-
蒸发岩是一种盐岩,它最初是在蒸发的驱动下从饱和卤水的表面或近表面的盐水中沉淀出来的[1],其特征与沉积环境息息相关。蒸发岩自身就是重要的矿产资源,如钾盐,石膏,硼等[2],又因为其储集性、可塑性和流动性,可以成为油气运移的优质通道,且其良好的封闭能力还可以成为油气赋存的圈闭[3]。国外沉积学家十分关注蒸发岩的沉积环境解释,早在100多年前,德国地质学家就从蒸发实验和潟湖咸化现象提出了蒸发岩形成环境的沙洲理论(Bar theory)[4],但是该理论不能很好地解释巨厚蒸发岩的形成环境;此后国外学者不断地对蒸发岩形成环境进行理论修正和更新,比如沙漠盆地或凹陷理论(The desert-basin theory)[5-6],还有修正的沙洲理论(“Modified bar-theory”)[7],Borchert et al.[8]提出了多级障坝和次级盆地的盐类沉积模式。到20世纪70年代,许靖华先生提出经典的地中海干化理论,掀起Messinian盐度危机大讨论[7,9-10],提出了地中海干化的概念以及深水深盆、浅水深盆和浅水浅盆三种不同的环境模式解释蒸发岩的成因,欧洲为此专门组建了DREAM计划(Deep-sea Record Mediterranean Messinian Events,地中海Messinian事件的深海记录)[11-13],还有从Kendall的相模式[14]到Warren的系列蒸发岩专门著作[1,15]。此外根据蒸发岩沉积特征的差异,很多国外学者进行了详细的分类研究,如原生、次生蒸发岩的改造与环境[16-18];还有结核状、带状、纹层状等的形态演化与环境的研究等[19-26]。这些蒸发岩沉积特征和沉积环境研究,不断推动蒸发岩沉积学在古气候、古水文、生物地球化学作用、油气及蒸发矿产方面的应用。
蒸发岩在我国广泛发育,地理上东到渤海湾盆地,西抵羌塘盆地和塔里木盆地,北至鄂尔多斯盆地,南到四川和兰坪—思茅盆地,时代从震旦纪跨越到第四纪[27],这是研究蒸发岩沉积特征和沉积环境的良好天然素材。与其他典型沉积岩不同,蒸发岩在传统沉积学分类中被归为“化学沉积岩类”,国内阐述蒸发岩的专著较少,仅见于袁见齐先生的多本沉积著作中,如《西北盐产调查实录》、《钾盐专辑 第1辑》和《钾肥与钾盐矿床》等[28-30],但距今较久;而国内沉积学教材仅把它作为一个分支来简单叙述,着墨不多。最重要的一点是,国内的相关研究散见于部分地区的实例研究,还没有系统性的总结。国内油气工业上虽然重视蒸发岩,但大都称蒸发岩为“膏盐岩”,但具体是石膏还是石盐并未仔细区分。因此,尽管蒸发岩作为一种重要的沉积岩类型,但并未在国内得到足够重视。鉴于此,本文运用Miall[31]的构架单元理论,详细总结了蒸发岩与沉积相的关系。首先从主要和最小的岩相成分进行分析,包括岩性(盐类)、结构和构造,其次解释最小岩相的水动力和沉积环境,最后通过岩相的划分确定基本的岩相组合来综合解释沉积环境。文章系统概括常见碳酸型、硫酸型、氯化物型蒸发岩的岩相和岩相组合对应的蒸发环境,抛砖引玉,以期引起国内同行对蒸发岩沉积特征和环境解释的重视。
-
常见的碳酸型蒸发盐矿物有文石(CaCO3),方解石(CaCO3),低镁方解石与高镁方解石((MgxCa1-x)CO3),白云石(Ca(1+x)Mg(1-x)(CO3)2),菱镁矿(MgCO3),苏打(Na2CO3·10H2O)、天然碱(NaHCO3·Na2CO32H2O)等。
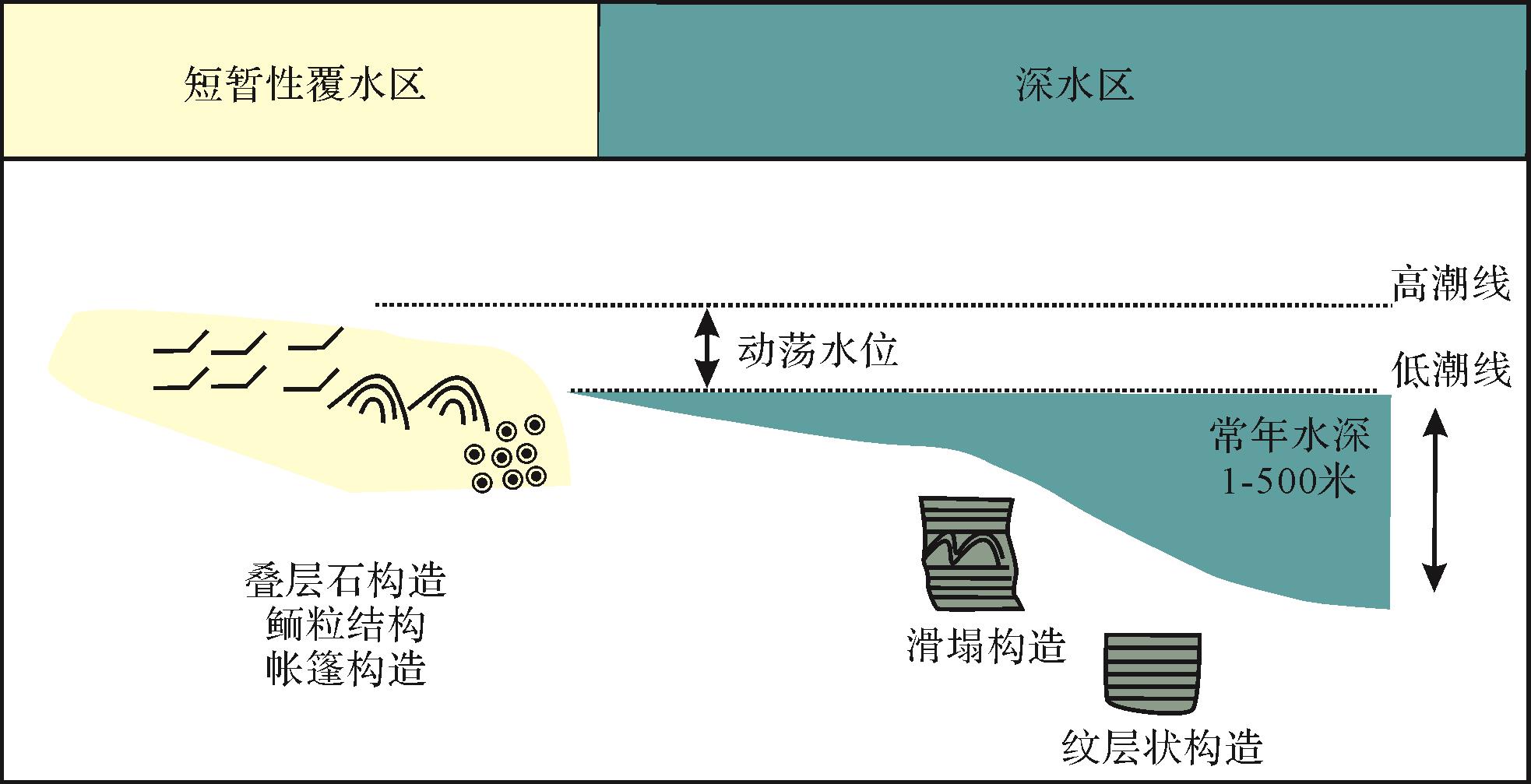
碳酸盐岩结构与环境动力条件、水深、沉积位置等密切相关(图1)。许多蒸发碳酸盐体系的滨岸带中的特征是叠层石、泥裂隐藻纹层(生物纹层)、豆粒、鲕粒、内碎屑、胶结结壳和帐篷构造的沉积组合[1](图2)。除了灰岩,白云岩也是地质历史时期广泛分布的常见蒸发碳酸盐岩,但是目前对白云岩的成因模式仍然争论不休。大多数学者认为白云石是交代成因并提出了很多白云岩化模式,明显发育在蒸发背景下的白云岩沉积模式有回流渗透和蒸发泵吸模式[53-59],这两种模式的核心都是蒸发导致盐度增高,高盐度卤水交代早期方解石形成白云石,所以本文仅对这两种蒸发模式沉积下的白云岩以其对应岩相进行详细描述(图3)。此外,我们对少量的菱镁矿,苏打和天然碱岩也做了岩相分析(图4)。

图 2 蒸发灰岩岩相与沉积环境解释
Figure 2. Evaporative limestone lithofacies and interpretation of sedimentary environment
-
中粒碳酸盐叠层石(Smc):中等大小的文石和镁方解石固结组成鲕粒和骨架砂,它们堆积聚集形成叠层石。沉积于潮间带和浅潮下的高能和强潮流的蒸发环境,可见于巴哈马群岛等地[32-33]。
粗粒碳酸盐叠层石(Scc):粗颗粒文石和镁方解石组成骨架砂堆积成叠层石。形成于中盐度海水、潮下和潮间蒸发带,偶尔暴露于高波能量下[34-36]。
含生物侵蚀纹层的叠层石灰岩(Slb):表现为层状、球状和细圆齿状叠层石构造,细圆齿是生物侵蚀导致的,主要由水镁石、文石组成。分布于沿海地区,高盐度和中盐度的大陆碳酸盐盐沼滨湖区[37-38]。
凝块叠层石(Ctc):文石和镁方解石矿物形成的孤立圆丘叠层石。这些圆丘的表面有不规则(“结节”)小突起。内部是无结构或粗糙的带状。沉积于波浪活动和水循环强烈的浅水、近岸区域的滨湖[39-41]。可见于美国犹他州大盐湖边缘,大的凝块叠层石代表暴露蒸发的环境。
丘形叠层石(Scd):圆丘形短柱状叠层石,内部为层状文石泥。沉积于碱性,中等盐度湖泊,滨湖剧烈暴露蒸发环境[42]。
树枝状凝块丘灰岩(Cmt):沉积于高碱性浅湖到深湖环境,矿物为方解石,表现为类似于植物树枝状结构。形态随深度而变化,在深水丘中发育最好的树枝状微结构[43]。
球粒灰岩(Cp):球粒生长在潮上带高盐环境中,不需要波浪搅动来沉淀同心层状颗粒。蒸发环境下窗格泥灰岩的强烈原位高盐蚀变也可形成球粒状颗粒[1,44-45]。
鲕粒灰岩(Co):高盐度环境下鲕粒呈现放射状,最初为文石沉积,沉积于高盐度沿岸蒸发滨浅湖环境[46-48]或低能高盐度潟湖环境[49-50],可见犹他州大盐湖的鲕粒沙坝。
帐篷构造灰岩(Ct):石灰岩壳或白云石壳常发育倒“V”形的帐篷构造。这些含有豆粒和窗格构造白云石或者文石胶结结壳沉积于潮间带到萨布哈的蒸发环境[1,51]。
纹层灰岩(Cl):代表季节性的纹层明暗交替,白色纹层是星状文石簇组成,文石簇形成于夏季的空气—盐水交界处,然后下沉沉积于深湖区。暗层由黏土、石英、碎屑方解石和方解石组成,代表了偶尔风暴期的洪水事件[52]。
-
蒸发环境常见两种成因模式白云岩化,第一种回流渗透模式首先由Adams et al.[83]提出,用以解释局限台地上由于蒸发作用产生盐度差发生卤水回流而形成的白云岩。由于蒸发作用,海水盐度升高,达到石膏过饱和程度;其后高Mg/Ca值的卤水由于存在盐度梯度向下流到台地或向海流经沉积物从而导致白云岩化的发生。第二种蒸发泵吸白云岩模式由Shinn et al.[84]提出,此后通过对巴哈马潮上带,波斯湾萨布哈等地的白云岩研究,得出白云石化的毛细管作用—蒸发泵吸作用的结论[85]。孔隙中咸水通过蒸发作用毛细管力经过海岸沉积物直接向上移动到空气界面进行蒸发作用,在这个过程中不断浓缩形成超咸水,从而沉积白云岩。因此,不同的成因形成的白云石晶体和沉积岩具有不同的特征(图3)。
层状白云岩(Dl):纹层—中层状,泥晶结构,晶体细小自行程度差。伴有少量细粉砂、生物碎屑和黄铁矿微晶等。回流渗透和蒸发泵吸都可以形成,常出现在低能盐沼、潮坪、盐水湖低洼地和萨布哈等地[60-62]。
颗粒状白云岩(Dg):层状或块状。颗粒为鲕粒/生屑。鲕粒以表皮鲕为主,被泥晶白云石呈组构交代。大部分生物碎屑也被白云石化显泥晶结构,有生物扰动构造出现。常出现低到中等环境动力条件下,在潮间—潮下带颗粒滩环境由盐水回流交代形成[60,63]。
藻纹层白云岩(Dal):白云石为粉晶结构,宏观上岩石呈明暗相间纹层状构造,亮色条带由粉晶白云岩组成,暗色条纹由粉晶白云岩和填充了藻类生物的残余结构的有机质晶间孔组成[64],并且保存原生的叠层构造。常出现在高能蒸发潮坪环境中[65]。
竹叶状白云岩(De):原生沉积的竹叶状内碎屑由粉晶白云石组成,并被同期白云石原地胶结成岩。岩溶作用产生了大量的溶蚀孔,胶结物发生了重结晶,常常沉积于高能蒸发潮坪环境[65]。
叠层石白云岩(Ds):层状白云石组合成柱状叠层石构造;极度干燥条件下部分发育帐篷构造和龟裂,同时沉积与帐篷构造相关的岩溶角砾岩。形成于浅水、低能、潮间带、有障壁蒸发潟湖和潮缘蒸发环境[63-67]。
结晶白云岩(Dc):结晶白云石组成无结构、不清晰的平行纹层白云岩,存在龟裂、帐篷构造和白云石假变形石膏,常见于潮坪上部蒸发环境和局限潟湖[66-68]。
-
块状/层状菱镁矿(Mm/Mlb):泥晶—粗晶结构,有块状、层状构造或叠层构造。沉积于大陆盐沼和海相萨布哈环境[66]。
透镜状菱镁矿(Ml):厚的砂糖状到粗粒亮晶的菱镁矿组成较纯净的菱镁矿岩,呈透镜体或不规则状[69],盐岩内有斜层理、结核状、波痕等构造[70],沉积特征与原始边缘海相沉积有关[1]。常见潮坪—潟湖环境,如辽宁早元古代大石桥组沉积菱镁矿。
水菱镁矿和文石交互层(Aha):水菱镁矿和文石颗粒较粗,它们以松散堆积形式成纹层、细纹层状;随水深加大水菱镁矿减少。沉积在浅水滨湖,有大陆卤水补充的环境下,可见于南澳大利亚Coroog湖周围的碱性湖泊[1,71]。
叠层石水菱镁矿(Hs):主要出现在近海滨湖/滨湖地带,可以在成岩过程中交代文石叠层石形成[72],或者在微生物作用下直接沉淀成数米高的原生水菱镁矿叠层石[73]。
层状天然碱(Tb):天然碱矿物以分选良好的微晶针状结构出现,堆积在分层的常年高盐度碱性盐湖中[74],形成中厚层的盐岩[75],常见于滨湖蒸发非海相环境[76]。
草状天然碱(Tgl):天然碱晶体呈垂直方向生长,截面呈草状/扇状[77]。类似于蒸发环境中垂直生长方向的石膏,沉积于一个周期性干燥的盐湖的滨湖环境,水深不超过几厘米[78]。
块状天然碱(Tm):整体为大厚块状,层理发育较差,内部由毫米级无定向天然碱晶体组成,少有其他碎屑沉积物[77]。水下形成并沉积于浅碱性湖[79]。
放射状棱柱体天然碱(Trp):切面方向上表现为毫米—厘米大小的叶片状天然碱晶体,叶片晶体集合呈放射状,块状构造[77]。
无定向构造天然碱(Tu):由散布在松散泥质沉积物中的毫米—厘米大小的天然碱晶体组成,成束排列成集合体。块状构造。放射棱柱体状天然碱和无定向构造天然碱是在干涸阶段干盐湖环境形成,或是在一个短暂周期性干燥的滨湖环境形成的[77]。
天然碱—白云岩互层(Atd):层状,灰色—灰黑色的白云岩与褐色,白色的天然碱互层,白云岩的有机质含量较高,因此也常常与油页岩互层,发育水平层理和小波状层理。常见碱性盐湖的半深湖和深湖环境,水体深度随季节波动[80]。
油页岩—盐碱矿—泥质白云岩韵律岩(Rsad):盐岩矿石为白色或灰绿色,块状构造,主要矿物成分为Na2CO3和NaCl。在盐岩中杂乱分布有针状、板条状天然碱。盐碱矿层内又由卤泥岩—碱—盐—碱—卤泥岩组成次一级的厚层状韵律,油页岩也是厚层状,见水平层理。常见于炎热干湿交替气候下的碱性浅湖静水环境[81]。
层状苏打石(Nl):层状苏打石由微晶苏打棱柱体堆积组成,覆盖下伏的结晶石盐壳和作为粒序浊积岩/块体流沉积的碎屑状苏打石[74],常见于滨湖蒸发环境。
块状苏打石(Nm):白色透明块状苏打石集合体,含有天然碱次生变化形成的白云石固体包裹体[77]。沉积在碱性水体的空气—水体界面上[82],然后下沉。
-
常见的硫酸型蒸发矿物很多,如石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)、硬石膏(CaSO4)、钙芒硝(Na2SO4·CaSO4)、芒硝(Na2SO4·10H2O)、硫酸镁石(MgSO4·H2O)等。仅就常见的石膏、硬石膏、钙芒硝和芒硝岩相进行描述。
石膏岩的结构与水动力、水深、沉积位置等密切相关(图5)。因此根据不同环境不同成因,可以分为原生和次生石膏(图6),次生石膏可以由硬石膏水化,其他含Ca和SO4的硫酸盐复盐(特别是钙芒硝),经水化作用形成。在萨布哈、盐沼、盐泥坪等环境中,由于盐水的波动与补充,经常出现石膏和硬石膏同时存在或者硬石膏水化为石膏的现象(图7),此外沉积岩剥露和现代地下水循环过程中的后期成岩作用和再水化也可以形成次生石膏[87]。
-
以含石膏矿床的形态、结构特征和成岩阶段(原生/次生)作为划分岩相的标准。
透镜状、球状交替薄层石膏(Glp):小的透镜状石膏和球状石膏层呈毫米级韵律交替。内含化石,局部有水流痕迹存在,化石和水流波痕表明小的透镜状石膏薄层在湖水稀释期形成,沉积于深湖环境[86]。
凝块状石膏(Gc):有薄层和厚块状结构,薄层凝块状石膏层显示不规则的、团块状的内部结构,如孔状、小结核或破碎变形的内碎屑结构。团块中常存在大石膏晶体围绕着小的晶体核,出现在浅湖环境[86]。大块凝块状石膏由固结的石膏形成块状,没有中间叠层。固结的石膏形状有半球形、小结核状,出现在浅湖环境但比薄层凝块状石膏沉积水浅[86]。
波状或韵律条带状石膏(Gr):由层状白云质石膏组成,具波状或韵律条带构造,泥晶白云岩与石膏条带构成厘米级韵律。石膏条带占主体,条带平行且连续。这种类型的白云质石膏岩与深灰色硅质白云岩或泥晶白云岩一起,产于海相局限台地相潮间坪亚相[88]。
鲕状石膏(Go):鲕粒核心石膏矿物呈现放射状,没有同心纹层。沉积于盐碱地或湖泊低能区如滨湖带[89-90]。
透明块状石膏(Gm):块状结构,较纯的白色到透明无色。形成于硫酸钙盐成盐鼎盛期,如咸化泥坪、干化泥坪和干盐湖阶段[91]。
底部生长石膏(Gbg):由垂直/近垂直的棱柱状或燕尾形晶体构成石膏层或波状石膏层,晶体镶嵌连接表现出示顶底结构。在暴露环境下可以脱水形成镶嵌状硬石膏,沉积于水下盐沼环境[92]。
纵向排列的规则透石膏(Sva):透石膏层中厚层,晶体呈燕尾双晶对齐然后纵向排列组成整齐的晶面[93]。发育在局限的潟湖盆地潮间带,代表了典型的浅水水底成核相[15,94-95]。
叠层状透石膏(Gss):由镶嵌的无定向粗晶组成,局部存在波状透镜状石膏晶体层,又称叠层状透石膏。在一些孔隙中,石膏晶体被拉长呈近垂直排列。晶体沿着不规则的生长带生长垂向上规则排列的透石膏。它与纵向排列的规则透石膏的环境条件没有显著差异,即潮间带或等深水体[93]。
厚块状/带状交替透石膏(Sm/Sag):厚层或块状结构,没有夹层。主要由密集堆积的晶体组成,栅栏结构发育。此外还可以与薄的、波状的、变形的薄层层状石膏交替沉积,它们偶尔与砂屑石膏基质混合。沉积于高度蒸发的条件下,如几米深的潮上带剧烈蒸发环境[95-96]。
弯刀形透石膏(Ssl):厚层状,由像弯刀一样的弯曲透石膏晶体组成;晶体生长方向较一致。常出现在浅水内台地潟湖(盐湖)[97],水深仅几米[98]。
骨架状透石膏(Ss):透石膏晶体在泥晶石膏基质中不定向生长,堆积成中厚层。横向变化为层状石膏和叠层石石膏,常见于几米深、高盐度且密度跃层频繁波动的内台地潟湖(盐湖)[97-98]。
生物扰动层状石膏(Gbl):薄层到中厚层状微晶或细粒石膏岩,含有生物扰动构造,这些扰动的大小不一的孔穴充填他形石膏胶结物,沉积于滨湖沼泽—浅湖环境[20,86]。
石膏浊积岩/石膏角砾岩(Gt/Gb):属于石膏层内变形,中厚层状石膏发生软沉积变形形成浊积岩和石膏角砾,浊积构造表现为石膏薄层的不连续、波状、扭曲和肠状结构,或者层内微滑塌/破裂,以及层内角砾岩堆积等变形结构。重力流成因,常见于中部湖区的浅湖斜坡到深湖[86]或深海半深海斜坡带[22]。
叠层石石膏(Gs):石膏和微生物席共存,可在很浅的盐水中发育成叠层石石膏圆丘[99],沉积于潮上带泥坪、萨布哈[100]。可见于红海沿岸。
“残影”石膏(Gg):很多古代硬石膏都由次生结构组成,但是仍然被残留的原始石膏结构或部分原始残余物称为“残影”,如生长整齐石膏后的不清晰的纹层、整齐结核和燕尾晶体的残影等[1,92]。这些残影结构表明了过饱和盐水足够浅以至于可以接触盆地底部沉积物[101],或者是上层淡水剧烈蒸发的同时整段盐水柱不断下沉接触盆地底部沉积物[1]。
泥质结构石膏土(GSm):按照石膏颗粒的大小可以分为石膏土、石膏砂和透石膏[102]。石膏土为泥质结构,超过一半的颗粒直径小于1/16 mm且大小分布较均匀,常见生物和植物扰动,中厚层状。在薄片中,石膏土是一种白色的、毡状的、囊状的小石膏晶体。肉眼观察石膏土呈白色或褐色,触摸有像滑石一样的细腻触感。在沿海萨布哈或大陆盐沼边缘坪中,石膏土在植被发育的新月形石膏砂丘上沉积,但在大陆盐沼中更为常见[103]。
X型层理石膏砂(GSx):石膏砂至少由一半以上的砂状石膏颗粒组成,中粗粒、分选好的石膏砂在盐沼边缘堆积形成新月形的石膏沙丘,暴露地表的石膏砂在风的作用下内部可形成X型层理构造,厚层状[1]。既存在于沿海的萨布哈,也存在于大陆盐沼。石膏颗粒是原生自形的,针状的,也有成对的石膏棱柱体[103]。
微结核石膏(Gmn):多晶微结核直径毫米级别,显示了硬石膏晶体的残余痕迹,和灰泥结构类似。脱水可以形成镶嵌状石膏(硬石膏),常见于盐沼和盐泥坪过渡的蒸发环境(相当于萨布哈环境)[92]。
纹层—条带状硬石膏(Alb):由薄层或条带状构造的细粒硬石膏组成,碳酸盐含量少。局部观察到类似于内碎屑或微结核的小颗粒。在显微镜下,这些硬石膏颗粒大多是石膏晶体假象。常见于潮上带,萨布哈环境[104]。
交替层状碳酸盐—硬石膏岩(Aab):由硬石膏薄层和碳酸盐层的不规则交替组成,存在硬石膏假晶。局部出现薄层碎屑支撑夹层,底部不规则或侵蚀特征。常见于潮间带或潮下带环境[104]。
不规则层状(圆齿状)硬石膏(Ai/Ac):由透石膏次生而来。厚层状,在这些岩相内形成常见夹层和角砾,存在假晶。常见浅水台地环境[105]。
块状硬石膏(Am):是一种硬石膏晶体分布均匀的岩石,但是含有原始层理的残余物如黏土、碳酸盐、沥青和有机物,还存在透石膏假晶[106],常见浅水台地环境[105]。
结核状石膏/硬石膏(Gn/An):结核状可以细分为结核状、结核—镶嵌状和镶嵌状[100],硬石膏可能是石膏脱水形成的[92],因此它们可以同时存在。1)结核状可以称为鸡笼铁丝状,结核呈椭圆形、球形或者拉长的肠状,当它们彼此接触时,就形成一个类似铁丝网的图案[107-108],拉长或肠状的硬石膏结核可能来源于石膏;鸡笼状描述的是硬石膏或石膏的多边形结核,由其他矿物(黏土或碳酸盐)的深色细脉分隔开[109]。2)结核—镶嵌状或镶嵌状表现为厚层状岩,石膏或硬石膏的结核沉积在含硅酸盐—碳酸盐—硫酸盐混合基质中,呈镶嵌结构[100]。镶嵌结构可能是由细小的石膏形成的,也可能是由成岩改造胶结物形成的[110]。沉积于海相萨布哈、大陆盐沼和浅水台地[105,111]。
微结核状硬石膏(Amn):微小的结核状(珍珠状)硬石膏薄层,会发育成细的层状/肠状结构,与不规则的(齿状)黏土质沥青薄层交替出现。这些微结节与生长在底部成层沉积物中的置换硬石膏的同沉积时期的孔隙生长有关[105]。该岩相有再沉积的特征,沉积于深海环境[100]。
肠状褶皱石膏(Gef):石膏层弯曲并成肠状,这可能与藻类微生物有关。微生物席暴露于卤水浓缩—稀释循环的变化环境,同时伴随强风的作用,强风吹拂使微生物席的堆积,微生物席在随后的蒸发中暴露在地面并与石膏一同岩化[112]。沉积于海相潮间带或者潮下带浅水区[91,94],并受到强风和卤水浓缩—稀释循环的影响[112]。
“远洋”层状硬石膏(Apl):往往沉积在远离蒸发岩台地的盆地中心,砂质和粉砂质硬石膏晶体在空气—卤水界面形成然后下沉,以“盐雨”形式向下形成非常规则的薄层,堆积于深部盆地[1],层内发育水平层理、包卷层理、粒序层理和浊积序列等[100],与方解石纹层/白云石/黏土交替连续沉积[100,113]。常见于半深湖—深湖[1,113]和台地外侧的深水斜坡或者深水盆地[105,114]。
交替纹层石盐—石膏(Has):晶体生长在一个静止的盐水体的最上部,在那里水分被迅速蒸发流失,盐度达到最高值,然后粉砂和沙粒大小的晶体沉降到盐水底部,形成累积成毫米级薄层。这种“盐雨”纹层岩通常由碳酸盐—硫酸盐/硫酸盐—石盐交替组合而成[1,115]。
薄层次生石膏(SGl):石膏晶体由硬石膏次生而成,没有明显的水流和波纹等机械再作用,表现为水平的薄层带状,晶体表现为大小相似的细粒状,或呈圆形及渐变状晶,岩层颜色从白灰色变化褐色[116],沉积于海相萨布哈环境[23]。
纤维状/棱形柱状石膏(Gf/Gp):由垂直生长的石膏晶体和缝隙充填的纤维状石膏晶体组成。纤维状/棱柱状石膏构成的石膏沉积存在燕尾石膏和硬石膏的残迹和残影,而裂缝充填的纤维石膏没有硬石膏存在,充填的晶体尺寸从边缘到中心不断减小,通常长轴方向垂直于裂缝。可以由底部生长石膏脱水演化形成,常见于浅水盐沼环境[92]。
结核—纹层状石膏(Gnl):这是陆相环境[117]最常见的次生石膏岩相,石膏薄层(白色)有非常规整的边界,薄层之间有结核[23]。这种结构由石膏层和石膏结核不规则的交替组成,表明浅水和陆上环境交替的变化[118-119]。
次生结核状石膏(SGn):可以由硬石膏和钙芒硝次生形成。结核聚合可形成结核带,这些带底部起伏不平[1]。有时结核状次生石膏伴有相关的光滑石膏脉,部分为斑状次生石膏[120]。沉积于海相萨布哈或者干盐湖盆地[20,107,121]。
粗晶质次生石膏(SGm):由微晶晶体和巨晶组成,或由斑状变晶石膏晶体组成[20,122]。常出现在干涸盐沼环境。
带状光滑次生石膏(SGa):由钙芒硝转化而来的次生石膏,存在大量钙芒硝的宏观假晶以及次生变化的微观结构,例如网状结构和针状结构[123]。露头上表现为带状、结核带状等,沉积于干盐湖盆地[20]。Bąbel认为带状透石膏岩相可能标志着在蒸发岩周期沉积中达到最干旱时期[124]。
-
钙芒硝(Na2Ca(SO4)2)是陆相盐湖中常见的暖相矿物。钙芒硝是原生的还是成岩过程中次生的,仍然是一个有争议的问题[20,125]。许多现代和古代硫酸钠型矿床的研究表明钙芒硝主要是盐滩环境中的成岩次生矿物[126],如交代石膏次生成因或水钙芒硝脱水而成[127]。此外也有研究表明,钙芒硝层有原生成因[125,127-128]。然而,目前对这种原生成因的描述并不多,钙芒硝的次生成因解释仍占主导地位[129]。芒硝(Na2SO4·10H2O)是典型的冷相矿物,常见于钙芒硝沉积后期温度下降的阶段[130]。钙芒硝和芒硝都是盐湖沉积后期常见的蒸发盐矿物。总之,这两种矿物都是盐湖沉积后期常见的蒸发盐矿物(图8)。

图 8 钙芒硝、芒硝岩相与沉积环境解释
Figure 8. Glauberite and mirabilite lithofacies and interpretation of sedimentary environment
层状/薄层钙芒硝岩(GLb)有两种形式:1)污浊的钙芒硝层,由于富含基质显得污浊,纹层—薄层结构,晶体具有均匀的菱形面并含有大量小的固体包裹体。存在明显的正粒序结构,但是缺少水流等介质搬运的证据。沉积在水底沉积物与水的界面附近,滨浅盐湖环境。2)透明干净的钙芒硝层,它们是细粒到中粒的,基质较少,由干净的石盐胶结成层,钙芒硝晶体具有干净明亮的自形结构或为细长板状镶嵌在一起,正逆粒序都常见。晶体沉积在盐水团内或气—水界面处,最后下沉成岩。常见于滨湖环境[125,128-129]。此外,沉积温度、湖盆构造和钙芒硝晶体形状密切相关。赵海彤等[131]通过研究罗布泊干盐湖巨厚钙芒硝层,认为污浊的菱形钙芒硝晶体可能属于浅水稍高温区的卤水中速结晶生长的结果,较洁净的长板状晶体可能属于湖盆深水稍低温区缓慢结晶生长的产物。
巨型结晶透明钙芒硝岩(GLc-Ⅰ):这种岩相由薄和厚的透明钙芒硝层组成。粗晶,晶形从等长到细长状,逆粒序结构。所有这些钙芒硝结构都由干净的石盐胶结,局部存在泥质基质。常见于水下滨湖环境[129]。
扭曲状钙芒硝岩(Glc-Ⅱ):定义为扭曲、褶皱状结构的钙芒硝岩,这些扭曲的结构是由于钙芒硝层的晶体、碎片和基质的含量的机械再分布引起的[20,125,132]。此外新生透明钙芒硝晶体随着变形同步世代生长,最晚的世代变成透明的石盐胶结。常见于毗邻盐湖的盐泥坪渗透带[132]。
层状芒硝岩(Ml):芒硝成薄层或厚层分布。呈中粗晶他形到自形、短柱状到粒状。芒硝是典型的冷相矿物,可以形成于钙芒硝沉积后期的较冷气候期[130,133],沉积在干盐湖环境。
-
海成氯化物岩基本上为海退期成盐,在现代盐湖中,氯化物岩是湖水水体高度萎缩和高度浓缩的结果[134-137]。它们沉积于封闭、半封闭的盐湖环境,盐湖根据原始沉积水体性质有陆相盐湖和蒸发海相盐湖之分。常见的氯化物型蒸发岩有石盐(NaCl)、钾石盐(KCl)、 光卤石岩(MgCl2 KCl·6H2O)等,本章重点叙述石盐结构与构造。
石盐结构与环境动力条件、水深、沉积位置等密切相关。在水侵、蒸发浓缩和干燥阶段,石盐可以发生不同的原生、次生变化(图9)。石盐壳中的晶体首先以向上生长的V形、立方体和角形晶体的形式沉淀在浅的高盐卤水的表层。保存了连续晶体生长边缘轮廓的V形结构被一层封闭的盐水包裹体所破坏,在古代石盐中保存的最常见的原始纹理是对齐的V字形残迹。丰富的包裹体使富含V形晶体的岩层呈现浑浊或乳白色外观。这一特征也可以在古代沉积物中用于区分原生石盐和次生或成岩石盐。富含乳白色包裹体的晶体可以累积为连续的生长排列棱柱层,也可以形成共轴过度生长晶和形成其他沉积到盐沼底部堆积成晶体层[1]。
根据石盐的形态、结构特征和成岩阶段(原生/次生)总结了13种典型的石盐岩相(图10)。
V字形晶底部成核层石盐岩(Hc):V字形又叫人字形。V形晶体的岩层常含有快速沉积时捕获的流体包裹体[96],呈现浑浊或乳白色外观。人字晶一般形成于浅水环境,在底部向上生长的底部成核结构[138]。沉淀石盐的盐水层深度小于几米,通常小于0.5 m[139],滨湖环境或者海洋萨布哈、潮上带环境。
漏斗形晶底部成核层石盐岩(Hh):是另一种由底部向上生长聚集而成的结构,底部由下沉的晶筏向上的过度生长形成的漏斗聚合体,漏斗晶和人字晶在同一层位同时出现时,指示了石盐沉积时是浅水环境且没有化学分层[140-141],在老挝他曲地区就出现石盐的漏斗晶和人字晶同时沉积的现象,表明极浅水的环境[142],其水体深度通常不超过60 cm[138,141],湖海可沉积,常见滨湖、潮上带或海相萨布哈环境。
晶筏石盐堆晶(Hr):石盐晶筏生长于气液界面[143-144],下沉到水底成为晶体堆积层[1]。或者在非常浅到短暂的卤水沼泽中的石盐筏和其他堆积晶体可能被风吹沿着湖面到岸带中,或被底部水流携带到岸带中以及障碍物处,聚集为陆上暴露的沿岸带的堆晶和在障碍物的前面形成盐堆[99],后期被盐类胶结[145-147]。
波纹碎屑石盐岩(Hrc):古堆积层晶体层在没有迅速被底部有核结壳覆盖时,有时会被风暴和波浪引起的底部洋流机械地改造成交叉层和波纹,甚至碎屑石盐[99]。显微镜下,碎屑岩盐由分选较差的细砂、粉砂至粗砂大小、多种形状晶体颗粒以及到砾石级的盐岩碎片组成。常见于在顺风方向的潮上带浅水区[99]。
鲕粒石盐(Ho):鲕粒由粗晶石盐核和放射状结构的石盐同心纹层组成[148]。这种包壳颗粒结构可见于非洲裂谷Asal湖沿岸带、土耳其的Tuz Golu以及死海的南端[148-149]。沉积于较浅的高能水动力近岸位置。
帐篷构造石盐(Hpt):干燥石盐壳暴晒干裂形成龟裂构造,垂向上表现为“帐篷”构造[99]。此类石盐岩相常见于干盐湖环境。
鱼骨状底部成核层石盐岩(Hfb):人字形晶体顶部被溶蚀,从而留下溶解缝或者 “鱼骨头”外形。这种鱼骨头样式可能反映了淡水沿石盐晶体生长边的选择性溶蚀作用[150],是淡水作用影响生成的次生底部成核石盐,可以在洪水期淡水作用或者干涸期大气淡水和低盐度地下水影响。
喀斯特溶洞/微喀斯特洞状充填石盐(Hk):宏观喀斯特表现为楔形凹坑,溶解呈垂直圆柱形。微观喀斯特溶解形状像一个不规则的立方体,有垂直溶蚀坑和裂缝,原生结构被粗粒的、清澈的石盐胶结物取代[146]或者通常充满自形石盐和灰色泥浆的混合物,原始水平分层的痕迹已经消失。与低盐度地下水影响有关[99,151]。
增生的石盐胶结物(Hog):在洪水期部分溶解的V形和多边形石盐晶体可能同向过度生长,形成干净的石盐胶结物。胶结物通常与原始V形和多边形晶体呈渐变、波状接触。这与地下卤水的作用有关[99]。
钟乳石状石盐岩(Hs):宏观上表现为柱状钟乳石,晶体通常形成于表面石盐壳的裂缝中,并作为钟乳石石盐形成于帐篷构造岩脊下方。这也是地下水或大气淡水的作用形成[99]。
层状透明石盐岩(Hbc):这种岩相是由透明的无包裹体晶体构成的[129]。透明石盐结构可能是由于洪水期间原生含包裹体浑浊石盐的溶解,随后在层或岩洞中的再沉淀造成的[143]。
交替纹层石盐—钾石盐(Sah):由互层的薄层条带状石盐和薄层钾石盐交替组成,钾石盐为主[152]。沉积于蒸发盐湖环境[153],可见于西班牙始新世埃布罗海相蒸发钾盐矿和柴达木马海盐湖钾矿床。
-
沉积环境的改变(如水体深度变化、盐度变化和构造运动等),可导致不止单一蒸发岩类出现,因此下文详细讨论常见的混合沉积蒸发岩与岩相(图11)。

图 11 混合蒸发岩岩相与沉积环境解释
Figure 11. Mixed evaporite lithofacies and interpretation of sedimentary environment
含石膏白云岩(DG):石膏和硬石膏以斑块状或矿物颗粒分散在较致密和均匀的缺乏原始颗粒结构或生物结构的泥晶/微晶白云岩中,白云岩是蒸发泵吸或回流渗透形成的。随着蒸发的加剧可以演化成白云质石膏岩,常见于萨布哈、蒸发潮上—潮间坪和局限蒸发台地环境[66,154]。
含石膏的杂乱沉积(GDc):由透石膏/石膏质粉砂岩、泥岩等混合沉积形成。存在侵蚀表面和内碎屑等河流的机械作用构造。常见于台地边缘的滨岸环境[155]。
硬石膏角砾岩(Ab):夹杂在碳酸盐和硫酸盐基质的厚层和不规则的盐岩薄层中,含有硬石膏、白云岩、泥岩、泥质黏土等内碎屑。内碎屑呈棱角或圆形,角砾呈变形构造并有液化构造[100,114],重力流成因。常见于台地外侧、斜坡和盆地内[105]。
石膏砂屑/砾屑岩(Ga/Gr):又叫层状碎屑石膏;碎屑石膏层为中厚层或厚块状,形状不规则,由分选性差的棱角状石膏砂屑或砾屑组成,含有破碎的透石膏晶体、双晶板状石膏晶体和生物壳等碳酸盐。存在水流波浪面、槽状交错层理和粒序层理,生物扰动和泥裂等构造。重力流或块体流成因,沉积于盆地边缘斜坡[23,120],较深水环境。
巨角砾石膏岩(Gmb):巨角砾岩由巨大的石膏块和较小的块状砂岩和碳酸盐岩组成。常见于深水斜坡带[156],构造作用或重力流成因。
石膏滑动岩体(GO):由米到数十米的石膏块体层和黏土岩、砂岩、泥灰岩夹杂在一起,常见软沉积变形构造。常见于深水斜坡带[1,155-156]。
碎屑状钙芒硝岩(GLc-Ⅲ):晶体呈细至中粒分散在碳酸盐基质中。晶体结构近平行至平行,与石盐互层,其中石盐被钙芒硝晶体所取代保存为石盐假晶。这种岩相被认为是洪水沉积成因,起源于径流期的原始钙芒硝再作用,常见滨湖—浅湖环境[125,129]。
块状钙芒硝岩(GLm):块状结构,含有大量泥质基质、钙芒硝内部无结构。晶体中—粗粒,呈等长到细长的菱形。局部可见大团簇状、结节或不规则团块,内部有透明的石盐胶结物,常见透明立方石盐晶体。常见于毛细管作用的盐泥坪地带和水下滨湖地带[129]。
透镜状/团块状天然碱(Tl):天然碱呈团块、透镜体状发育在油页岩、白云岩内,向上可沉积厚的层状纯天然碱岩。常见炎热干湿交替气候下的碱性湖的浅湖静水环境中[84]。
芒硝岩或含芒硝岩组(MA):含有芒硝、钙芒硝、石膏、粉砂和黏土等,混合沉积在一起。随着含量变化可以变化为含石膏粉砂岩、砂质钙芒硝、芒硝岩,含芒硝粉砂岩或粉砂岩等。芒硝呈褐色,细到粗晶,常见盐湖沉积末期沉积环境,上覆地层常见干盐湖沉积岩。碎屑或石膏沉积出现在盐湖稀释阶段[130]。
盐扰动结构石盐岩(Hht):由有孔虫、碎屑石膏、泥粒和砂粒组成的地下沉积物被包裹进石盐壳中并胶结。这一过程破坏了岩盐外壳和下伏沉积物之间的接触和原始沉积物的结构,形成多变的盐扰动结构。常见于干盐湖边缘,受地下卤水影响[99]。
光卤石角砾(Db):钾石盐胶结的光卤石角砾碎屑混积或呈条带状光卤石和石盐、泥岩层和少量钾石盐互层沉积。常见于海相萨布哈,代表最大浓缩阶段[152,157]。
含杂卤石块状石盐砂(Hm):石盐细晶块状构造,受风吹和降水影响,结构比较松软潮湿,含有杂卤石。常见于干盐湖陆相沉积环境[130]。
含杂卤石层状石膏(PG):层状石膏沉积由于浓缩海水的渗流导致石膏晶体被杂卤石替换,是早期成岩作用的产物。见与近海萨布哈沉积环境[158-159]。
-
通过沉积结构与构造来推断沉积环境是沉积学中的一种方法[160]。研究表明,不同蒸发岩相的蒸发盐类型多样,产状,沉积构造复杂多变,此外还有不同的盐类矿物组合沉积出现,因此不同的盐类构造和类型往往代表着不同的沉积环境和沉积相,可以作为沉积相和环境划分的重要标志。不同环境中可能有相同的蒸发矿物和结构,如纹层状石膏可以存在于深湖或远洋环境,滑塌构造可能是海相也可能是非海相,大部分原生石盐在内陆盐湖和海相萨布哈环境都可以沉积。因此单个岩相不能确定沉积环境,需要通过岩相组合判断环境动力条件推测沉积环境(表1)。梳理本文相类型、岩相、结构总结不同环境的相组合如下。
表 1 蒸发岩相组合与沉积环境的划分
相 亚相 岩相组合 海相 萨布哈 Ct,Dl,Mm/Mlb,Gm,Gbg,Gs,GSm,GSx,Alb,Gf/Gp,Gn/An,Gmn,SGl,SGn,Hc,Hh,Hpt,Hfb,Hk,Hog,Hs,Hbc,Sah,DG,Hht,PG 潮上带 Cp,Ct,Dl,Dal,De,Dc,Ml,Hs,Gr,Sm/Sag,Gs,Alb,Gn/An,Hc,Hh,Hr,Hrc,DG,GDc 潮间—潮下带 Smc,Scc,Co,Dg,Ds,DG,Sva,Gss,Ssl,Ss,Gg,Ai/Ac,Gef,Am,Aab 半深海—深海 Ga/Gr,Gt/Gb,GO,Gmb,Ab,Amn,Has,Apl 陆相 大陆萨布哈 Dl,Mm/Mlb,Trp,Tu,Gm,Gbg,Gf/Gp,GSm,GSx,Gn/An,Gmn,Gnl,SGn,SGm,SGa,Ml,Hh,Hr,Hpt,Hfb,Hk,Hog, Hs,Hbc,Sah,Hm,Hht,GLm,Glc-Ⅱ,MA,Db 滨湖 Slb,Ctc,Scd,Co,Dl,Aha,Hs,Tb,Tm,Tgl,Trp,Tu,Nl,Go,Sm/Sag,Ssl,Ss,Gbl, Gmn,GLc-Ⅰ,Glc-Ⅱ, Hc,Hh,Hr,Hrc,Ho,GDc,GLc-Ⅲ,GLm 浅湖 Cmt,Rsad,Nm,Gc,Gbl,Gg,GLc-Ⅲ,Tl 半深湖—深湖 Cmt,Cl,Atd,Glp,Gt/Gb,Gmb,Has,Apl,Ab,Ga/Gr,GO -
海相蒸发岩常出现在海岸萨布哈、潮上带、潮间和潮下带(包括潟湖和近海的海源局限盆地,它们仍然受到海水的影响,如海水渗流和特大潮海水补给),半深海或深海沉积的蒸发岩多半是机械再沉积的产物。在深盆深水蒸发模式下[161]可以沉积原始蒸发岩,这些沉积在深水环境的原始蒸发岩有明显的远洋特征,比如很薄的水平纹层构造,以及与碳酸盐互层沉积等。
-
萨布哈指在正常高潮线以上的局限海平原,在干旱到半干旱气候条件下形成的潮上沉积环境,在沿海潟湖和潮间带以上靠近大陆方向的平坦地带。具有蒸发盐、潮洪、泥坪或沙坪混合沉积和风化沉积的特点。萨布哈向海一侧为海相沉积,向陆一侧为陆相沉积,以波斯湾海岸的一片荒芜低平的盐碱地最为代表。对海洋环境潮上带的盐坪称海岸萨布哈,陆内干旱盆地形成的盐泥坪、干盐湖等则称为陆内萨布哈。一个完整的萨布哈序列包括三部分:基底是纹层状潮间带藻类,有泥岩夹层(常含有分散的、透镜状石膏);中间有分散的、结核状石膏或硬石膏等,基质包含碳酸盐、硅质碎屑岩或砂泥混合;上部被流水,风化侵蚀面横切[94]。
萨布哈环境最明显的特点就是沉积物大部分暴露在水面之上,容易受风吹、大气降水和地下水的影响。在萨布哈沉积相的最顶部,由于蒸发加剧盐水蒸干,沉积物表面受暴晒导致干裂,沉积物直接暴露,表面发育为帐篷构造灰岩(Ct)、多边形断裂和帐篷构造石盐壳(Hpt)等。除了干裂构造,萨布哈表面常见松散堆积的光卤石角砾(Db)等蒸发盐堆积物、有成壤特征并可能发育植物的泥质结构石膏土(GSm),石膏土的下部岩相为石膏砂,来源于强风对石膏颗粒的分选和改造,最典型的是阿拉伯湾的夏马风,风的机械作用下可以把盐沼上漂浮的晶筏石盐吹到岸边堆积或者把原始的岸边松散堆积发育呈风成层理,如X型层理石膏砂(GSx)。当极度干旱季节结束,随着大气降水或河流的到来,暴露的石盐岩受到明显的淡水溶解作用形成次生构造如鱼骨状底部成核层石盐岩(Hfb)和喀斯特溶洞/微喀斯特洞状充填石盐(Hk)。当石盐溶解的盐水渗透到帐篷构造石盐下方,由于盐度达到石盐沉淀浓度,常见石盐钟乳石发育(钟乳石石盐岩;Hs)。在季节性洪水期,沉积物受到阶段性强水动力,在石盐喀斯特和盐扰动结构石盐岩(Hht)内常见流水冲刷带入的砂泥和微生物混合堆积在一起。萨布哈的另一部分沉积物发育在浅的盐水下,盐沼的水浅、蒸发作用大、盐度高,因此大部分时间里,表现为弱水动力沉积构造,几乎不受生物扰动等机械作用的影响,以化学沉淀为主,呈纯的、少杂基的纹层—层状或块状蒸发岩,如层状白云岩(Dl)、块状/层状菱镁矿岩(Mm/Mlb)、底部生长石膏(Gbg)、纤维状/棱形柱状石膏(Gf/Gp)、透明块状石膏(Gm)、V字形晶底部成核层石盐岩(Hc)和漏斗形晶底部成核层石盐岩(Hh)等。在盐水波动频繁的地带常见结核状石膏/硬石膏(Gn/An)和结核—纹层状石膏(Gnl)岩相。结核状石膏可以同生沉积和早期成岩同时出现,结核状石膏/硬石膏从鸡笼铁丝状或肠状原生结构变为镶嵌结核状结构,此时原生石膏经历了早期成岩作用,发生石膏脱水作用并且石膏与硬石膏结核紧压在一起形成镶嵌结构,它们发生在地下水以上近盐沼处毛细管作用很强的蒸发带,且水体变浅的沉积层序中[117,162]。结核—纹层状石膏(Gnl)表明浅水(形成层状石膏)和陆上(先形成结节状硬石膏,硬石膏水化次生作用为石膏)环境的变化[118-119]。
-
潮上带指位于平均高潮线与最大涨潮线之间的平坦区域。正常潮汐作用不能到达,但在大潮或风暴潮时,海水可以淹没。潮上带因大部分时间出露于水面之上,很少受到海水的作用,只在偶然风暴或特大潮时才被海水淹没,出现干化标志如帐篷构造灰岩(Ct)。海洋潮上带蒸发泵吸和回流渗透作用强,剖面上如出现的白云岩夹于大套石灰岩与蒸发岩之间,可能是因为沉积于滨临海岸盐湖或蒸发海岸带,可经常得到海源直接或渗流补给[163]。潮上带水动力较弱,蒸发作用强,藻类微生物繁盛,白云岩或者石膏会保存藻类和叠层构造,常见的岩相有球粒灰岩(Cp)、含石膏白云岩(DG)、藻纹层白云岩(Dal)和叠层石石膏(Gs)等。潮上带下部水动力渐强,发育竹叶状、波状和波纹构造沉积岩,常见竹叶状白云岩(De)、波状或韵律条带状石膏(Gr)和波纹碎屑石盐岩(Hrc)。潮上带蒸发盐多为浅水水下沉积蒸发盐,如底部成核V字形和漏斗形石盐(Hc、Hh)。透石膏也发育在非常浅的蒸发水下环境,水深从厘米到米[95-96],潮上带常见厚块状/带状交替透石膏(Sm/Sag)。海退时期蓄水洼地成为蒸发盐沼,常见透镜状、层状蒸发盐如透镜状菱镁矿岩(Ml)、层状白云岩(Dl)和纹层—条带状硬石膏(Alb)等,层状石膏是滨岸盐沼环境最常见的沉积物[117]。靠近内陆的岸带常发育三角洲,可能受河流影响混合沉积碎屑—蒸发盐,如含石膏杂乱沉积(GDc),该岩相存在侵蚀表面、内碎屑、交叉层、波纹等机械作用构造说明了河流作用影响与蒸发环境水动力的改变。
-
潮间带,是指平均最高潮位和最低潮位间的海岸,也就是海水涨至最高时所淹没的地方开始至潮水退到最低时露出水面的范围,水动力较强。潮下带指位于平均低潮面以下,浪基面以上的浅水带。即潮间浅滩外面广阔的水下岸波。水深一般3~5 m,波浪和水流动力作用较强。潮间—潮下带可以发育在潟湖内,当海水入侵与广海相连,此时沉积物以正常海相沉积物为主,是典型的潟湖碳酸盐台地;当海退并伴随剧烈蒸发时,潟湖变为一个局限蒸发盐湖,所以在纵向沉积序列从广海碳酸盐到蒸发盐,如四川盆地中三叠纪的雷口坡组[163]。
潮间带弱水动力带,蒸发作用大,水体较浅,藻类等微生物作用明显,常见叠层石白云岩(Ds)、不规则层状(圆齿状)硬石膏(Ai/Ac)、含石膏白云岩(DG)和肠状褶皱石膏(Gef)。在波浪和水流动力作用较强的潮间—潮下带,灰岩颗粒在波浪作用下会分选、磨圆,颗粒较粗大,如鲕粒、生屑和骨架砂等,蒸发条件下它们容易被白云石交代,常见岩相包括中粒碳酸盐叠层石(Smc)、粗粒碳酸盐叠层石(Scc)、鲕粒灰岩(Co)、颗粒状白云岩(Dg)等。由于水动力加强,水平纹层蒸发盐几乎不发育,而是沉积粗颗粒的蒸发晶体,典型的有弯刀形透石膏(Ssl)和骨架状透石膏(Ss)。由于水深比潮上带深,石膏晶体有足够的位置发育纵向规则排列构造透石膏(Sva),它代表了典型的潮间带浅水水底成核相[15,94-95]。此外,在蒸发加剧的条件下,上层盐水柱向下移动,将发育“残影”石膏(Gg)岩相。由于水体波动较频繁,盐度和水深变化也大,蒸发盐与碳酸盐互层构造随之出现,常见岩相有交替层状碳酸盐—硬石膏岩(Aab)和块状硬石膏(Am),块状硬石膏含有黏土、碳酸盐、沥青和有机物,说明其前身可能沉积于还原深水环境。
-
蒸发岩沉淀大多发生在浅水,因为浅水环境蒸发作用大,盐度高,容易沉淀盐类矿物并保存下来,而半深海和深海环境水体较深,蒸发盐类较少。环境比较安静,不易受到风和波浪的影响,水动力很弱,沉积物总体细粒,以纹层构造为主,常见岩相组合有交替纹层石盐—石膏(Has)。再作用和再分布的蒸发岩也可以沉积到更深的水域,如台地外潟湖、斜坡和近深海平原[100]。斜坡常见再沉积和滑塌的浊积和角砾蒸发岩,发育滑塌变形和角砾构造,它们存在明显的再沉积特征,如发育浅水环境下的流水冲刷痕和生物碎屑。滑塌等再作用沉积物可以发生在蒸发盐内部,如发育软沉积变形构造,典型的有石膏浊积岩/石膏角砾岩(Gt/Gb);也可以是大块石膏角砾滑塌与其他沉积物混合沉积成岩,如石膏砂屑/砾屑岩(Ga/Gr)、石膏滑动岩体(GO)、巨角砾石膏岩(Gmb)和硬石膏角砾岩(Ab)。在剧烈蒸发环境下,典型的如Messinian时期的深水深盆模式,在深水盆地中心,蒸发盐晶体在空气—卤水界面形成后以“盐雨”形式[1]下沉堆积成岩,常见“远洋”纹层或交替纹层构造,发育远洋层状硬石膏(Apl)。由于深海缺氧还原环境,有机质可以保存下来并且和再沉积的蒸发盐互层,如微结核状硬石膏(Amn)就与沥青黏土岩互层出现[100]。
-
陆相蒸发岩环境包括陆内萨布哈(包括干盐湖)与湖泊(滨湖,浅湖,深湖)。陆相湖盆远离海洋,受海洋环境影响较小而大气降水和河流影响更大,它们的成盐卤水来源更加复杂,有残留海水,大气降水,河流汇入,深源补给等[1]。
-
陆内萨布哈是干盐湖和泥坪复合沉积的一部分,范围从盆地边缘的冲积扇/短暂河流/漫滩到砂坪、干泥坪、盐泥坪(含水)、最后到位于中心的湖泊或干盐湖[1]。陆内萨布哈前身为陆内蓄水湖泊,在蒸发期形成干盐湖和盐坪,表面大面积发育干裂构造的岩盐,如帐篷构造石盐(Hpt)。陆内萨布哈蒸发沉积物与海洋萨布哈很相似,但陆内萨布哈常见典型的陆相指相矿物如天然碱等矿物,含杂卤石块状石盐砂岩(Hm),由于远离海洋缺少足够的镁离子补给,因此陆内萨布哈白云石岩相减少,常见碳酸型蒸发岩相组合有放射棱柱体状天然碱(Trp)、无定向构造天然碱(Tu)、层状白云岩(Dl)、块状/层状菱镁矿岩(Mm/Mlb),它们在碱湖和大陆卤水补充盐盆非常普遍。陆内萨布哈与外海完全隔离,因此与广海沉积物不相连,底部沉积序列常见正常湖泊、三角洲、冲积扇和河流沉积物。进入蒸发阶段之后,原生蒸发岩受到强烈的大气降水、地下水和洪水期影响而被改造为次生构造的盐岩,常见岩相组合有次生结核状石膏(SGn)、粗晶质次生石膏(SGm)、带状光滑次生石膏(SGa)、鱼骨状底部成核层石盐岩(Hfb)、喀斯特溶洞/微喀斯特洞状充填石盐(Hk)、增生石盐胶结物(Hog)、钟乳石石盐岩(Hs)和盐扰动结构石盐岩(Hht)等。在干盐湖顶部除了发育大面积干裂构造盐岩,风的机械作用还能改造蒸发岩颗粒,直接把表面沉积物堆积成岩,如泥质结构石膏土(GSm)、X型层理石膏砂(GSx)、晶筏石盐堆晶(Hr)等。在盐沼水下,常见透明块状石膏(Gm)、结核状石膏/硬石膏(Gn/An)、微结核石膏(Gmn)、底部生长石膏(Gbg)、纤维状/棱形柱状石膏(Gf/Gp)、V字形底部成核和漏斗形晶底部成核层石盐岩(Hc,Hh)。当干旱炎热气候结束进入短暂的干冷气候蒸发时,盐湖沉积从钙芒硝变为典型的冷相矿物芒硝,岩相组合为块状钙芒硝岩(GLm)、扭曲状钙芒硝岩(Glc-Ⅱ)、层状芒硝岩(Ml)、芒硝岩或含芒硝岩组(MA)。交替纹层石盐—钾石盐(Sah)和带状光滑次生石膏(SGa)常代表盐湖沉积进入最干旱的时期。
-
滨湖位于正常浪基面之上到洪水面之间的地带,水动力从弱到较强。滨湖沉积带分为两部分,最上部是枯水面到洪水面之间的地带,周期性暴露在水面之上,水动力很弱,存在暴露标志;向下过渡到枯水面和正常浪基面之间,水浅但始终在水下,遭受湖浪和湖流扰动,水动力较强,常见鲕粒和生物碎屑,多种层理发育,还有浪成波痕等。
上部沉积物由于周期性暴露水面,水动力很弱,蒸发作用很强,发育块状钙芒硝岩(GLm)、扭曲状钙芒硝岩(Glc-Ⅱ)、凝块叠层石(Ctc)、丘形叠层石(Scd)、叠层石水菱镁矿岩(Hs)、层状白云岩(Dl)、晶筏石盐堆晶(Hr)、层状和块状天然碱(Tb、Tm)和微结核石膏(Gmn)等。滨湖下部是枯水面到正常浪基面之间环境,水浅但始终位于水下,可沉积底部生长的蒸发盐,常见岩相组合有草状天然碱(Tgl)、放射棱柱体状天然碱(Trp)、无定向构造天然碱(Tu)、厚块状/带状交替透石膏(Sm/Sag)、巨型结晶透明钙芒硝岩(GLc-Ⅰ)等。此外滨湖水下环境的水动力强,颗粒遭受湖浪波动作用,发育放射状鲕粒灰岩(Co)、鲕粒石盐(Ho)、弯刀形透石膏(Ssl)、骨架状透石膏(Ss)、波纹碎屑石盐岩(Hrc)。浅水滨湖的盐度中等,氧气充足,透光性好因此生物繁盛,蒸发岩受到生物扰动的影响发育生物扰动构造且常与燧石结核、硅质壳体伴生,这种构造指示了低含氯盐湖滨湖沼泽环境[20],常见含生物侵蚀纹层的叠层石灰岩(Slb)、生物扰动层状石膏(Gbl)。受河流或季节性洪水影响,滨岸沿岸发育内有侵蚀表面、内碎屑、交叉层、波纹等机械作用构造、基质支撑的混合硅质碎屑—碳酸盐—硫酸盐沉积物和碎屑状钙芒硝岩(GLc-Ⅲ)等混合蒸发岩。在水下滨湖环境的低能带,如沙丘、障壁后的水洼或沼泽,水动力较弱,发育低能沉积构造,常见低能鲕状石膏(Go)、水菱镁矿和文石交互层(Aha)、层状苏打石(Nl)。
-
浅湖位于正常浪基面之下,风暴浪基面之上,处于弱氧化—弱还原环境,水动力中等到弱,沉积物仅受湖流和风暴浪影响,一般波浪难以波及。正常浅湖沉积相以黏土、粉砂岩为主,低能水平层理较发育,偶有小的波状纹层或风暴沉积。由于水体呈弱还原环境,有机质含量较高,在干热气候条件下与蒸发盐互层沉积,如油页岩—盐碱矿—泥质白云岩韵律岩(Rsad)和透镜状/团块状天然碱(Tl)等。水动力比滨湖环境弱,因此常见岩相组合有树枝状凝块丘灰岩(Cmt)、块状苏打石(Nm)、凝块状石膏(Gc)、纤维状/棱形柱状石膏(Gf/Gp)和“残影”石膏(Gg)。浅湖生物活动减少,变为薄层小规模生物扰动层状石膏(Gbl)。洪水沉积带来的碎屑状钙芒硝岩(GLc-Ⅲ)可以沉积在内湖区,即浅湖环境。
-
深湖位于湖泊水体最深位置,波浪作用不能涉及,水体缺氧岩性总体为细粒沉积岩,颜色较深,有机质含量较高。蒸发盐常见纹层与交替纹层构造,岩相组合有纹层灰岩(Cl)、天然碱—白云岩互层(Atd)、透镜状/球状交替薄层石膏(Glp)、交替纹层石盐—石膏(Has)和“远洋”层状硬石膏(Apl)。深水斜坡有滑塌重力流、块体流和浊积发育,标志有盐层扭曲、滑塌/破裂,以及角砾岩堆积,软沉积变形、侵蚀与冲刷痕,常见岩相组合有石膏浊积岩/石膏角砾岩(Gt/Gb)、巨角砾石膏岩(Gmb)、硬石膏角砾岩(Ab)、石膏砂屑/砾屑岩(Ga/Gr)和石膏滑动岩体(GO)。此外碱湖深湖区还可以发育树枝状凝块丘灰岩(Cmt)。
-
本文系统的岩相总结和环境分析表明萨布哈环境是蒸发岩最有利的沉积场所:陆内萨布哈盐湖为牛眼或泪滴形状沉积带,海相萨布哈在沿海潟湖和潮间带以上靠近大陆方向的平坦地带。总的来说海陆萨布哈环境很相似,共同特点是沉积物大部分暴露在水面之上,常见大面积的盐壳和干裂构造沉积物,它们容易受到风吹、大气降水和地下水共同影响,因此也是次生蒸发盐组合与混合蒸发岩发育的绝佳位置。萨布哈水下沉积的蒸发岩表现为纹层、堆晶和块状结构,由于盐度大,水浅,几乎不受生物扰动影响。陆相与海相萨布哈蒸发岩蒸发背景和卤水来源不同会导致不同的岩相发育,天然碱盐岩仅发育在陆内萨布哈。滨湖和潮上带是次一级的蒸发岩沉积有利场所,蒸发作用较萨布哈弱,但是有直接的盐水补给,如海水/湖水周期性淹没潮上带和滨湖区,因此成盐物质来源充足,在强烈蒸发环境下可以沉积厚层蒸发岩。此外潮上带和滨湖环境水动力变化很大,生物繁盛,蒸发岩相组合中既有弱水动力的纹层构造也有强水动力波状和强生物扰动构造。海洋环境的横向分布较湖泊更宽广平坦,因此潮间带—潮下带的蒸发岩比浅湖更常见,它的水动力比潮上带强,蒸发岩受到的波浪作用更剧烈。深水环境,包括半深湖—深湖和半深海—深海,水动力很弱,原生蒸发岩多为纹层蒸发岩,次生蒸发岩为滑塌、浊积蒸发岩,它们可以单独成岩或者混合沉积,由于水体深,水体缺氧,纹层常见深色有机质。
蒸发岩沉积特征与环境解释不仅涉及到沉积地质学、水化学,而且还涉及构造地质学、环境地质学甚至微生物地质学等问题;不仅涉及同生、准同生时期的地质环境和水文条件,而且还涉及埋藏成岩和成岩后期的复杂变化。特别是不同地区的蒸发岩具有不同特点。即使在同一地区, 也会因环境的不断演变而有所变化。就我国而言,主要由华南板块、华北板块、塔里木板块以及一些小板块拼合而成,从古生代开始经历了多期次的碰撞—聚合旋回,板块多而碎,盆地类型多样,沉积范围广,成盐期次多,盐类沉积特征复杂[164]。因此,长期以来对于这些蒸发岩特征,古环境和成因的研究还不够深入。但我们对国内的蒸发岩岩相分析一定不能完全照搬国外的沉积模式,应该在借鉴国外沉积岩相解释的基础上,结合国内的具体实例,进行综合分析。首先,国内蒸发盆地构造复杂造就了多变的蒸发沉积环境,我们更应该细分最小蒸发岩岩相的不同,不应笼统归纳。例如结核状石膏,国外认为结核状石膏的三种演化对应具体的环境改变(见上文),国内仅仅归为萨布哈成因的结核状。第二,蒸发岩的杂基变化很少有学者关注。蒸发岩的杂基成分或者特殊构造也能很好地反映沉积环境。例如国外从重力流、块体流、河流和季节性洪水作用对混合蒸发岩的杂基有非常详细的解释。在我国的一些裂谷蒸发盆地,例如江陵凹陷古近纪卤水有多种来源,包括海源、深源补给和大气降水等[165],众说纷纭,至今没有明确的定论。因此如果能找到典型的反映沉积现象的混合蒸发岩,从杂基入手分析环境也不失为一个解释卤水来源的好方法。第三,应该重视深水环境。国内对蒸发岩岩相组合与沉积环境的解释大多归为浅水蒸发环境,如萨布哈、潮坪等,少见其他环境解释。事实上如果盆地为干旱炎热气候,断陷盆地在“深盆深水”模式下完全可能在盆地中心的深水环境发育蒸发岩,甚至和高有机质岩同时沉积,形成优质的生储盖条件。例如我国的桐柏吴城盆地五里堆组的油页岩,作为天然碱矿层的底板与天然碱、盐岩和白云岩等构成了多个韵律旋回,为完整的生储盖组合[84]。第四,应重视蒸发岩的成因。蒸发岩的成因研究可以为沉积环境解释提供依据,对沉积盆地古地理演变提供重要支撑。世界上巨型蒸发岩盐盆都是海相成因,非海相成因的蒸发岩盆不仅在地质历史上,而且在第四纪时期都不甚发育。因此按照将今论古的原则,如果仅由于地层为陆相,就把这种巨型蒸发岩沉积解释为陆相是不合理的。如兰坪—思茅和泰国呵叻—沙空那空盆地在白垩纪中期发育巨型蒸发岩,不少学者依据地层中无海相化石解释为非海相成因。近年来作者研究却发现了该蒸发岩为海相成因的多种证据。最后,还应重视蒸发岩沉积与微生物作用的关系。由于蒸发岩常与油气紧密联系,油气或甲烷导致的厌氧细菌的生化反应会使硬石膏或石膏发生还原,形成微生物碳酸盐岩。那么是否是巨型蒸发岩的沉积导致了深部微生物多样性的发展?
Evaporite Sedimentary Characteristics and Environment: A review
-
摘要: 蒸发岩是由于蒸发作用从卤水中化学作用沉淀出来的一种含盐岩类,明显受控于沉积环境。蒸发岩是重要战略资源和优质的储层之一,中国的矿床和石油学界都在致力于寻找大型蒸发岩矿床。近几十年来国内外学者都对不同类型的蒸发岩做了地区性的研究,提供了丰富的实际资料,对蒸发岩成矿沉积环境理论也有相应的修正和补充,但是蒸发岩分类繁多,成因复杂,国内对蒸发岩岩相及其常见组合所对应的环境综合解释并未具体着墨。通过梳理国内外有关蒸发岩文献、应用Miall构架单元理论,从结构、构造整理了29种碳酸型、37种硫酸型、11种氯化物型以及13种混合蒸发盐型岩相与其对应的沉积环境与岩相组合。蒸发沉积环境按海相和陆相划分,亚相细分为萨布哈、潮上带、潮间带—潮下带和半深海—深海环境,以及陆内萨布哈(包括干盐湖)、滨湖、浅湖和半深湖—深湖,对每一个亚相出现的常见蒸发岩组合进行了概述,这对中国进一步寻找大型蒸发岩矿床具有重要的借鉴意义。Abstract: Evaporites are salt-bearing rocks precipitated from saline water, influenced by their sedimentary environment. They are among the most important strategic high-quality reservoirs of hydrocarbon resources. Regional studies of evaporites in China and globally have produced abundant observational data that gives a revised understanding of the sedimentary environments of evaporites; however, the origins of the many kinds of evaporites are complex, and in China no overall environmental interpretation of evaporite facies and associated common assemblages has previously been determined. The present conclusive study of the structure and texture of evaporites worldwide, adopting the architectural-element analysis approach proposed by Miall (1985), produced 29 classes of carbonate lithofacies, 37 sulfuric acid lithofacies, 11 chloride lithofacies and 13 mixed evaporite lithofacies, together with their sedimentary environments and associations in marine and terrestrial deposits. These are subdivided into marine sabkhas (supratidal mudflat or sandflat), supratidal zone, intertidal/subtidal zone, and semi-deep and deep-sea environments; and continental sabkhas, shore, shallow lake and semi-deep to deep lake environments. The common evaporite lithofacies association in each subfacies is summarized, providing an important reference for future evaporite deposit exploration in China.
-
表 1 蒸发岩相组合与沉积环境的划分
相 亚相 岩相组合 海相 萨布哈 Ct,Dl,Mm/Mlb,Gm,Gbg,Gs,GSm,GSx,Alb,Gf/Gp,Gn/An,Gmn,SGl,SGn,Hc,Hh,Hpt,Hfb,Hk,Hog,Hs,Hbc,Sah,DG,Hht,PG 潮上带 Cp,Ct,Dl,Dal,De,Dc,Ml,Hs,Gr,Sm/Sag,Gs,Alb,Gn/An,Hc,Hh,Hr,Hrc,DG,GDc 潮间—潮下带 Smc,Scc,Co,Dg,Ds,DG,Sva,Gss,Ssl,Ss,Gg,Ai/Ac,Gef,Am,Aab 半深海—深海 Ga/Gr,Gt/Gb,GO,Gmb,Ab,Amn,Has,Apl 陆相 大陆萨布哈 Dl,Mm/Mlb,Trp,Tu,Gm,Gbg,Gf/Gp,GSm,GSx,Gn/An,Gmn,Gnl,SGn,SGm,SGa,Ml,Hh,Hr,Hpt,Hfb,Hk,Hog, Hs,Hbc,Sah,Hm,Hht,GLm,Glc-Ⅱ,MA,Db 滨湖 Slb,Ctc,Scd,Co,Dl,Aha,Hs,Tb,Tm,Tgl,Trp,Tu,Nl,Go,Sm/Sag,Ssl,Ss,Gbl, Gmn,GLc-Ⅰ,Glc-Ⅱ, Hc,Hh,Hr,Hrc,Ho,GDc,GLc-Ⅲ,GLm 浅湖 Cmt,Rsad,Nm,Gc,Gbl,Gg,GLc-Ⅲ,Tl 半深湖—深湖 Cmt,Cl,Atd,Glp,Gt/Gb,Gmb,Has,Apl,Ab,Ga/Gr,GO -
[1] Warren J K. Evaporites: A geological compendium[M]. 2nd ed. Switzerland: Springer, 2016. [2] 刘成林,焦鹏程,王弭力. 盆地钾盐找矿模型探讨[J]. 矿床地质,2010,29(4):581-592. Liu Chenglin, Jiao Pengcheng, Wang Mili. A tentative discussion on exploration model for potash deposits in basins of China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(4): 581-592. [3] Warren J K. Evaporites through time: Tectonic, climatic and eustatic controls in marine and nonmarine deposits[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 98(3/4): 217-268. [4] Peterson J A, Hite R J. Pennsylvanian evaporite-carbonate cycles and their relation to petroleum occurrence, southern Rocky Mountains[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1969, 53(4): 884-908. [5] Middleton G V. Johannes Walther's law of the correlation of facies[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1973, 84(3): 979-988. [6] Zheng M, Hou X, Zhang Y, et al. Progress in the investigation of potash resources in western China[J]. China Geology, 2018, 1(3): 392-401. [7] Hsü K J, Montadert L, Bernoulli D, et al. History of the Mediterranean salinity crisis[J]. Nature, 1977, 267: 399-403. [8] Borchert H, Muir R O. Salt deposits: The origin, metamorphism and deformation of evaporites[M]. London: Van Nostrand, 1964. [9] Hsü K J, Ryan W B F, Cita M B. Late Miocene desiccation of the mediterranean[J]. Nature, 1973, 242(5395): 240-244. [10] Hsü K J. The Messinian salinity crisis: Evidence of Late Miocene eustatic changes in the world ocean[J]. Naturwissenschaften, 1978, 65(3): 151. [11] Cita M B, McRenzie J A. The terminal Miocene event[M]//Hsü K J. Mesozoic and Cenozoic oceans. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 1986: 123-140. [12] Martín J, Braga J C. Messinian events in the sorbas Basin in southeastern spain and their implications in the recent history of the mediterranean[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3/4): 257-268. [13] [14] Kendall A C. Facies models 12. Subaqueous evaporites [M]// Walker R G. Facies models. Geoscience Canada, 1978, 5(3):124-139. [15] Warren J K. Evaporites: Sediments, resources and hydrocarbons[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006. [16] El Tabakh M, Schreiber B C, Warren J K. Origin of fibrous gypsum in the Newark rift Basin, eastern North America[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1998, 68(1): 88-99. [17] Stefano L, Vinicio M, Marco R. Charlotte S B. The primary Lower gypsum in the mediterranean: A new facies interpretation for the first stage of the Messinian salinity crisis[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 297(1): 83-99. [18] Al Rajaibi I M, Hollis C, Macquaker J H. Origin and variability of a terminal Proterozoic primary silica precipitate, Athel Silicilyte, South Oman salt Basin, Sultanate of Oman[J]. Sedimentology, 2015, 62(3): 793-825. [19] Buick R, Dunlop J S R. Evaporitic sediments of early archaean age from the warrawoona group, North Pole, western Australia[J]. Sedimentology, 1990, 37(2): 247-277. [20] Ortí F, Rosell L. Evaporative systems and diagenetic patterns in the Calatayud Basin (Miocene, central Spain)[J]. Sedimentology, 2000, 47(3): 665-685. [21] Alonso‐Zarza A M, Sánchez‐Moya Y, Bustillo M A, et al. Silicification and dolomitization of anhydrite nodules in argillaceous terrestrial deposits: An example of meteoric‐dominated diagenesis from the Triassic of central Spain[J]. Sedimentology, 2002, 49(2): 303-317. [22] Manzi V, Lugli S, Lucchi F R, et al. Deep‐water clastic evaporites deposition in the Messinian Adriatic foredeep (northern Apennines, Italy): Did the Mediterranean ever dry out?[J]. Sedimentology, 2005, 52(4): 875-902. [23] Tekin E, Varol B, Ayyıldız T. Sedimentology and paleoenvironmental evolution of Messinian evaporites in the Iskenderun–Hatay Basin complex, southern Turkey[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 229(4): 282-298. [24] Morsilli M, Bosellini F R, Pomar L, et al. Mesophotic coral buildups in a prodelta setting (Late Eocene, southern Pyrenees, Spain): A mixed carbonate–siliciclastic system[J]. Sedimentology, 2012, 59(3): 766-794. [25] Ortí F, Rosell L, Playà E, et al. Meganodular anhydritization: A new mechanism of gypsum to anhydrite conversion (Palaeogene–Neogene, Ebro Basin, North‐east Spain)[J]. Sedimentology, 2012, 59(4): 1257-1277. [26] Benavente C, Mancuso A, Cabaleri N, et al. Comparison of lacustrine successions and their palaeohydrological implications in two sub‐basins of the Triassic Cuyana rift, Argentina[J]. Sedimentology, 2015, 62(7): 1771-1813. [27] 张彭熹. 中国蒸发岩研究中几个值得重视的地质问题的讨论[J]. 沉积学报,1992,10(3):78-84. Zhang Pengxi. Discussion on some geological problems of the research of evaporite in China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1992, 10(3): 78-84. [28] 宣之强,王连第. 中国钾盐50年[J]. 化工矿产地质,1999,21(3):181-187. Xuan Zhiqiang, Wang Liandi. 50 years of Chinese potassium industry[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 1999, 21(3):181-187. [29] 袁见齐. 钾盐专辑第1辑[M]. 北京:中国工业出版社,1963. Yuan Jianqi. Potash album No.1[M]. Beijing: China Industrial Industry Press, 1963. [30] 袁见齐. 钾肥与钾盐矿床[M]. 北京:石油化学工业出版社,1977. Yuan Jianqi. Potash fertilizer and potash deposits[M]. Beijing: Petrochemical Industry Press, 1977. [31] Miall A D. Architectural-element analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1985, 22(4): 261-308. [32] Bowlin E M, Klaus J S, Foster J S, et al. Environmental controls on microbial community cycling in modern marine stromatolites[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 263-264: 45-55. [33] Visscher P T, Reid R P, Bebout B M. Microscale observations of sulfate reduction: Correlation of microbial activity with lithified micritic laminae in modern marine stromatolites[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(10): 919-922. [34] Allen M A, Goh F, Burns B P, et al. Bacterial, archaeal and eukaryotic diversity of smooth and pustular microbial mat communities in the hypersaline lagoon of Shark Bay[J]. Geobiology, 2009, 7(1): 82-96. [35] Reid R P, James N P, Macintyre I G, et al. Shark Bay stromatolites: Microfabrics and reinterpretation of origins[J]. Facies, 2003, 49(1): 299. [36] Jahnert R J, Collins L B. Characteristics, distribution and morphogenesis of subtidal microbial systems in Shark Bay, Australia[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 303-306: 115-136. [37] Walter M R, Golubic S, Preiss W V. Recent stromatolites from hydromagnesite and aragonite depositing lakes near the Coorong Lagoon, South Australia[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1973, 43(4): 1021-1030. [38] Warren J K. Sedimentology and mineralogy of dolomitic Coorong lakes, South Australia[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1990, 60(6): 843-858. [39] Halley R B. Textural variation within Great Salt Lake algal mounds[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 1976, 20: 435-445. [40] Pedone V A, Folk R L. Formation of aragonite cement by nannobacteria in the Great Salt Lake, Utah[J]. Geology, 1996, 24(8): 763-765. [41] Pedone V A, Dickson J A D. Replacement of aragonite by quasi-rhombohedral dolomite in a Late Pleistocene tufa mound, Great Salt Lake, Utah, U.S.A.[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2000, 70(5): 1152-1159. [42] Farías M E, Poiré D G, Arrouy M J, et al. Modern stromatolite ecosystems at alkaline and hypersaline high-altitude lakes in the Argentinean Puna[M]//Tewari V, Seckbach J. STROMATOLITES: Interaction of microbes with sediments. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011: 427-441. [43] Laval B, Cady S L, Pollack J C, et al. Modern freshwater microbialite analogues for ancient dendritic reef structures[J]. Nature, 2000, 407(6804): 626-629. [44] Gerdes G, Dunajtschik‐Piewak K, Riege H, et al. Structural diversity of biogenic carbonate particles in microbial mats[J]. Sedimentology, 1994, 41(6): 1273-1294. [45] Mazzullo S J, Birdwell B A. Syngenetic formation of grainstones and pisolites from fenestral carbonates in peritidal settings[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1989, 59(4): 605-611. [46] Williamson C R, Picard M D. Petrology of carbonate rocks of the Green River Formation (Eocene)[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1974, 44(3): 738-759. [47] Milroy P G, Wright V P. A highstand oolitic sequence and associated facies from a Late Triassic lake basin, south‐west England[J]. Sedimentology, 2000, 47(1): 187-209. [48] Husinec A, Read J F. Transgressive oversized radial ooid facies in the Late Jurassic Adriatic Platform interior: Low-energy precipitates from highly supersaturated hypersaline waters[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2006, 118(5/6): 550-556. [49] Winland H D, Matthews R K. Origin and significance of grapestone, Bahama Islands[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1974, 44(3): 921-927. [50] Hird K, Tucker M E. Contrasting diagenesis of two Carboniferous oolites from South Wales: A tale of climatic influence[J]. Sedimentology, 1988, 35(4): 587-602. [51] Lokier S, Steuber T. Large‐scale intertidal polygonal features of the Abu Dhabi coastline[J]. Sedimentology, 2009, 56(3): 609-621. [52] Garber R A, Levy Y, Friedman G M. The sedimentology of the Dead Sea[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 1987, 2(1): 43-57. [53] 华东石油学院岩矿教研室. 沉积岩石学[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,1982:177-221. Department of Rock and Mineral Resources, East China Petroleum UniversityFeng Zengzhao. Sedimentary petrology (volume 1)-introduction to carbonate rocks [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1982:, 177-221. [54] Purser B H, Tucker M E, Zenger D H. Problems, progress and future research concerning dolomites and dolomitization[M]//Purser B, Tucker M, Zenger D. Dolomites: A volume in honour of dolomieu. Hoboken: The International Association of Sedimentologists, 1994: 3-20. [55] Warren J. Dolomite: Occurrence, evolution and economically important associations[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2000, 52(1/2/3): 1-81. [56] Braithwaite C J R, Rizzi G, Darke G. The geometry and petrogenesis of dolomite hydrocarbon reservoirs[M]. Bath: Geological Society of London, 2004: 99-139. [57] 汤朝阳,王敏,姚华舟,等. 白云石化作用及白云岩问题研究述评[J]. 东华理工学院学报,2006,29(3):205-210. Tang Zhaoyang, Wang Min, Yao Huazhou, et al. Current topics about dolomitization and the problem of dolostones[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 2006, 29(3): 205-210. [58] 赫云兰,刘波,秦善. 白云石化机理与白云岩成因问题研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2010,46(6):1010-1020. He Yunlan, Liu Bo, Qin Shan. Study on the dolomitization and dolostone genesis[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2010, 46(6): 1010-1020. [59] 黄思静. 碳酸盐岩的成岩作用[M]. 北京:地质出版社,2010:226-261. Huang Sijing. Carbonate diagenesis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010: 226-261. [60] 廖静,董兆雄,翟桂云,等. 渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷沙河街组一段下亚段湖相白云岩及其与海相白云岩的差异[J]. 海相油气地质,2008,13(1):18-24. Liao Jing, Dong Zhaoxiong, Zhai Guiyun, et al. Feature of Oligocene shahejie Lower-1st member lacustrine Dolostone in qikou Depression, Bohaiwan Basin, and difference of it from marine dolostone[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2008, 13(1): 18-24. [61] 沈安江,郑剑锋,潘文庆,等. 塔里木盆地下古生界白云岩储层类型及特征[J]. 海相油气地质,2009,14(4):1-9. Shen Anjiang, Zheng Jianfeng, Pan Wenqing, et al. Types and the characteristics of Lower Paleozoic dolostone reservoirs in Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2009, 14(4): 1-9. [62] 刘春,张惠良,张荣虎,等. 库车坳陷古近系白云岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 沉积学报,2010,28(3):518-524. Liu Chun, Zhang Huiliang, Zhang Ronghu, et al. Geochemistry characteristic and origin of Paleogene dolomite in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(3): 518-524. [63] 张婷婷,刘波,秦善. 川东北二叠系—三叠系白云岩成因研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2008,44(5):799-809. Zhang Tingting, Liu Bo, Qin Shan. The origin of Permian and Triassic Dolostones in Northeastern Sichuan province, China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2008, 44(5): 799-809. [64] 顾家裕. 塔里木盆地下奥陶统白云岩特征及成因[J]. 新疆石油地质,2000,21(2):120-122. Gu Jiayu. Characteristics and origin analysis of dolomite in Lower Ordovician of Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2000, 21(2): 120-122. [65] 陈永权,周新源,赵葵东,等. 塔里木盆地塔中1井藻纹层白云岩与竹叶状白云岩成因:基于岩石学、元素与同位素地球化学的厘定[J]. 地质学报,2008,82(6):826-834. Chen Yongquan, Zhou Xinyuan, Zhao Kuidong, et al. Geochemical research on straticulate dolostone and spatulate dolostone in Lower Ordovician strata of well Tazhong-1, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(6): 826-834. [66] Melezhik V A, Fallick A E, Medvedev P V, et al. Palaeoproterozoic magnesite: Lithological and isotopic evidence for playa/sabkha environments[J]. Sedimentology, 2001, 48(2): 379-397. [67] 由雪莲,孙枢,朱井泉. 塔里木盆地中上寒武统叠层石白云岩中微生物矿化组构特征及其成因意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2014,44(8):1777-1790. You Xuelian, Sun Shu, Zhu Jingquan. Significance of fossilized microbes from the Cambrian stromatolites in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2014, 44(8): 1777-1790. [68] 黄可可,胡作维,李小宁,等. 川东北飞仙关组储层结晶白云岩的形成机制与白云化模式[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014,41(5):612-624. Huang Keke, Hu Zuowei, Li Xiaoning, et al. Forming mechanism and dolomitization model of Triassic crystalline dolomite in Northeast Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2014, 41(5): 612-624. [69] Pohl W. Comparative geology of magnesite deposits and occurrences[J]// Möller P. Monograph Series on Mineral Deposits, 1989, 28: 1-13. [70] 陈从喜,倪培,蔡克勤,等. 辽东古元古代富镁质碳酸盐岩建造菱镁矿滑石矿床成矿流体研究[J]. 地质论评,2003,49(6):646-651. Chen Congxi, Ni Pei, Cai Keqin, et al. The minerogenic fluids of magnesite and talc deposits in the pal eoproterozoic mg-rich carbonate formations in eastern Liaoning province[J]. Geological Review, 2003, 49(6): 646-651. [71] von der Borch C. The distribution and preliminary geochemistry of modem carbonate sediments of the Coorong area, South Australia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1965, 29(7): 781-799. [72] Coshell L, Rosen M R, McNamara K J. Hydromagnesite replacement of biomineralized aragonite in a new location of Holocene stromatolites, Lake Walyungup, western Australia[J]. Sedimentology, 1998, 45(6): 1005-1018. [73] Braithwaite C J R, Zedef V. Living hydromagnesite stromatolites from Turkey[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 92(1/2): 1-5. [74] Jagniecki E A, Lowenstein T K. Evaporites of the Green River Formation, bridger and Piceance Creek Basins: Deposition, diagenesis, paleobrine chemistry, and Eocene atmospheric CO2 [M]//Smith M E, Carroll A R. Stratigraphy and paleolimnology of the Green River Formation, western USA. Dordrecht: Springer, 2015: 277-312. [75] [76] Lowenstein T K, Jagniecki E A, Carroll A R, et al. The Green River salt mystery: What was the source of the hyperalkaline lake waters?[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 173: 295-306. [77] García-Veigas J, Gündoğan İ, Helvacı C, et al. A genetic model for Na-carbonate mineral precipitation in the Miocene Beypazarı trona deposit, Ankara province, Turkey[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2013, 294: 315-327. [78] Eugster H P. Geochemistry of evaporitic lacustrine deposits[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1980, 8: 35-63. [79] Fahey J J, Ross M, Axelrod J M. Loughlinite, a new hydrous sodium magnesium silicate[J]. American Mineralogist, 1960, 45(3/4): 270-281. [80] 陈小军,罗顺社,张建坤,等. 安棚地区天然碱矿沉积特征及成因研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2009,29(3):42-46. Chen Xiaojun, Luo Shunshe, Zhang Jiankun, et al. Deposition and genesis of the trona deposits in the Anpeng region, Henan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2009, 29(3): 42-46. [81] 周珍琦,董清水,厚刚福,等. 与盐碱矿共生的油页岩形成环境及沉积演化:以桐柏吴城盆地油页岩矿床为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2006,36(6):1001-1005. Zhou Zhenqi, Dong Qingshui, Hou Gangfu, et al. The forming environment and sedimentary evolution of the oil shale intergrowthing with salt alkali mine- with the oil shale deposit of Wucheng, Tongbai Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2006, 36(6): 1001-1005. [82] Lowenstein T K, Demicco R V. Elevated Eocene atmospheric CO2 and its subsequent decline[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5795): 1928. [83] Adams J E, Rhodes M L. Dolomitization by seepage refluxion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1960, 44(12): 1912-1920. [84] Shinn E A, Ginsburg R N, Lloyd R M. Recent supratidal dolomite from Andros Island Bahamas[M]//Pray L, Murray R. Dolomitization and limestone diagenesis. Tulsa: Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, 1965. [85] Friedman G M. Occurrence and origin of Quaternary dolomite of Salt Flat, west Texas[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1966, 36(1): 263-267. [86] Ortí F, Rosell L, Anadón P. Deep to shallow lacustrine evaporites in the Libros Gypsum (southern Teruel Basin, Miocene, NE Spain): An occurrence of pelletal gypsum rhythmites[J]. Sedimentology, 2003, 50(2): 361-386. [87] El Tabakh M, Schreiber B C, Utha‐Aroon C, et al. Diagenetic origin of basal anhydrite in the Cretaceous Maha Sarakham salt: Khorat Plateau, NE Thailand[J]. Sedimentology, 1998, 45(3): 579-594. [88] 彭勇民,张荣强,陈霞,等. 四川盆地南部中下寒武统石膏岩的发现与油气勘探[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2012,39(1):63-69. Peng Yongmin, Zhang Rongqiang, Chen Xia, et al. Discovery and significance of the Middle-Lower Cambrian gypsolith in the south of Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2012, 39(1): 63-69. [89] Bąbel M, Kasprzyk A. Gypsum ooids from the Middle Miocene (Badenian) evaporites of southern Poland[J]. Acta Geologica Polonica, 1990, 40(3/4): 215-239. [90] Tekin E, Varol B, Ayyildiz T. A rare natural gypsum ooide (Gypsolites) in an evaporitic playa lake of Late Miocene (?) to Pliocene age in central Anatlia, Turkey[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2008, 23(1): 50-59. [91] 刘庆,张林晔,宋国奇,等. 利用石膏产状研究汶东盐湖相沉积与烃源岩特征[J]. 高校地质学报,2009,15(3):371-379. Liu Qing, Zhang Linye, Song Guoqi, et al. Application of occurrences of gypsum minerals in saline lacustrine facies analysis and source rocks organic geochemistry evaluation: A case study of wendong subdepression[J] Geological Journal of China Universities, 2009, 15(3): 371-379. [92] Abrantes Jr F R, Nogueira A C R, Soares J L. Permian paleogeography of west-central Pangea: Reconstruction using sabkha-type gypsum-bearing deposits of Parnaíba Basin, northern Brazil[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 341: 175-188. [93] Rossi C, Vilas L, Arias C. The Messinian marine to nonmarine gypsums of Jumilla (northern Betic Cordillera, SE Spain): Isotopic and Sr concentration constraints on the origin of parent brines[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 328: 96-114. [94] Schreiber B C, El Tabakh M. Deposition and early alteration of evaporites[J]. Sedimentology, 2000, 47(Suppl.1): 215-238. [95] Bąbel M. Models for evaporite, selenite and gypsum microbialite deposition in ancient saline basins[J]. Acta Geologica Polonica, 2004, 54(2): 219-249. [96] Schreiber B C, Lugli S, Bąbel M. Evaporites through space and time[M]. London: Geological Society of London, 2007: 75-178. [97] Kasprzyk A. Sedimentary evolution of Badenian (Middle Miocene) gypsum deposits in the northern Carpathian Foredeep[J]. Kwartalnik Geologiczny, 1999, 43(4): 449-465. [98] Peryt T M, Yuan W, Min L. Palaeogeographical zonation of gypsum facies: Middle Miocene Badenian of Central Paratethys (Carpathian Foredeep in Europe)[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013, 2(3): 225-237. [99] Taj R J, Aref M A. Structural and textural characteristics of surface halite crusts of a supratidal, ephemeral halite pan, South Jeddah, Red Sea Coast, Saudi Arabia[J]. Facies, 2015, 61(2): 2. [100] Kasprzyk A. Sedimentological and diagenetic patterns of anhydrite deposits in the Badenian evaporite Basin of the Carpathian Foredeep, southern Poland[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 158(3/4): 167-194. [101] [102] Schreiber B C. Environments of subaqueous gypsum deposition[M]//Dean W E, Schreiber B C. Marine evaporites. Oklahoma City: Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, 1978. [103] Warren J K. The hydrological setting, occurrence and significance of gypsum in Late Quaternary salt lakes in South Australia[J]. Sedimentology, 1982, 29(5): 609-637. [104] Ortí F, Salvany J M. Coastal salina evaporites of the Triassic-Liassic boundary in the Iberian Peninsula: The Alacón borehole[J]. Geologica Acta, 2004, 2(4): 291-304. [105] Kasprzyk A, Ortí F. Palaeogeographic and burial controls on anhydrite genesis: The Badenian Basin in the Carpathian Foredeep (southern Poland, western Ukraine)[J]. Sedimentology, 1998, 45(5): 889-907. [106] Kasprzyk A. Gypsum-to-anhydrite transition in the Miocene of southern Poland[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1995, 65(2a): 348-357. [107] Schreiber B C, Friedman G M, Decima A, et al. Depositional environments of Upper Miocene (Messinian) evaporite deposits of the Sicilian Basin[J]. Sedimentology, 1976, 23(6): 729-760. [108] De Putter T, Rouchy J M, Herbosch A, et al. Sedimentology and palaeo-environment of the Upper Visean anhydrite of the Franco—Belgian Carboniferous Basin (Saint-Ghislain borehole, southern Belgium)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(1/2): 77-93. [109] Dean W E, Davies G R, Anderson R Y. Sedimentological significance of nodular and laminated anhydrite[J]. Geology, 1975, 3(7): 367-372. [110] Kendall A C, Harwood G M. Marine evaporites: Arid shorelines and basins[M]//Reading H G. Sedimentary environments: Processes, facies and stratigraphy. Blackwell: Blackwell Science, 1996: 281-324. [111] Hussain M, Warren J K. Nodular and enterolithic gypsum: The “sabkha-tization” of Salt Flat playa, west Texas[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1989, 64(1/2/3): 13-24. [112] Escavy J I, Herrero M J. Enterolithic folds in evaporites as microbially induced sedimentary structures: New model of Formation and interpretation in the geological record[J]. Sedimentology, 2019, 66(6): 2214-2233. [113] Kirkland D W, Denison R E, Dean W E. Parent brine of the Castile evaporites (Upper Permian), Texas and New Mexico[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2000, 70(3): 749-761. [114] Peryt T M. Resedimentation of Basin centre sulphate deposits: Middle Miocene Badenian of Carpathian Foredeep, southern Poland[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 134(3/4): 331-342. [115] Yoshimura T, Kuroda J, Lugli S, et al. An X‐ray spectroscopic perspective on Messinian evaporite from Sicily: Sedimentary fabrics, element distributions, and chemical environments of S and Mg[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2016, 17(4): 1383-1400. [116] Gindre‐Chanu L, Warren J K, Puigdefabregas C, et al. Diagenetic evolution of Aptian evaporites in the Namibe Basin (south‐west Angola)[J]. Sedimentology, 2015, 62(1): 204-233. [117] Playà E, Ortı́ F, Rosell L. Marine to non-marine sedimentation in the Upper Miocene evaporites of the eastern Betics, SE Spain: Sedimentological and geochemical evidence[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 133(1/2): 135-166. [118] Ortí F, Rosell L, Fallick A, et al. Chert in continental evaporites of the Ebro and Calatayud basins (Spain): Distribution and significance[M]//Ramos A, Bustillo M A. Siliceous rocks and culture. Granada: Universidad de Granada, 1997: 75-89. [119] [120] Testa G, Lugli S. Gypsum–anhydrite transformations in Messinian evaporites of central Tuscany (Italy)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 130(3/4): 249-268. [121] Kinsman D J J. Modes of formation, sedimentary associations, and diagnostic features of shallow-water and supratidal evaporites[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1969, 53(4): 830-840. [122] Shearman D J, Mossop G, Dunsmore H, et al. Origin of gypsum veins by hydraulic fracture[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy B, 1972, 81: 149-155. [123] Ortí F, Rosell L, Lascorz A. Fábricas cristalinas del yeso secundario de reemplazamiento de glauberita: Aplicación en prospección de sulfato sódico[J]. Geogaceta, 1995, 17: 49-52. [124] Bąbel M. Depositional environments of a salina-type evaporite Basin recorded in the Badenian gypsum facies in the northern Carpathian Foredeep[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2007, 285(1): 107-142. [125] Ortí F, Gündogan I, Helvaci C. Sodium sulphate deposits of Neogene age: The Kirmir Formation, Beypazari Basin, Turkey[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 146(3/4): 305-333. [126] Smoot J P, Lowenstein T K. Depositional environments of non-marine evaporites[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 1991, 50: 189-347. [127] 魏东岩. 盐类沉积中的钙芒硝及其成因[J]. 矿物岩石,1988, 8(2):92-98. Wei Dongyan. Glauberite in salt deposits and its genesis[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology Mineral Rock, 1988, 8(12): 92-98. [128] Mees F. Textural features of Holocene perennial saline lake deposits of the Taoudenni–Agorgott Basin, northern Mali[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1999, 127(1/2): 65-84. [129] Salvany J M, García‐Veigas J, Ortí F. Glauberite–halite association of the Zaragoza Gypsum Formation (Lower Miocene, Ebro Basin, NE Spain)[J]. Sedimentology, 2007, 54(2): 443-467. [130] 刘成林,焦鹏程,陈永志,等. 罗布泊盐湖晚更新世末期芒硝岩沉积及其古气候意义[J]. 地球学报,2008,29(4):397-404. Liu Chenglin, Jiao Pengcheng, Chen Yongzhi, et al. Late Pleistocene mirabilite deposition in the lop Nur Saline Lake, Xinjiang, and its paleoclimate implications[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2008, 29(4): 397-404. [131] 赵海彤,刘成林,焦鹏程,等. 罗布泊干盐湖钙芒硝形貌特征及生长影响因素[J]. 矿物学报,2014,34(1):97-106. Zhao Haitong, Liu Chenglin, Jiao Pengcheng, et al. Morphology characteristics and influential factors of glauberite growth from lop Nur Salt Lake, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2014, 34(1): 97-106. [132] Salvany J M, Ortí F. Miocene glauberite deposits of Alcanadre, Ebro Basin, Spain: Sedimentary and diagenetic processes[M]//Renaut R W, Last W M. Sedimentology and geochemistry of modern and ancient saline lakes models. Tulsa: SEPM, 1994: 203-215. [133] Wang N A, Li Z L, Li Y, et al. Younger Dryas event recorded by the mirabilite deposition in Huahai lake, Hexi Corridor, NW China[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 250: 93-99. [134] 袁见齐,霍承禹,蔡克勤. 高山深盆的成盐环境:一种新的成盐模式的剖析[J]. 地质论评,1983, 29(2):159-165. Yuan Jianqi, Huo Chengyu, Cai Keqin. The high mountain-deep Basin saline environment: A new genetic model of salt deposits[J]. Geological Review, 1983, 29(2): 159-165. [135] 钱自强,曲一华,刘群. 钾盐矿床[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1994. Qian Ziqiang, Qu Yihua, Liu Qun. Potash deposit[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994. [136] 刘群,杜之岳,陈郁华. 陕北奥陶系和塔里木石炭系钾盐找矿远景[M]. 北京:原子能出版社,1997:30-37. Liu Qun, Du Zhiyue, Chen Yuhua. Potash salt-searching prospects in northern Shanxi Ordovician and Tarim Carboniferous[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1997: 30-37. [137] 刘成林,王弭力,焦鹏程,等. 世界主要古代钾盐找矿实践与中国找钾对策[J]. 化工矿产地质,2006,28(1):1-8. Liu Chenglin, Wang Mili, Jiao Pengcheng, et al. The exploration experiences of potash deposits in the world and probing of countermeasures of China's future potash-deposits investigation[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2006, 28(1): 1-8. [138] Handford C R. Halite depositional facies in a solar salt pond: A key to interpreting physical energy and water depth in ancient deposits?[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(8): 691-694. [139] Logan B W. The MacLeod evaporite Basin, western Australia: Holocene environments, sediments and geological evolution[M]. Tulsa, Okla: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1987. [140] Benison K C, Goldstein R H. Permian paleoclimate data from fluid inclusions in halite[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 154(1/2/3/4): 113-132. [141] Zambito J J, Benison K C. Extremely high temperatures and paleoclimate trends recorded in Permian ephemeral lake halite[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(5): 587-590. [142] 张华, 刘成林, 赵艳军,等. 老挝他曲地区石盐流体包裹体特征、氢氧同位素组成及成盐物质补给方式[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(011):2134-2140. Zhang Hua, Liu Chenglin, Zhao Yanjunet al. Characteristics and hydrogen-oxygen isotopic compositions of halite fluid inclusions in the Thakhek Area, Lao, and the way of salt material supplies[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2015, 89(011):2134-2140. [143] Shearman D J. Recent halite rock, Baja California, Mexico[J]. Trans Min Metall, 1970, 79B: 155-162. [144] Rouchy J M, Bernet-Rollande M C, Maurin A F. Descriptive petrography of evaporites: Application in the field, subsurface and laboratory[M]//Majithia M. Evaporite sequences in petroleum exploration: Geological methods. Editions Technip, Paris: 1994. [145] Casas E, Lowenstein T K, Spencer R J, et al. Carnallite mineralization in the nonmarine, Qaidam Basin, China; Evidence for the early diagenetic origin of potash evaporites[J]. Journal of sedimentary Research, 1992, 62(5): 881-898. [146] Hovorka S. Depositional environments of marine‐dominated bedded halite, Permian San Andres Formation, Texas[J]. Sedimentology, 1987, 34(6): 1029-1054. [147] Schubel K A, Lowenstein T K. Criteria for the recognition of shallow-perennial-saline-lake halites based on recent sediments from the Qaidam Basin, western China[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1997, 67(1): 74-87. [148] Tekin E, Ayyildiz T, Gündoğan İ, et al. Modern halolites (halite oolites) in the Tuz Gölü, Turkey[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2007, 195(3/4): 101-112. [149] Castanier S, Perthuisot J P, Matrat M, et al. The salt ooids of Berre salt works (Bouches du Rhône, France): The role of bacteria in salt crystallisation[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1999, 125(1/2): 9-21. [150] Lowenstein T K, Hardie L A. Criteria for the recognition of salt‐pan evaporites[J]. Sedimentology, 1985, 32(5): 627-644. [151] Gornitz V M, Schreiber B C. Displacive halite hoppers from the Dead Sea; some implications for ancient evaporite deposits[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1981, 51(3): 787-794. [152] 王立成,刘成林,王延路. 前陆盆地钾盐矿床成因及模式:以西班牙北部埃布罗盆地为例[J]. 矿床地质,2016,35(6):1243-1256. Wang Licheng, Liu Chenglin, Wang Yanlu. Genesis and Formation model of potash deposits in foreland basins: A case study of Ebro Basin, northern Spain[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2016, 35(6): 1243-1256. [153] 马金元,胡生忠,田向东. 柴达木盆地马海钾盐矿床沉积环境与开发[J]. 盐湖研究,2010,18(3):9-17. Ma Jinyuan, Hu Shengzhong, Tian Xiangdong. Sedimentary environment and exploitation of maihai potash deposits in Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2010, 18(3): 9-17. [154] 郑剑锋,沈安江,刘永福,等. 塔里木盆地寒武系与蒸发岩相关的白云岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(1):89-98. Zheng Jianfeng, Shen Anjiang, Liu Yongfu, et al. Main controlling factors and characteristics of Cambrian dolomite reservoirs related to evaporite in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(1): 89-98. [155] Cornée J J, Münch P, Achalhi M, et al. The Messinian erosional surface and early Pliocene reflooding in the Alboran Sea: New insights from the Boudinar Basin, Morocco[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 333: 115-129. [156] Carrillo-Chávez A, Salas-Megchún E, Levresse G, et al. Geochemistry and mineralogy of mine-waste material from a “skarn-type” deposit in central Mexico: Modeling geochemical controls of metals in the surface environment[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 144: 28-36. [157] Taberner C, Cendón D I, Pueyo J J, et al. The use of environmental markers to distinguish marine vs. continental deposition and to quantify the significance of recycling in evaporite basins[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 137(3/4): 213-240. [158] Holser W T. Diagenetic polyhalite in recent salt from Baja California[J]. American Mineralogist, 1966, 51(1/2): 99-109. [159] Perthuisot J P. Recent polyhalite from Sebkha el Melah (Tunisia)[J]. Nature Physical Science, 1971, 232(35): 186-187. [160] Liu Z F, Wang C S. Facies analysis and depositional systems of Cenozoic sediments in the Hoh Xil Basin, northern Tibet[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2001, 140(3/4): 251-270. [161] Walker R G, Plint A G. Wave- and storm-dominated shallow marine systems[M]//Walker R G, James N P. Facies models-response to sea level changes. St. John’s: Geological Association of Canada, 1992: 219-238. [162] Warren J K. Evaporite sedimentology: Importance in hydrocarbon accumulation[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 1989: 285. [163] 林耀庭,陈绍兰. 论四川盆地下、中三叠统蒸发岩的生成模式、成盐机理及找钾展望[J]. 盐湖研究,2008,16(3):1-10. Lin Yaoting, Chen Shaolan. Discussion on the evaporite generating modes, saltforming mechanism and potassium-hunting prospect of Lower-Middle Triassic in Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2008, 16(3): 1-10. [164] 刘成林,吴驰华,王立成,等. 中国陆块海相盆地成钾条件与预测研究进展综述[J]. 地球学报,2016,37(5):581-606. Liu Chenglin, Wu Chihua, Wang Licheng, et al. Advance in the study of forming condition and prediction of potash deposits of marine basins in China’s Small blocks: Review[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2016, 37(5): 581-606. [165] 王春连,刘成林,王立成,等. 钾盐矿床成矿条件研究若干进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2013,28(9):976-987. Wang Chunlian, Liu Chenglin, Wang Licheng, et al. Reviews on potash deposit metallogenic conditions[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2013, 28(9): 976-987. -





 下载:
下载: