HLL02钻孔的孢粉记录及其古环境演变[J]. 地质调查与研究,2020,43(4):341-347. Jiang Xingyu, Wang Lin, Hao Xiudong, et al. Late Pliocene palynological record and paleoenvironmental change from the borehole HLL02 in the south coast of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2020, 43(4): 341-347. [81] 季军良,郑洪波,李盛华,等. 山西平陆黄河阶地与古三门湖消亡、黄河贯通三门峡时代问题的探讨[J]. 第四纪研究,2006,26(4):665-672. Ji Junliang, Zheng Hongbo, Li Shenghua, et al. The terraces of the Huanghe River in Pinglu county, Shanxi province and their relationship with the disappearance of the Sanmen palaeolake and the formation of the Huanghe[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(4): 665-672. [82] 王苏民,吴锡浩,张振克,等. 三门古湖沉积记录的环境变迁与黄河贯通东流研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑):地球科学,2001,31(9):760-768. Wang Sumin, Wu Xihao, Zhang Zhenke, et al. Environmental changes in the sedimentary records of Sanmen ancient lake and research on the eastward flow of the Yellow River[J]. Science China (Seri. D): Earth Sciences, 2001, 31(9): 760-768. [83] 岑敏,董树文,施炜,等. 大同盆地形成机制的构造研究[J]. 地质论评,2015,61(6):1235-1247. Cen Min, Dong Shuwen, Shi Wei, et al. Structural analysis on the formation mechanism of Datong Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(6): 1235-1247. [84] 吉云平,王贵玲,赵华,等. 河北阳原盆地中更新世湖相地层顶部文石的发现及其科学意义[J]. 地学前缘,2016,23(3):178-185. Ji Yunping, Wang Guiling, Zhao Hua, et al. The discovery of aragonite sedimentary on the top of lacustrine sedimentary in the Middle Pleistocene in Yangyuan Basin, Hebei province and its scientific significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(3): 178-185. [85] Zhao H, Lu Y C, Wang C M, et al. ReOSL dating of aeolian and fluvial sediments from Nihewan Basin, northern China and its environmental application[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2010, 5(2/3): 159-163. [86] 年小美,周力平,袁宝印. 泥河湾陆相沉积物光释光年代学研究及其对古湖泊演化的指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2013,33(3):403-414. Xiaomei Nian, Zhou Liping, Yuan Baoyin. Optically stimulated luminescence dating of terrestrial sediments in the Nihewan Basin and its implication for the evolution of ancient Nihewan Lake[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(3): 403-414. [87] Ao H, Liu C R, Roberts A P, et al. An updated age for the Xujiayao hominin from the Nihewan Basin, North China: Implications for Middle Pleistocene human evolution in East Asia[J]. Journal of Human Evolution, 2017, 106: 54-65. [88] Dennell R W, Martinón-Torres M, Bermúdez De Castro J M. Hominin variability, climatic instability and population demography in Middle Pleistocene Europe[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(11/12): 1511-1524. [89] Harington C R. The evolution of Arctic marine mammals[J]. Ecological Applications, 2008, 18(2 Suppl): S23-S40. [90] Barnosky A D. Effects of Quaternary climatic change on speciation in mammals[J]. Journal of Mammalian Evolution, 2005, 12(1/2): 247-264. [91] Lister A M. The impact of Quaternary ice ages on mammalian evolution[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2004, 359(1442): 221-241. [92] Gao J X, Yu D, Liu H Z. Phylogeographic analysis revealed allopatric distribution pattern and biogeographic processes of the widespread pale chub Opsariichthys acutipinnis-evolans complex (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in southeastern China[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2023, 11: 1142810. -





 下载:
下载: