-
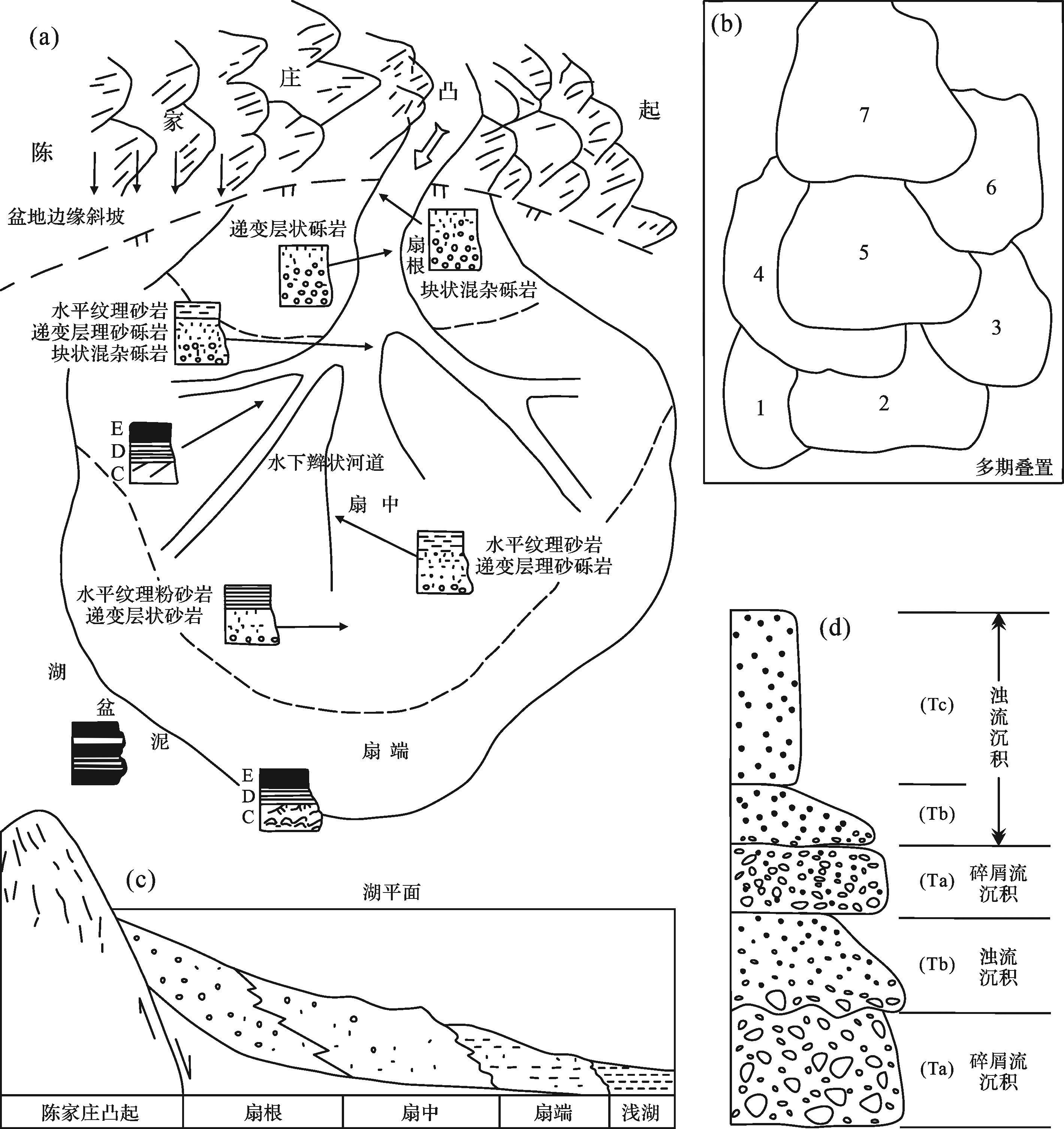
Walker[1]1978建立的海底扇(submarine fan)沉积模式一经问世就引发了国内外地质学家的广泛关注[2⁃4],并孕育了“近岸水下扇”一词的雏形。1987年,赵澄林等[4]将其应用于我国的油区岩相古地理领域,彼时称之为“陡岸湖底扇”。在后续研究过程中,因其形成环境的特殊性,国内学者对这一概念的认知也存在一定分歧,水下冲积扇、水下扇、近岸扇、近岸水下冲积扇、近岸水下扇、重力流水下扇等概念不断涌现[5⁃10]。孙永传等[5]定义的水下冲积扇和董荣鑫等[6]提出的近岸水下冲积扇意指“由近源的山间洪水携带大量陆源粗粒碎屑直接进入湖盆所形成的水下扇形体”,强调“除具有沉积物密度流(或浊流)特性外,仍然表现出一定的冲积性质”,虽在形态上类似于陆上冲积扇,却发育在湖盆底部[5⁃6]。该认识在曾洪流等[7]的研究中得到认可,并指明近岸水下扇是发育在凹陷陡坡带断层根部、与暗色泥岩互层的扇形粗碎屑岩体,而端木合顺等[8]将其形成过程进一步细化为突变性洪水事件(水下滑坡)—水下碎屑流—高密度浊流—低密度浊流,“重力流水下扇”一词凸显了水下扇的重力流流体性质。吴崇筠[9]在总结湖盆砂体类型时同样划分出水下冲积扇,但认为是山地河流出山口后就直接进入湖盆滨浅水区堆积,形成全部没于水下的扇形砂砾岩体,灰绿色、浅灰色泥岩和浅水生物化石均表明其形成于滨浅湖环境。徐怀大等[10]则指出,作为陆上产物的冲积扇与“水下”二字有自相矛盾之嫌,建议推行“水下扇”一词,以强调其全然产于水下。不难发现,早期有关近岸水下扇的争议主要在于其形成环境和发育机制,是浅水还是深水?是重力流成因还是兼具冲积性质?对此,张金亮等[11]、朱筱敏等[12]、刘家铎等[13]、张萌等[14]等诸多学者在20世纪90年代相继明确了近岸水下扇的基本发育特征:在断陷湖盆陡坡靠近断层下降盘一侧,近源洪水携带大量陆源碎屑物质直接进入深水区,在重力流作用下快速堆积形成的砂砾岩扇体。
受强构造活动[15⁃17]、湿热古气候[16⁃18]、高山深湖古地貌[13⁃14]、阵发性洪水[14,17,19]、近物源供给[19⁃20]以及湖盆基准面变化[21⁃22]等因素控制,近岸水下扇砂体表现出紧靠边界断裂、近源快速堆积、扇体多期叠置、岩石组构复杂的显著特征[17⁃18,20⁃21,23],平面呈宽缓连片的扇形且分带明显,垂向则多种沉积作用叠置呈正旋回(图1)[13,23⁃24]。目前,基本认为近岸水下扇沉积相可划分为三个亚相,以扇根、扇中、扇端(缘)的分类稍占主流[13,16,22⁃24],另有部分学者将其划分为内扇、中扇、外扇[12,17,25];但限于沉积过程不明、研究工区特性等因素,针对沉积微相的划分可谓百家争鸣,扇根主要由主水道和主水道间(侧缘)两个微相组成[12⁃13,16,22,26],并将主水道侧缘细分为水下天然堤、决口扇两个微相;扇中亚相相对复杂,以辫状水道(分流水道)、水道间、扇中前缘三个微相为主[12⁃13,16,24],另有学者认为还发育支间天然堤、前缘朵状体和决口扇等沉积微相[26],而白立科等[23]引入成因依据,建议扇中亚相亦可分为水下河道微相和河道边缘微相,于景强等[19]则从水槽模拟实验角度强调了坡积朵叶体微相的发现与发育机制;除扇端泥微相之外,扇端亚相还发育扇端席状砂微相和滑塌浊积体微相[13,19,24,26]。在流动机制方面,近岸水下扇兼具重力流和牵引流双重成因,但以重力流为主,这明显区别于以牵引流为主的扇三角洲沉积[14,17,23]。碎屑流与浊流在近岸水下扇中可同期发育,一般粒序下部发育黏结性较高的碎屑流,上部为弥散式浊流(图1);随着搬运距离的增加,碎屑流逐渐向浊流转化,最后至扇端处可见牵引构造[23]。
显然,作为陆相断陷湖盆特有的一种沉积类型,我国学者针对近岸水下扇的研究持续而热烈,这不仅丰富了事件沉积学的研究范式,更是为油气资源的勘探开发提供了重要的科学依据。近岸水下扇砂体或呈楔形插入半深湖—深湖泥岩中,或通过断层沟通源储系统,成藏条件十分优越,已然成为中国东部断陷湖盆油气勘探的重要接替阵地[5⁃6,20,27⁃28]。以济阳坳陷北部陡坡带为例,包括近岸水下扇在内的砂砾岩体具有勘探面积广(近2 600 km2)、探明储量高(11.47×108 t)、勘探潜力大(剩余资源量达10.0×108 t)等显著特点。“十一五”之后,东营凹陷陡坡带油气勘探目标逐渐向深层转移,目前已形成“沟扇对应、横向连片、纵向叠置、扇根封堵、扇中富集”等重要地质认识[18⁃21,27,29]不仅有力地指导了盐家、胜坨等区块砂砾岩体油气藏的勘探开发实践,也极大地丰富了陆相油气地质学理论。时至今日,“砂砾岩多源多期多圈闭立体勘探”思路愈发清晰,工作要求更加精细,但新的问题也接踵而至。在前人认识基础上,以沉积学、地球物理学及石油地质学等学科理论为指导,借助水槽实验模拟、地球物理分析和典型油藏解剖等手段对近岸水下扇的沉积微相类型、砂体发育规律和油气圈闭样式及响应特征进行系统梳理迫在眉睫。同时,这对拓展我国断陷湖盆油气勘探空间具有重要的指导意义。
-
东营凹陷在构造区带上从属于渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷,整体沿东西向展布,并分别以东部青坨子凸起、北部陈家庄—滨县凸起、西部青城凸起和南部鲁西隆起—广饶凸起为界[18,30⁃31]。凹陷内包括3个正向构造带(北部陡坡带、南部缓坡带、中央背斜带)和4个负向构造带(民丰洼陷、利津洼陷、博兴洼陷和牛庄洼陷);受陈南铲式边界断层和滨南—利津断层两套断裂系统控制,整体形成“北断南超、山高谷深、沟梁相间”的古地貌格局,为中国东部陆相箕状凹陷的典型代表(图2)[30,32]。古近系沙河街组沙四段—沙三段,济阳坳陷正处于断陷湖盆扩张阶段,在干—湿交替古气候背景和半深湖—深湖咸水环境下[30,33⁃34],来自陈家庄凸起的陆源粗粒碎屑在东营凹陷北部陡坡带形成近岸水下扇沉积相(图2),成为非常重要的油气储集体。目前,已发现滨南、单家寺、利津、胜坨、盐家等9个油田,累计上报探明石油地质储量3.1×108 t;扇体之间盐227井、利943井的成功和稳产进一步揭示了近岸水下扇具备连片含油的潜力。

图 2 东营凹陷构造地质简图及沙四段沉积相平面图
Figure 2. Geological profile and sedimentary facies of Es4 member in Dongying Depression
然而,利斜572井显示,夹持在浅层扇体与深层扇体之间的砂砾岩储层物性则很差,测试也以干层为主。分析认为,邻近断层、多期叠置的近岸水下扇一般具有横纵向相变迅速、内部结构复杂、岩相类型多样等特征[20⁃21,23,35],且经过长期的埋藏和复杂的成岩改造后,不同岩相单元的储层非均质性极强[36⁃38],如孔渗参数、孔喉结构等,最终导致扇体间和扇体内的含油差异极大。对比、解剖济阳坳陷陡坡带钻遇近岸水下扇的探井和开发井发现,有效储层分布的复杂性和矛盾性主要表现在以下三方面,其无一不与沉积规律密切相关。
(1) 与“扇根物性封堵”的矛盾:在大型古冲沟控制扇体发育的基础上,前人认为早期机械渗滤的黏土主要富集在扇根亚相;在经历强压实、杂基重结晶和碳酸盐强胶结作用后,纵向叠置的扇根物性较差,可视为侧向封堵层和局部盖层,利于形成深层扇根封堵岩性油藏[27,29,39]。这一重要认识指导盐家、胜坨等区块新增探明储量7 652.7×104 t。然而,后期部署在扇根部位的利853-23井、利853-17井均揭示了有效储层的发育,孔隙度最高约16.2%,渗透率最高约18.23×10-3 μm2。
(2) 与“扇中储利油富”的矛盾:扇中辫状水道单期厚度可达10 m,岩性以含砾粗砂岩、中—细砂岩为主,在受到湖浪反复淘洗后具备一定的分选,结构成熟度、成分成熟度相应提高,加之溶蚀作用较为发育,储集性能得到有效改善,使之成为优势储油相带[22,35,37]。东营凹陷利津洼陷利943井压裂后长期稳产在24 t/d以上,利567X1井产能也较高,但邻近的利567井、利94X1井则产能差,压裂后仅稳产在1 t/d。可见,研究区扇中沉积微相类型仍需明确,有利砂体展布亦待明晰。
(3) 对“扇端泥多砂少”的忽视:山间洪水携带的砂泥沉积物到达扇端时密度明显降低,以形成具似鲍马序列的浊积岩为主,砂泥多呈薄互层发育并向沉积中心逐渐过渡为湖相暗色泥岩[14,17]。在以往勘探工作中,富泥而少砂的扇端亚相尚未引起足够重视,而近期有学者指出“泥石流(碎屑流)主要在扇根与扇中卸载沉积,但塑性流体底部的滑水机制可使其搬运较远而靠近扇端沉积”[23];此外,扇根及扇中部分也发育滑塌型重力流成因的砂砾岩体[24,40]。东营凹陷利92井、利911井勘探证实,近岸水下扇扇体前端不仅发育厚8~10 m的中—细砂岩,且物性较好,平均孔隙度10%~15%,压裂后产能约5 t/d。因此,扇端是否发育新的砂体类型也急需准确认识。
研究团队已通过水槽沉积模拟实验发现,扇中和扇端部位发育坡积朵叶体,其具有独特的前积式反粒序旋回,SP曲线呈漏斗形,地震反射中—强且向四周尖灭;另外,在扇端地形平缓区域还发育透镜状滑塌浊积体[19]。同时,扇体沉积形态与其储集性能关系密切,扇体推进越远,分选越充分,物性相对较好;反之,则物性较差。基于此,本文尝试对传统的近岸水下扇亚相三分模式(扇根、扇中和扇端)进行细化,以期新的沉积认识可以解决上述突出矛盾并指明下一步勘探方向。
-
在系统解析东营凹陷陡坡带沙四段地形坡度、边界断层活动性、沉积环境、物质组成等特征的基础上,通过开展水槽模拟实验探究近岸水下扇沉积亚相类型与特征,并建立基于实验室地质模型的沉积模式。沉积模拟实验在长江大学CNPC油气储层沉积模拟重点实验室完成,实验装置、实验方案、关键参数等设计遵照团队前期报道[19],限于篇幅和报道重点,此文不再赘述。
-
在断层幕式活动和干—湿交替气候条件下,泥石流、阵发性洪水和间洪期正常河流等多种性质的流体在陡坡带有序发育形成近岸水下扇。其中,强水动力泥石流(碎屑流)属于黏滞性极高的塑性流体,搬运沉积机制以块状搬运、整体固结为特征[23];高杂基含量的粗碎屑物质紧靠边界断层堆积形成展布范围小、单层厚度大、分选磨圆差、沉积分异不明显的扇根亚相(图3)。随着地形坡度变缓,流体在推进过程中能量不断下降,颗粒支撑也逐渐向杂基支撑转变,碎屑流整体固结的块状层理砂砾岩演变为以递变层理含砾砂岩、粗砂岩为特征的高密度浊流[14,23];分散的洪水水流在冲蚀扇中早期沉积物时形成延伸距离较远的水下辫状水道,其底部常见冲刷—充填构造,正粒序明显;在远离物源区的扇中前端,由于流体能量不断衰减和碎屑物质迅速卸载,流体性质演变为低密度浊流,以形成具鲍马序列的经典浊积岩为特征,粒序底部侵蚀能力下降而顶部可见牵引流沉积构造[12,14,17];平面上,单期次扇中主体常呈舌状展布,水道间发育弱水动力粉砂岩、泥岩,在辫状水道不断迁移摆动下构成多期叠置扇体(图3)。伴随着沉积物的大量卸载和水动力的持续减弱,扇端位置不再具备形成冲蚀水道的水流强度,而是发育以砂、泥为主的低密度浊积岩,多见鲍马序列的BE、CE组合,并向湖盆方向逐渐过渡为湖相暗色泥岩[12,17]。此外,扇端前缘可发育滑塌浊积扇体,常因重力滑塌或间歇性的断层活动所致[19,24,35],亦有学者认为其可能是低密度的异重流远距离搬运成因[23]。

图 3 基于水槽模拟实验的近岸水下扇沉积微相平面分布图
Figure 3. Sedimentary microfacies plane of nearshore subaqueous fan from flume simulation experiment
水槽沉积模拟实验揭示,在传统的扇根、扇中、扇端亚相基础上,多物源沉积体系形成的近岸水下扇还可能发育扇间亚相,其位于两个扇主体之间,沉积物富泥而贫砂(图3)。在水体变浅、物源充足背景下,部分出露水面的扇主体侧缘具有优势可容空间,从而导致水流携带的碎屑物质“因势就形”形成扇间扇体。扇间亚相包括侧向迁移朵叶体和扇间泥两个微相,前者主要发育正粒序含砾砂岩、细砂岩,砂体向扇根方向尖灭并侧向嵌入扇间泥。
在扇中亚相则证实了坡积朵叶体微相的存在[19],其整体与其他扇体脱离,并沿水流方向呈长舌状分布在洪水期扇体斜坡的中下部,规模大小不一(图3)。实验中,规模较大的朵叶体长1.5~2.0 m,宽0.6~1.0 m,较小者仅长0.5 m,宽0.2 m,据此预测自然界中坡积朵叶体的展布规模在0.5 km2左右。前人指出,在物源供给、边界断层活动性、水动力条件及地形坡度等因素约束下,坡积朵叶体上倾部位砾岩、细砂岩、粉砂岩及泥岩共存,但以砾岩为主,结构混杂、杂乱分布;随着水流推进至下倾部位,岩性逐步转变为颗粒支撑的粉—细砂岩,分选变好;末端为湖相泥页岩,夹杂滑脱入湖的薄层砂质条带[19]。持续增强的水动力条件和物源输入有利于坡积朵叶体的发育,随着后期流体向前逐层推进,沉积体形成前积序列,相序上表现出明显的“下细上粗”反韵律特征(图4a)。在沉积构造上,上部含砾带可见较强水动力背景下形成的平行层理、交错层理(图4b);中部砂岩带以斜层理和平行层理为主,偶见羽状交错层理,揭示出水流改道现象的存在(图4b);底部泥岩带则主要发育水平层理,砂条发育位置可见同生变形构造(图4b),如包卷层理、砂枕构造、滑塌构造等[19]。
-
陡坡带边界断层通常活动较剧烈,断陷湖盆迅速扩张并处于饥饿欠补偿状态,各期扇体以向岸退积为主,基岩之上依次发育扇根、扇中、扇端亚相;而在湖平面控制下,东营凹陷早期退积型扇体之上还发育晚期进积型扇体[18]。垂向完整的近岸水下扇自下而上由泥石流沉积、阵发性洪水沉积、间洪期正常河流和湖相悬浮沉积叠加构成;在扇体不同位置,可能缺失某种沉积序列,但均表现为正旋回特征。断层幕式活动早期,构造活动强烈、陆源碎屑物质供应充足,主要发育泥石流、阵发性洪水沉积;随着构造活动减弱、陆源碎屑物质供应强度降低,断层幕式活动中—后期以发育气候控制下的阵发性洪水和间洪期正常牵引流为主;至末期,构造活动基本停歇,陆源碎屑供应极弱,湖相悬浮沉积占据主导;虽其沉积速率较慢但时间较长,扇体顶部理应普遍披覆湖相泥岩,但扇根和扇中部位多遭受后期强水动力侵蚀而流失,扇端部位则稳定发育,并成为重要的沉积期次界面。
在减少基底沉降量以模拟断层活动减弱时,枯水期扇体在早期洪水期扇中斜坡上形成了坡积朵叶体,垂向粒序可分为底部泥岩层、中部砂岩层和顶部砾岩层,前积反旋回特征显著。纵剖面上,坡积朵叶体多向上超覆在早期扇体斜坡之上,向下可延伸至湖相泥岩;在扇体远端地形转平区域,滑塌浊积体常呈透镜体状包裹在湖相泥岩中(图4a)。横剖面上,坡积朵叶体一般位于洪水期扇体的侧上方或扇间位置,填平补齐特征显著并常具有“底凹上凸”的结构特点,部分主水道可见下蚀现象。在沉积构造相标志方面,顶部砾岩层发育平行层理、交错层理;中部砂岩层以斜层理及平行层理为主,偶见羽状交错层理,响应水流改道现象;底部泥岩层则以水平层理为主,砂条发育区可见冲刷构造(图4b)。
-
综上认为,由多物源体系供应形成的近岸水下扇可划分为扇根、扇中、扇端及扇间4个亚相,并包含9种沉积微相(表1)。扇根亚相可划分为主水道及水道间两种微相,主水道微相以砾石为主,混杂堆积;水道间微相以泥岩为主,含薄层砂条(图5a)。扇中亚相可分为辫状水道、辫状水道间、坡积朵叶体三种沉积微相类型,其中,辫状水道微相以含砾砂岩为主,底冲刷和侵蚀充填现象明显;坡积朵叶体微相同样以含砾砂岩、粗—细砂岩为主,但呈反粒序,外部形态底凹上凸,内部发育多种类型的层理构造;分支辫状水道间微相主要沉积细砂岩,其厚度相对较薄(图5b)。扇间亚相可识别侧向迁移朵叶体和扇间泥微相,前者的发育机理类似于侧向加积:由于河道水流的侧向摆动、改道,沉积物容易沿前期扇体斜坡堆积在扇体之间的凹地处,结构上嵌入扇间泥;砂体向扇根主水道方向尖灭,外部具沉积充填特征,内部则以发育正粒序中—细砂岩为主(图5b);测井曲线上表现为钟形或锯齿状钟形。扇端亚相包括扇缘斜坡和滑塌浊积体两种微相,扇缘斜坡以粉—细砂岩和泥质沉积为主,正粒序,水平层理发育;滑塌浊积体外部形态呈透镜体状,内部主要为粉—细砂岩,含少量砾石,可见鲍马序列(图5c)。
表 1 近岸水下扇沉积微相分类
亚相类型 微相类型 沉积特征 扇根 主水道 砾石为主,混杂堆积 主水道间 泥岩为主,含薄层砂条,沉积构造少见 扇中 辫状水道 含砾砂岩为主,下蚀加厚现象明显 辫状水道间 泥岩、粉砂岩为主,厚度相对较薄 坡积朵叶体 含砾砂岩、粗—细砂岩为主,反粒序,底凹上凸特征 扇端 扇缘斜坡 粉—细砂岩为主,正粒序,水平层理 滑塌浊积体 粉—细砂岩为主,含少量砾石,正粒序,透镜体形态 扇间 侧向迁移朵叶体 细砂岩为主,正粒序,沉积充填特征 扇间泥 泥岩为主,含少量薄层砂条 
图 5 近岸水下扇不同沉积微相纵剖面发育特征
Figure 5. Characteristics of sedimentary microfacies in longitudinal section of nearshore subaqueous fan
在济阳坳陷陡坡带,钻井和模拟实验已经证实,坡积朵叶体和侧向迁移朵叶体是近岸水下扇沉积相内普遍存在的微相类型,其在测井、录井、地震等多方面信息中亦有明显响应。总结前人提出的成因机制和影响因素[19],认为两种沉积微相的发育综合受控于边界断层活动性、物源供给强度、水动力条件及沉积坡度等多种因素。
在边界断层活动性减弱后,湖盆内水体相应变浅,早期扇体前方或侧缘较大的水下可容空间将引导沉积物在这些区域迅速卸载,易于形成坡积朵叶体和侧向迁移朵叶体;随着沉积物供给增强,后期扇体越过前期扇体持续进积,且扇体规模不断加大;在较强水动力背景下,粗粒砂体的强冲刷能力导致早期扇体遭受破坏,尤其是沉积坡度较陡位置,在重力和水流搬运作用下发生整体垮塌、滑动,形成与扇主体脱离的滑塌成因坡积朵叶体;若砂体继续演化为浊流并远距离搬运,则可能形成扇缘的滑塌浊积体,由断层沉降引发的地震活动会明显促进滑塌作用的发生。
值得强调的是,扇中亚相坡积朵叶体、扇间亚相侧向迁移朵叶体和扇端亚相滑塌浊积体的发现进一步丰富了近岸水下扇的沉积样式,将原有“扇中有储”的地质认识拓宽至“扇间有储、扇前有储”,为断陷湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩体油气勘探提供了实验模型和理论支撑。
-
根据扇根、扇中、扇端及扇间的沉积微相类型及其地层岩性组合结构的差异,近岸水下扇发育不同类型的圈闭,且呈明显的规律性分布。除扇根地层超覆圈闭、扇中扇端构造回倾圈闭外,扇中坡积朵叶体、扇间侧向迁移朵叶体和扇端滑塌浊积体均可形成岩性圈闭。
-
地层超覆圈闭成藏是近岸水下扇扇根亚相最主要的成藏模式,其关键要素在于不同期次的扇体之间是否发育泥岩隔层,可以使其形成各自独立的成藏系统。另外,扇根亚相与基底太古界基岩直接对接,也可形成良好的侧向对接封堵条件,属于基岩―隔夹层共同控制的地层圈闭类型。
在研究区,该类型圈闭多发育在湖盆快速扩张的沙四上亚段—沙三下亚段,对应沉积层序的水进体系域[18,30]。由于地层埋藏相对较浅,储层物性保持较好;同时,炎热、潮湿的古气候背景[34]更有利于泥岩发育。利津地区沙四段纯上时期扇根砂砾岩体超覆于太古界基岩之上,且多期砂砾岩体之间发育稳定的泥岩隔层,良好的储盖配置形成了有效的地层超覆圈闭并最终富集油气,利斜965井即钻遇该类型油藏。
-
构造回倾圈闭主要发育在扇中和扇端部位,具体包括扇中背斜构造圈闭和扇端回倾构造圈闭两种样式,是扇体沉积后因边界断层长时间活动而发生构造形变所致。扇体沉积后,其形变受控于边界断层活动导致的逆牵引构造和深层盐底辟构造等构造应力作用[41⁃42]。受喜山期区域性张扭活动的影响[43],东营凹陷北部陡坡带边界断层两盘中间出现较大空隙,为了补偿这一空间,已沉积地层会在重力作用下产生自然挠曲,当挠曲增加到一定程度就形成了逆牵引背斜。同时,济阳坳陷孔店组—沙四下亚段发育盐湖沉积[44],强塑性膏盐层在上覆地层重压下向湖盆中心挤压形成盐底辟构造。在逆牵引作用及盐底辟上拱作用下,上覆近岸水下扇地层产状发生了不同程度的形变,且地层埋藏深度越大、边界断层活动越强、持续时间越长,扇体构造变形的程度就越高、越利于形成构造回倾圈闭。
盐家地区盐22井区勘探证实了构造回倾圈闭是近岸水下扇的主要成藏类型。通过高精度地层标定和横向连井对比发现,同期发育的近岸水下扇扇中、扇端亚相位于构造高点,而扇根亚相回倾至构造低部位,这也合理解释了扇中、扇端成藏而扇根出水的现象(图6)。
-
发育在扇主体斜坡前端的坡积朵叶体常紧邻半深湖—深湖区域,具备油气优先充注的烃源基础;不断推进的前积作用有利于颗粒在湖浪中反复淘洗,良好的分选有效提高了储层的储集性能;同时,前积层反映了沉积上的某个独立旋回,顶部多为间洪期—枯水期的泥质悬浮沉积物所覆盖,有效阻止了烃类逸散。优越的烃源、储层条件及储盖组合造就了其可以形成独立于扇主体的岩性油气藏,并具有相对独立的油水系统。利853-23井、利853-9井、利85井等证实了利津地区沙四段纯上时期发育了广布的坡积朵叶体,在沿物源推进方向的剖面上,油藏由沙四纯下亚段的连片成藏体系转变为沙四纯上亚段的坡积朵叶体岩性圈闭成藏系统[19]。
侧向迁移朵叶体与主扇具有相似的沉积充填特征,岩性同样以含砾砂岩、细砂岩为主并表现为正粒序。平面上,砂体呈朵状或扇状嵌入扇间泥;垂向上,砂体向上倾的扇根方向尖灭,可形成独立的岩性圈闭。部署在扇间部位的利943井获得高产工业油气流,证实了扇间亚相侧向迁移朵叶体的成藏潜力。
在外界触发机制下,如地震、断裂、洪水或自身重力等,扇中和扇端未固结沉积物沿斜坡滑动至深水区形成滑塌浊积体[45⁃46]。其常见于湖盆扩张阶段的湖侵—高水位体系域,岩性以砂岩、含砾砂岩为主,外部形态呈透镜状、扇状或席状包裹在半深湖—深湖相泥岩中,可形成典型的透镜型岩性圈闭。
-
基于沉积模拟实验和沉积充填过程建立的坡积朵叶体、侧向迁移朵叶体沉积模式修正了以往“扇间无储、扇缘劣储”的认知,以沉积学思维拓展了近岸水下扇的油气勘探空间。得益于这一新认识的指导,济阳坳陷近期在东营凹陷、沾化凹陷等工区接连取得新突破,表明我国东部断陷湖盆近岸水下扇砂砾岩体仍具有良好的勘探前景。
-
车镇凹陷车西地区在构造上位于埕南断层下降盘,具明显的“洼梁相间”特征,是济阳坳陷内重要的砂砾岩体探区。沙三下亚段沉积时期,区内发育来自北部埕子口凸起的近岸水下扇,岩性以砾岩和含砾砂岩为主。由南向北,扇体逐渐增厚至约1 100 m,沉积期次也逐渐增多,并层层超覆退积于埕南断层的断面之上。据沉积相和地震相分析,区内由西向东依次发育车58扇体、车572东扇体和车古25扇体,其扇体厚度大、分布范围广、纵向多期叠置、平面叠合连片,整体沿埕南断层呈裙带状分布(图7a)。

图 7 车镇凹陷车西地区沙三段近岸水下扇分布特征
Figure 7. Distribution characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fan in Chexi area, Chezhen Depression
部署在埕南断层下降盘的车71井位于主扇体前接近扇端区域,在地震结构上与北部主扇体脱离(图7b),自然电位曲线则呈“下细上粗”的漏斗形结构,反映了典型的坡积朵叶体特征[19]。投产初期,车71井日产油8.8 t,石油地质储量为234.95×104 t,目前已累产油1.71×104 t、累产气2.06×104 m3,取得了良好的勘探效益。
-
永安镇地区位于东营凹陷北带的东段,是济阳坳陷砂砾岩体油气发现最早、勘探程度最高的地区。以永安镇永55井区为例,永1块在1986—1988年间探明储量1 134×104 t,永551块在1993年探明储量92×104 t。
沙四段盆地扩张期,区内陈南大断层活动强度明显增加,东营凹陷陡坡带形成了以北部陈家庄凸起为物源,呈典型裙带状分布的近岸水下扇沉积(图2)。永安镇古地貌刻画结果显示,受控于北部陈家庄凸起的两个小型沟槽,永551块与永1块之间仍有可能发育永斜560扇体(图8a)。三套独立扇体的物源均来自陈家庄凸起,但属于不同的物源分支。钻井证实,永斜560井、永559井扇体的扇中含砾砂岩储层品质较好,孔隙度介于4.40%~14.03%,渗透率介于0.12×10-3~16.39×10-3 μm2,扇根受压实、胶结等成岩作用影响形成致密干层,可形成岩性上倾尖灭油藏(图8b)。

图 8 东营凹陷永安镇地区沙四段近岸水下扇油藏发育特征
Figure 8. Development of Es4 nearshore subaqueous fan in Yong'an area, Dongying Depression
继永559-2井试油峰值52.93 t/d、累产2 261.0 t之后,永斜558井、永斜560井、永560-X1井日产油量也稳定增长,分别为11.16 t/d、14.45 t/d和27.3 t/d,累计上报预测储量1 285×104 t、控制储量742.18×104 t。在侧向迁移朵叶体沉积模式指导下,永安镇地区实现了扇间砂砾岩体油气勘探的不断突破。
-
(1) 通过沉积充填过程解析,将传统的近岸水下扇亚相三分模式扩充为扇根、扇中、扇间、扇端4种亚相类型,并包含主水道、主水道间、辫状水道、辫状水道间、坡积朵叶体、侧向迁移朵叶体、扇间泥、扇缘斜坡和滑塌浊积体共9种微相类型。
(2) 扇中坡积朵叶体整体与主扇脱离,纵向呈独特的前积式反旋回并表现出“底凹上凸”的外部形态;扇间侧向迁移朵叶体以发育正粒序中—细砂岩为主,具沉积充填特征;二者均与湖相泥岩或扇间泥岩紧密接触,可形成岩性圈闭。
(3) 在济阳坳陷陡坡带识别、刻画的近岸水下扇坡积朵叶体、侧向迁移朵叶体冲破了以往“扇间无储、扇缘劣储”的认知瓶颈,完善后的扇体分布模式为合理解释研究区“扇根见储、扇中失序、扇缘含储”的油气勘探矛盾提供了地质模型,多口高产、稳产工业油气井在勘探实践中不断落实,彰显了我国东部断陷湖盆砂砾岩体的勘探潜力和韧性。
New Sedimentary Understandings of Nearshore Subaqueous Fan and Its Re-practice on Oil-gas Exploration:Take the steep slope zone of Jiyang Sag as a case
-
摘要: 在济阳坳陷砂砾岩体油气勘探中,砂体复杂分布和油水差异聚集等问题引发了对现有近岸水下扇沉积充填样式的思考、探索和补充。为完善断陷湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩体发育模式提供实验素材和地质实例,在系统梳理前人研究硕果的基础上,通过开展水槽沉积模拟实验、解析沉积充填过程,并结合油气勘探实践论证。可将断陷湖盆陡坡带近岸水下扇分为扇根、扇中、扇间和扇端4种沉积亚相,并包括9种沉积微相;较之以往,补充建立了扇中坡积朵叶体微相和扇间侧向迁移朵叶体微相,前者多超覆在早期扇主体斜坡之上,纵向呈独特的前积式反旋回并表现为“底凹上凸”的外部形态,后者则以发育正粒序中—细砂岩为主,沉积充填特征显著;二者均与半深湖—深湖泥岩、扇端和扇间泥岩紧密接触,利于形成岩性圈闭;济阳坳陷陡坡带以坡积朵叶体和侧向迁移朵叶为勘探目标的多口井接连获得高产、稳产工业油气流,在勘探实践中验证了近岸水下扇扇体沉积新认识,拓宽了断陷湖盆砂砾岩体的勘探新空间。科学发展的动力之一来源于理论与实验的矛盾,油气地质学更是着重表现出“问题由实践中来,认识到实践中去”的特点,基于水槽模拟实验的沉积充填模式探讨是促进沉积学繁荣发展的有效手段。Abstract: In the oil⁃gas exploration of glutenite bodies in the Jiyang Depression, the complex sand distribution and differential accumulation of oil and water have led us to ponder, explore and supplement the evident deposition filling pattern of nearshore subaqueous fans, which provides experimental materials and geological examples for perfecting the glutenite development patterns in the steep slope of faulted lacustrine basin. Based on systematically sorting out the previous research results, by conducting the flume simulation experiments, analyzing the sedimentation filling process, and combining with the oil and gas exploration practice, it is considered that nearshore subaqueous fans in the steep slope zone of a fault-depressed lacustrine basin is divided into four sedimentary subfacies: fan-root, fan-middle, fan-inter and fan-terminal, including nine sedimentary microfacies. Compared with previous studies, the microfacies of slope accumulation lobes in fan-middle and lateral migrating lobes in fan-inter are established. The slope accumulation lobes mostly overlie the early fan body with an external form of “concave bottom and convex top” having a longitudinal cycle presenting a unique reverse rhythm. Lateral migrating lobes are characterized by positive-rhythm medium and fine sandstones, with notable sedimentary filling characteristics. Both of these are in close contact with semi- and deep-lake mudstones, fan-terminal mudstones and fan-inter mudstones, which is conducive to the formation of lithological traps. In the steep slope zone of the Jiyang Depression, many exploration wells targeting slope accumulation lobes and lateral migrating lobes have successfully established high, stable industrial oil⁃gas flows. This verifies the new sedimentary understandings of nearshore subaqueous fans in oil⁃gas exploration practice, and suggests a new exploration space for glutenite bodies in fault-depressed lacustrine basins. One of the driving forces of scientific development stems from the contradiction between theory and experiment. Petroleum geology especially shows the discipline characteristics of "problems come from practice, and knowledge goes into practice". The study of sedimentary filling model based on flume simulation experiment is an effective means to promote the development of sedimentology.
-
表 1 近岸水下扇沉积微相分类
亚相类型 微相类型 沉积特征 扇根 主水道 砾石为主,混杂堆积 主水道间 泥岩为主,含薄层砂条,沉积构造少见 扇中 辫状水道 含砾砂岩为主,下蚀加厚现象明显 辫状水道间 泥岩、粉砂岩为主,厚度相对较薄 坡积朵叶体 含砾砂岩、粗—细砂岩为主,反粒序,底凹上凸特征 扇端 扇缘斜坡 粉—细砂岩为主,正粒序,水平层理 滑塌浊积体 粉—细砂岩为主,含少量砾石,正粒序,透镜体形态 扇间 侧向迁移朵叶体 细砂岩为主,正粒序,沉积充填特征 扇间泥 泥岩为主,含少量薄层砂条 -
[1] Walker R G. Deep-water sandstone facies and ancient submarine fans: Models for exploration for stratigraphic traps[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1978, 62(6): 932-966. [2] Richards M, Bowman M. Submarine fans and related depositional systems II: Variability in reservoir architecture and wireline log character[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1998, 15(8): 821-839. [3] Saito T, Ito M. Deposition of sheet-like turbidite packets and migration of channel-overbank systems on a sandy submarine fan: An example from the Late Miocene-Early Pliocene forearc basin, Boso Peninsula, Japan[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 149(4): 265-277. [4] 赵澄林,吴崇筠. 油区岩相古地理[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,1987. Zhao Chenglin, Wu Chongyun. Lithofacies palaeogeography of oil area[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1987. [5] 孙永传,郑浚茂,王德发,等. 水下冲积扇:一个找油的新领域[J]. 石油实验地质,1980,2(3):32-41. Sun Yongchuan, Zheng Junmao, Wang Defa, et al. Subaqueous alluvial fan: A new field for oil exploration[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1980, 2(3): 32-41. [6] 董荣鑫,苏美珍. 近岸水下冲积扇相特征及实例[J]. 石油实验地质,1985,7(4):294-302. Dong Rongxin, Su Meizhen. Characteristic of beachy underwater alluvial fan facies ― with a practical example[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1985, 7(4): 294-302. [7] 曾洪流,张万选,张厚福. 廊固凹陷沙三段主要沉积体的地震相和沉积相特征[J]. 石油学报,1988,9(2):12-18. Zeng Hongliu, Zhang Wanxuan, Zhang Houfu. Seismic and depositional characteristics of major sedimentary bodies in 3RD section of Shahejie Formation Longgu Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1988, 9(2): 12-18. [8] 端木合顺,朱莲芳. 酒西盆地下白垩统下沟组重力流水下扇沉积[J]. 沉积学报,1990,8(2):75-85. Duanmu Heshun, Zhu Lianfang. Gravity-flow-submerged-fan deposits of Lower Crataceous Xiagou Formation, Jiuxi Basin, Gansu[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1990, 8(2): 75-85. [9] 吴崇筠. 湖盆砂体类型[J]. 沉积学报,1986,4(4):1-27. Wu Chongyun. Sandbodies in lake basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1986, 4(4): 1-27. [10] 徐怀大,王世凤,陈开远. 地震地层学解释基础[M]. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,1990. Xu Huaida, Wang Shifeng, Chen Kaiyuan. Interpretation fundamentals of seismic stratigraphy[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1990. [11] 张金亮,沈凤. 乌尔逊凹陷大磨拐河组近岸水下扇储层特征[J]. 石油学报,1991,12(3):25-35. Zhang Jinliang, Shen Feng. Characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fan reservoir in Damoguaihe Formation, Wuerxun Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1991, 12(3): 25-35. [12] 朱筱敏,查明,张卫海,等. 陆西凹陷上侏罗统近岸水下扇沉积特征[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版),1995,19(1):1-6. Zhu Xiaomin, Zha Ming, Zhang Weihai, et al. Sedimentary features of Upper Jurassic nearshore subaqueous fan in Luxi Depression[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 1995, 19(1): 1-6. [13] 刘家铎,田景春,何建军,等. 近岸水下扇沉积微相及储层的控制因素研究:以沾化凹陷罗家鼻状构造沙四段为例[J]. 成都理工大学学报,1999,26(4):365-369. Liu Jiaduo, Tian Jingchun, He Jianjun, et al. A study of sedimentary microfacies and controlling factors of the reservoirs of the nearshore subaqueous fan: Taking the Fourth member of the Shahejie Formation in the Luojia Nose, Zhanhua Depression for an example[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1999, 26(4): 365-369. [14] 张萌,田景春. “近岸水下扇”的命名、特征及其储集性[J]. 岩相古地理,1999,19(4):42-52. Zhang Meng, Tian Jingchun. The nomenclature, sedimentary characteristics and reservoir potential of nearshore subaqueous fans[J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 1999, 19(4): 42-52. [15] 远光辉,操应长,王艳忠. 东营凹陷民丰地区沙河街组四段—三段中亚段沉积相与沉积演化特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2012,33(2):277-286. Yuan Guanghui, Cao Yingchang, Wang Yanzhong. Sedimentary facies and their evolution of the 4th-middle 3rd members of Shahejie Formation in Minfeng area, Dongying Sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(2): 277-286. [16] 曹正林,苟迎春,郑红军,等. 酒西坳陷下白垩统近岸水下扇沉积特征及控制因素分析[J]. 天然气地球科学,2009,20(6):896-901. Cao Zhenglin, Gou Yingchun, Zheng Hongjun, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of Lower Cretaceous nearshore subaqueous fans in Jiuxi Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(6): 896-901. [17] 王星星,朱筱敏,张明君,等. 洪浩尔舒特凹陷下白垩统近岸水下扇沉积特征[J]. 沉积学报,2015,33(3):568-577. Wang Xingxing, Zhu Xiaomin, Zhang Mingjun, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of near-shore subaqueous fans of the Lower Cretaceous in the Honghaoershute Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(3): 568-577. [18] 邱隆伟,韩晓彤,宋璠,等. 东营凹陷盐22区块沙四上亚段近岸水下扇岩相特征及沉积演化[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2021,40(1):26-37. Qiu Longwei, Han Xiaotong, Song Fan, et al. Lithofacies characteristics and sedimentary evolution of the near-shore subaqueous fans in the upper submember of Es4 in block Yan22 of Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2021, 40(1): 26-37. [19] 于景强,韩宏伟. 近岸水下扇坡积朵叶体沉积模式与成因机制[J]. 沉积学报,2020,38(2):411-419. Yu Jingqiang, Han Hongwei. Sedimentary model and genetic mechanism for the alluvial lobes of the offshore underwater fan slope[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(2): 411-419. [20] 鄢继华,陈世悦,姜在兴. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带近岸水下扇沉积特征[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版),2005,29(1):12-16,21. Yan Jihua, Chen Shiyue, Jiang Zaixing. Sedimentary characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fans in steep slope of Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 2005, 29(1): 12-16, 21. [21] 路智勇. 济阳坳陷东营凹陷陡坡带盐18地区重力流沉积特征与沉积模式[J]. 天然气地球科学,2012,23(3):420-429. Lu Zhiyong. Sedimentary characteristics and model of gravity flows in Yan 18 area of the steep slope in Dongying Sag of Jiyang Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(3): 420-429. [22] 吴群,杨云飞,王树芳. 南阳凹陷黑龙庙地区近岸水下扇沉积特征研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(1):33-44. Wu Qun, Yang Yunfei, Wang Shufang. Sedimentary characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fans in the Heilongmiao area of the Nanyang Sag[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2020, 42(1): 33-44. [23] 白立科,邱隆伟,杨勇强,等. 近岸水下扇微相划分研究及意义初探:以滦平盆地下白垩统西瓜园组为例[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(8):2446-2459. Bai Like, Qiu Longwei, Yang Yongqiang, et al. Preliminary microfacies division and significance study of nearshore subaqueous fan: A case study from the Lower Cretaceous Xiguayuan Formation, Luanping Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(8): 2446-2459. [24] 赵红兵,严科. 近岸水下扇砂砾岩沉积特征及扇体分布规律[J]. 断块油气田,2011,18(4):438-441. Zhao Hongbing, Yan Ke. Depositional characteristics of glutenite and distribution pattern of fan on nearshore subaqueous fan[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2011, 18(4): 438-441. [25] 董艳蕾,朱筱敏,耿晓洁,等. 泌阳凹陷东南部核桃园组近岸水下扇与扇三角洲沉积特征比较及控制因素分析[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2015,36(2):271-279. Dong Yanlei, Zhu Xiaomin, Geng Xiaojie, et al. Sedimentary characteristics comparison and controlling factors analyses of nearshore subaqueous fan and fan delta in the Hetaoyuan Formation of southeastern Biyang Sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(2): 271-279. [26] 杨树彬,庄升,李伟. 欢喜岭地区沙三段大凌河油层近岸水下扇沉积特征[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2010,25(4):10-13. Yang Shubin, Zhuang Sheng, Li Wei. Sedimentary characteristics of the nearshore subaqueous fan of Dalinghe reservoir of Es3 in Huanxiling area[J]. Journal of Xian Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 25(4): 10-13. [27] 隋风贵,操应长,刘惠民,等. 东营凹陷北带东部古近系近岸水下扇储集物性演化及其油气成藏模式[J]. 地质学报,2010,84(2):246-256. Sui Fenggui, Cao Yingchang, Liu Huimin, et al. Physical properties evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of Paleogene nearshore subaqueous fan in the eastern north margin of the Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(2): 246-256. [28] 梁官忠,谭建财,魏莉,等. 内蒙古二连盆地阿北凹陷下白垩统近岸水下扇沉积特征[J]. 古地理学报,2013,15(1):31-42. Liang Guanzhong, Tan Jiancai, Wei Li, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fans of the Lower Cretaceous in Abei Sag of Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013, 15(1): 31-42. [29] 刘鑫金,宋国奇,刘惠民,等. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带砂砾岩油藏类型及序列模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2012,19(5):20-23. Liu Xinjin, Song Guoqi, Liu Huimin, et al. Study of conglomerate reservoir types and distribution in north slope zone, Dongying Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2012, 19(5): 20-23. [30] 陈扬,胡钦红,赵建华,等. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷湖相富有机质页岩纹层特征和储集性能[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2022,43(2):307-324. Chen Yang, Hu Qinhong, Zhao Jianhua, et al. Lamina characteristics and their influence on reservoir property of lacustrine organic-rich shale in the Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 307-324. [31] 彭军,许天宇,于乐丹. 东营凹陷沙河街组四段湖相细粒沉积特征及其控制因素[J]. 岩性油气藏,2020,32(5):1-12. Peng Jun, Xu Tianyu, Yu Ledan. Characteristics and controlling factors of lacustrine fine-grained sediments of the Fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Dongying Depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(5): 1-12. [32] 王鑫,林承焰,马存飞,等. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带利563区块沙四上亚段砂砾岩扇体沉积特征及沉积模式[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2020,50(3):705-720. Wang Xin, Lin Chengyan, Ma Cunfei, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and sedimentary model of glutenite fans in upper Es4 in L563 area, north steep slope of Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(3): 705-720. [33] 王永诗,唐东. 咸化断陷湖盆典型页岩剖面地质特征:以东营凹陷为例[J]. 油气藏评价与开发,2022,12(1):181-191,203. Wang Yongshi, Tang Dong. Geological characteristics of typical shale profile in a saline lacustrine rift basin: A case study of Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(1): 181-191, 203. [34] 茆书巍,郝雪峰,巩建强,等. 东营凹陷民丰地区沙四段古水体量化恢复及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评,2021,67(增刊1):105-106. Mao Shuwei, Hao Xuefeng, Gong Jianqiang, et al. Quantitative reconstruction and geological significance of paleo-water of Es4 member in Minfeng area, Dongying Sag[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(Suppl.1): 105-106. [35] 鲜本忠,王永诗,周廷全,等. 断陷湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩体分布规律及控制因素:以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷车镇凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2007,34(4):429-436. Xian Benzhong, Wang Yongshi, Zhou Tingquan, et al. Distribution and controlling factors of glutinite bodies in the actic region of a rift basin: An example from Chezhen Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(4): 429-436. [36] Kra K L, Qiu L W, Yang Y Q, et al. Sedimentological and diagenetic impacts on sublacustrine fan sandy conglomerates reservoir quality: An example of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation (Es4s member) in the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin (East China)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2022, 427: 106047. [37] 马奔奔,操应长,王艳忠,等. 渤南洼陷北部陡坡带沙四上亚段成岩演化及其对储层物性的影响[J]. 沉积学报,2015,33(1):170-182. Ma Benben, Cao Yingchang, Wang Yanzhong, et al. Diagenetic evolution and its influence on physical properties of Es4 sreservoir in the northern steep zone of the Bonan Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(1): 170-182. [38] 朱筱敏,吴冬,张昕,等. 东营凹陷沙河街组近岸水下扇低渗储层成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2014,35(5):646-653. Zhu Xiaomin, Wu Dong, Zhang Xin, et al. Genesis of low permeability reservoirs of nearshore subaqueous fan in Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(5): 646-653. [39] 刘惠民,刘鑫金,贾光华. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带深层砂砾岩扇体成岩圈闭有效性评价[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2015,22(5):7-14. Liu Huimin, Liu Xinjin, Jia Guanghua. Evaluation on trap effectiveness for deep fan diagenetic trap in the northern steep slope zone of Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2015, 22(5): 7-14. [40] 隋风贵. 断陷湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩扇体成藏动力学特征:以东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2003,24(4):335-340. Sui Fenggui. Characteristics of reservoiring dynamic on the sand-conglomerate fanbodies in the steep-slope belt of continental fault basin: A case study on Dongying Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(4): 335-340. [41] 李伟,王峙博,王光增,等. 东营凹陷穹窿构造断裂体系特征及其封闭性评价[J]. 高校地质学报,2014,20(1):93-104. Li Wei, Wang Zhibo, Wang Guangzeng, et al. The fault system and its fault sealing properties of the dome structure in Dongying Sag, East China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2014, 20(1): 93-104. [42] 田巍. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷边界断裂生长联接及其相关褶皱研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2015. Tian Wei. Study on the growth, linkage of boundary faults and fault-related folds in Zhu I Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2015. [43] 张伟忠,张云银,查明,等. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷扭张断裂成因模式及控藏作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2019,40(2):262-270. Zhang Weizhong, Zhang Yunyin, Zha Ming, et al. Genetic model of transtensional faults in Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, and its controls over hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(2): 262-270. [44] 马立民,李志鹏,林承焰,等. 东营凹陷沙四下盐湖相沉积序列[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2014,38(6):24-31. Ma Limin, Li Zhipeng, Lin Chengyan, et al. Sedimentary sequences of salt-lake facies in lower Es4 of Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Sciences), 2014, 38(6): 24-31. [45] Soh W, Tanaka T, Taira A. Geomorphology and sedimentary processes of a modern slope-type fan delta (Fujikawa fan delta), Suruga Trough, Japan[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1995, 98(1/2/3/4): 79-95. [46] 张关龙,陈世悦,鄢继华,等. 三角洲前缘滑塌浊积体形成过程模拟[J]. 沉积学报,2006,24(1):50-55. Zhang Guanlong, Chen Shiyue, Yan Jihua, et al. Simulation of luxoturbidite in front of delta[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(1): 50-55. -





 下载:
下载: