-
致密油是非常规油气资源的重要类型,目前已成为我国非常规石油勘探中最现实的领域之一,我国鄂尔多斯盆地、准噶尔盆地、松辽盆地等均在致密油勘探开发方面取得了重要的进展[1⁃2]。扶余油层是松辽盆地南部最主要的含油层系,其对应的下白垩统泉四段为一套陆相河流—三角洲沉积体系产物,砂岩成分成熟度较低,在普遍致密的背景下,局部地区形成相对高孔渗的储层而形成岩性油藏[3⁃5]。目前,扶余油层勘探面临的主要问题是剩余勘探目标以低品味、致密储集层为主。2012年吉林油田确定以扶余油层为重点,针对河道砂岩储集体开展水平井钻探+体积压裂技术攻关,实现超低渗透油层有效动用,表明扶余油层已进入致密油勘探阶段。储层物性的好坏受原始沉积相带和后期埋藏过程中成岩演化的控制,成岩作用在致密砂岩埋藏过程中对储层的改造起着关键作用[6⁃14]。以往的研究已认识到扶余油层“甜点”受分流河道砂体分布的控制,并开展了很多砂体展布特征和储层预测的研究[15⁃16]。除了受沉积微相的控制和影响,扶余油层致密油储层的分布受成岩作用影响显著,虽然前人讨论了研究区成岩作用对储层物性和含油性的影响[17⁃20],但并没有进行成岩作用影响下储层分布规律的研究。而查明成岩作用对致密油储层分布规律的影响,从而为储层预测提供依据,对致密油勘探有着至关重要的作用。因此,本文以松南让字井斜坡带泉四段扶余油层为例,通过岩石薄片、黏土矿物X衍射、扫描电镜实验分析及物性、高压压汞等实验资料,开展储层成岩作用及演化阶段研究,阐明成岩作用对致密油储层分布规律的影响,以期对研究区致密油勘探有所助益。
-
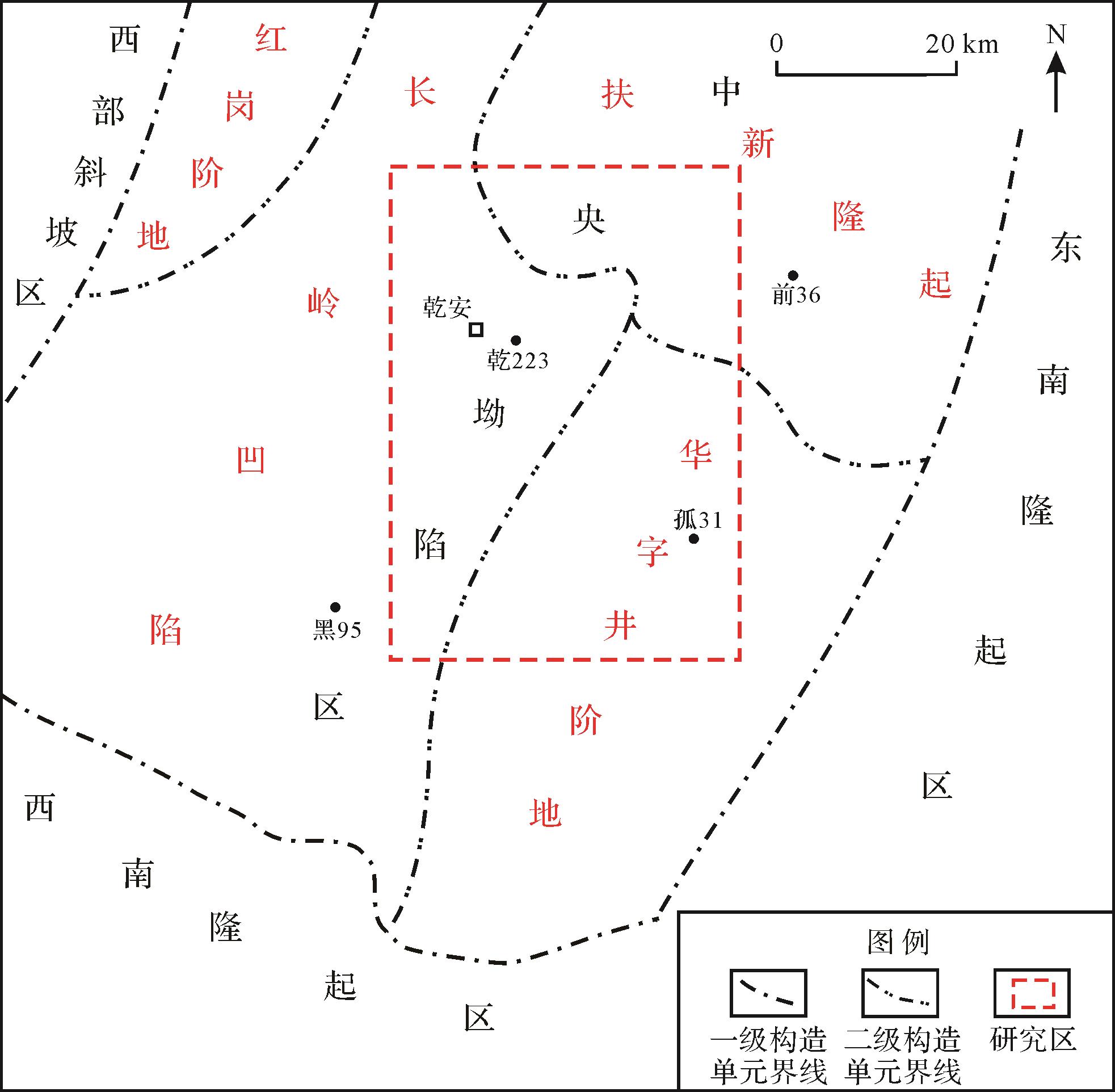
松辽盆地南部中央坳陷区为东南西三面隆起,北部平缓的“U”形凹陷,进一步划分红岗阶地、长岭凹陷、华字井阶地及扶新隆起带4个二级构造单元(图1)。让字井斜坡带是松辽盆地南部重要的富油气区之一,地跨长岭凹陷、扶新隆起、华字井阶地3个二级构造单元[20]。白垩系为松辽盆地主要的沉积盖层,自下而上依次发育下白垩统火石岭组、沙河子组、营城组、登娄库组、泉头组(自下而上划分为泉一段、泉二段、泉三段、泉四段),上白垩统青山口组、姚家组、嫩江组、四方台组、明水组[21]。扶余油层是松辽盆地南部最主要的含油层系,为上覆青山口组烃源岩与下伏泉头组四段致密砂岩形成的“上生下储”型岩性油藏[4,16]。按照国内致密油的定义,松辽盆地南部扶余油层埋深大于1 750 m,储层孔隙度小于12%、渗透率小于1.0×10-3 μm2(覆压基质渗透率为0.1×10-3 μm2),为未经过长距离运移,广覆式成藏、无统一油水界面、无明显油藏边界的典型致密油[16]。其面积大约为5 000 km2,主要分布在红岗阶地、长岭凹陷、华字井阶地北部及扶新隆起带西部[16]。
研究区泉四段埋深1 400~2 600 m,地层分布稳定,厚度为100~120 m,厚度变化较小。研究表明,泉头组沉积时期,松南中央坳陷区的物源主要来自坳陷西、西南和东南方向,该时期地势平坦,古地形坡度小于1°,为大型浅水三角洲的发育提供了稳定沉降的盆地构造基础[3,21]。中央坳陷区浅水三角洲分流河道砂体广泛分布,发育分流河道、水下分流河道,不发育河口坝和远砂坝[21]。单个河道砂体的规模大小不等,厚度一般小于5 m,垂向上多个间断正韵律相互叠置,形成厚达十几米甚至几十米的复合砂体,砂地比大于40%,砂体厚度为35~80 m,盆地范围内广泛分布[16]。
松辽盆地扶余油层致密油具有上生下储式“倒灌”成藏特点,泉四段顶面断裂发育,断裂沟通上覆青一段烃源岩与泉四段致密砂岩储层,由于储集层较致密,孔隙及喉道狭小,原油富集到致密储层中,形成大面积分布的致密油藏[4,22]。
-
对研究区扶余油层15口取心井220块铸体薄片的观察鉴定表明,储层砂岩成分成熟度较低,岩石类型主要为长石岩屑砂岩和岩屑长石砂岩。陆源碎屑主要见石英、长石和岩屑,其中石英含量为20%~45%,平均34%;长石含量15%~40%,平均28%;岩屑以火成岩岩屑为主,含量为25%~45%,平均36%。颗粒间杂基与胶结物共存,杂基以泥质杂基为主,含量一般小于5%;胶结物以石英、方解石、白云石、自生黏土矿物为主,以及少量黄铁矿和菱铁矿。颗粒粒径一般为0.07~0.30 mm,主要为细砂岩,其次为中砂岩和粉砂岩,含极少量粗砂岩。分选好—中等,磨圆度以次棱角—次圆为主。颗粒间多为孔隙式和接触式胶结。
根据岩心实测物性资料,研究区扶余油层储层孔隙度主要分布范围为2%~14%,平均8.54%,其中孔隙度小于10%的储层占70.04%;渗透率主要分布范围为(0.01~5)×10-3 μm2,平均0.493×10-3 μm2,其中小于1×10-3 μm2的储层占92.80%;根据高压压汞资料,储层孔喉半径分布范围为0.1~2 μm,平均0.206 μm,总体上储层孔喉细小。孔喉分选系数介于0.55~4.4,平均2.7,分选系数较大,孔喉分选较差。储层排驱压力为0.1~2.8 MPa,平均0.7 MPa。按照储层孔隙结构参数分级,研究区扶余油层总体上物性差,为一套低孔特低渗致密砂岩储层。
-
通过偏光显微镜和扫描电镜观察,研究区扶余油层致密油储层成岩作用主要有压实作用、胶结作用、溶蚀作用及交代作用,溶蚀作用改善致密油储层物性,形成了低孔渗有效储集层。
-
强压实作用是研究区扶余油层储层致密的重要原因。偏光显微镜下见到储层颗粒之间以线—凹凸接触为主,云母等塑性颗粒的挠曲变形,火山岩屑被压实后呈假杂基状等现象(图2a)。研究区致密油储层形成于三角洲平原及前缘沉积环境,岩石粒度细,以细砂岩为主,且成分成熟度低,岩屑主要为塑性的火山岩屑,岩石抗压性差,强烈的压实作用导致大量的原生孔隙损失,颗粒间紧密接触,孔喉变得细小,最终导致岩石的致密化。因此,强压实作用是造成储层致密最重要的原因。
-
研究区扶余油层致密油储层硅质胶结物普遍出现,产状主要为石英次生加大,以及少量微晶石英,含量介于1%~3%(图2b,c)。自生石英加大边宽度小于0.05 mm,加大级别为Ⅱ~Ⅲ级[16]。微晶石英虽然含量较少,但堵塞孔隙和喉道,导致储层物性变差。硅质胶结物的含量与砂岩中石英含量呈明显的正相关关系,随石英含量增加,硅质胶结物含量增高。另外,随着储集层埋藏深度的增加,硅质胶结作用增强。
-
碳酸盐胶结也是导致储层物性变差的因素。研究区扶余油层致密油储层碳酸盐胶结物主要为铁方解石和铁白云石,通常呈嵌晶状充填在颗粒之间或交代骨架颗粒,含量一般小于3%(图2d)。这种碳酸盐胶结物形成时间较晚,主要为中成岩期产物,通常与有机酸脱羧作用及长石、火山岩屑骨架颗粒的溶解有关[11]。随着储层埋藏深度的增加,铁方解石、铁白云石含量增加。
另外,在分流河道沉积旋回底部的滞留沉积或旋回顶部天然堤相粉细砂岩中,常见方解石呈基底式连晶胶结,含量介于5%~18%,形成钙质胶结砂岩,往往成为储层之间的封隔层。在这种基底式胶结的钙质砂岩中,碎屑颗粒呈漂浮状,反映了钙质胶结的形成时间较早,可能为成岩早期直接从过饱和碱性湖水介质中析出的产物[23⁃24]。
-
研究区扶余油层砂岩储集层中的黏土矿物具有含量低、晶形好的特点,主要为自生成因。根据扶余油层致密油储层47块岩心样品X衍射全岩及黏土矿物实验分析,黏土矿物的绝对含量通常为6%~37.7%,平均为15.1%。黏土矿物种类主要为伊/蒙混层(I/S)、伊利石(I)、高岭石(K)、绿泥石(C)。其中伊蒙混层相对含量为29%~87%,平均68.4%,通常呈颗粒包膜和孔隙充填形式;伊利石相对含量为10%~24%,平均15.2%,通常呈丝网状在孔隙中搭桥式生长(图2e)。纵向上,随着深度的增加伊利石相对含量有逐渐增加的趋势;自生高岭石相对含量为0~44%,平均11.4%,呈片状或蠕虫状充填孔隙(图2e)。高岭石是在酸性条件下钾长石和富长石的火山岩屑溶蚀作用形成的黏土矿物,通常情况下,高岭石含量高的地方,往往预示着次生孔隙发育带[25];绿泥石相对含量为0~26%,平均2.5%,多呈孔隙衬垫式产出(图2f)。值得指出,这种以孔隙衬垫式产出的自生绿泥石在我国中新生代陆相含油气盆地储层砂岩中广泛存在,Baker et al.[8]认为其是淡水作用下的近岸海相沉积环境的良好相标志,一些学者认为这种孔隙衬垫式绿泥石膜的生长能够抑制石英次生加大,从而对孔隙及储层保护具有积极意义,其大量存在可能指示了陆相三角洲的推进[26⁃27]。总体上,黏土矿物在孔隙内沉淀,阻塞孔隙和喉道,对储层物性起破坏作用。
除上述三种主要的胶结作用外,储层中还可见少量的长石加大、黄铁矿胶结作用,对储层物性影响较小。
-
薄片观察表明,研究区扶余油层致密油储层孔隙类型主要是次生溶蚀孔和残余原生孔(图2g,h),在扫描电镜下可见清楚的颗粒溶蚀微孔和粒间黏土矿物晶间孔(图2i~l)。次生溶蚀孔隙溶蚀成分主要为长石及火山岩屑,常见长石沿其解理缝或双晶面溶蚀,以及火山岩屑被溶解成蜂窝状或完全溶蚀后形成颗粒溶孔、铸模孔。值得注意的是,呈假杂基状的火山岩屑溶蚀后,经常造成孔隙是原生孔隙的假象,但仔细观察孔隙内普遍见很多火山岩屑溶蚀后的残余(图2g,h)。溶蚀作用改善了储层物性,形成了低孔渗有效储集层。次生溶蚀孔隙发育的有效储层多为细—中粒、富含刚性颗粒的三角洲水下分流河道、分流河道砂岩(图3),分析其原因主要是河道砂岩粒度较粗,石英等刚性颗粒含量较高,烃源岩有机质成熟过程中生成的酸性流体易进入形成次生溶蚀孔隙;而分流河道间沉积的粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩粒度细,杂基含量高,抗压实能力弱,强压实作用下次生溶蚀孔隙不发育,形成河道砂岩储层之间的封隔层。
-
研究区扶余油层储层中交代作用十分普遍,既有自生矿物对颗粒的交代,如碳酸盐胶结物对长石及火山岩屑颗粒的交代;也有自生矿物之间的交代,如铁方解石、铁白云石等碳酸盐胶结物对石英加大边的交代,铁白云石胶结物对铁方解石胶结物的交代等现象。
-
随着储层埋深增大,成岩作用增强,成岩阶段发生变化,储集性亦随之发生变化。行业内通常采用I∕S混层黏土矿物的演变作为划分成岩阶段的主要依据[11,28]。本文根据研究区泉四段扶余油层泥岩I∕S混层比,结合其他的成岩作用特征来确定致密油储层所处的成岩阶段。根据研究区五口井(乾223井、乾238井、查45井、让53井、乾144井)泉四段不同埋藏深度67块泥岩X衍射黏土分析测试结果,结合自生矿物特征、有机质成熟度等资料,按照成岩阶段划分标准(表1),认为研究区扶余油层致密油储层目前处在中成岩A2~B期。总体上,由斜坡区向坳陷区,研究区扶余油层成岩演化阶段依次由中成岩A2期向中成岩B期过渡。
表 1 (I/S)混层比与成岩阶段关系表[28]
(I∕S)混层类型 混层转化带 (I∕S)混层比/(%) 有机质成熟度 碎屑岩成岩阶段划分标准 蒙皂石 蒙皂石带 >70 未成熟 早成岩A期 无序混层 渐变带 50~70 半成熟 早成岩B期 有序混层 部分有序 第一迅速转化带 35~50 低成熟 中成岩期 A A1 有序 第二迅速转化带 15~35 成熟 A2 超点阵 第三转化带 <15 高成熟 B 伊利石 过成熟 晚成岩期 研究区泉四段泥岩I∕S混层比介于25%~5%,且随着埋藏深度的增大,I∕S混层比逐渐降低,同时随着埋藏深度的增大,储层孔隙度、渗透率总体上也呈逐渐降低的趋势。如图4所示,在埋藏深度1 750~2 250 m,I∕S混层比为25%~15%,对应的成岩阶段为中成岩A2期。这一时期随着储层埋藏深度的增大,压实作用持续增强及硅质、碳酸盐、黏土矿物等自生矿物的大量胶结,储集层物性已明显变差。这一时期Ro介于0.9%~1.3%,有机质正处于成熟—高成熟阶段,有机质的成熟生烃促进了储层中长石、火山岩屑等不稳定组分在酸性环境下溶蚀,是次生溶蚀孔隙发育时期。此深度带为次生溶蚀孔隙发育带,目前致密油开采多在本带。当埋藏深度大于2 250 m时,泥岩I∕S混层比小于15%,对应的成岩阶段为中成岩B期。这一时期Ro大于1.3%,有机质处于过成熟阶段。随着埋藏深度增大,储层压实作用及自生矿物胶结、交代作用进一步增强,孔隙迅速地减少,储层进一步致密。
-
基于上述宏观规律认识,本文应用物性及压汞实验资料,将研究区扶余油层划分为常规储层、Ⅰ类致密油储层、Ⅱ类致密油储层与Ⅲ类致密油储层。纵向上,储层物性在很大程度上受控于后期成岩作用,随埋藏深度的增加,各类储层依次出现,储集性能逐渐变差(图5)。

图 5 研究区扶余油层储层类型划分
Figure 5. Diagenetic stages and reservoir property changes in Fuyu reservoir in the study area
常规储层:埋深主要介于1 400~1 750 m,目前处于中成岩A2期,薄片观察表明颗粒之间为点—线接触,孔隙类型为残余原生孔隙和次生溶蚀孔隙并存。孔隙度为10%~18%,渗透率为(1~10)×10-3 μm2;压汞曲线中—粗歪,排驱压力小于0.5 MPa,压汞资料分析表明对渗透率起贡献的主力孔喉分布范围为0.7~4 μm。
Ⅰ类致密油储层:埋深主要介于1 750~2 000 m,目前处于中成岩A2期,颗粒之间以线接触为主,少量凹凸接触,孔隙类型为次生溶蚀孔隙和残余原生孔隙并存。孔隙度为8%~12%,渗透率为(0.1~1)×10-3 μm2;压汞曲线为中歪,排驱压力0.5~1 MPa,对渗透率起贡献的主力孔喉分布范围为0.3~2 μm。
Ⅱ类致密油储层:埋深主要介于2 000~2 250 m,目前处于中成岩A2期,颗粒之间为线接触—凹凸接触,孔隙类型为次生溶蚀孔隙和少量残余原生孔隙。孔隙度为5%~8%,渗透率为(0.05~0.1)×10-3 μm2;压汞曲线为细歪,排驱压力1~2 MPa,对渗透率起贡献的主力孔喉分布范围为0.15~0.5 μm。
Ⅲ类致密油储层:埋深一般大于2 250 m,成岩演化阶段已进入中成岩B期,颗粒之间主要为凹凸接触,孔隙类型主要为次生溶蚀溶蚀微孔。孔隙度小于5%,渗透率小于0.05×10-3 μm2;压汞曲线极细歪,排驱压力通常大于2 MPa,对渗透率起贡献的主力孔喉分布一般小于0.2 μm。
-
平面上,让字井斜坡带各类储层分布主要受埋深的控制,总体上由东部的隆起区向西部凹陷区依次为常规储层、Ⅰ类致密油储层、Ⅱ类致密油储层和Ⅲ类致密油储层(图6)。构造高部位的常规储层虽然物性好,但以含水为主,而致密油储层分布区连片含油。从勘探效果来看,该研究区致密油勘探最有利的是Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类致密油储层,即最有利的勘探深度范围为1 750~2 250 m。
-
(1) 松辽盆地南部让字井斜坡带扶余油层以细砂岩为主,砂岩成分成熟度较低,岩石类型主要为长石岩屑砂岩和岩屑长石砂岩,物性总体较差,为一套低孔特低渗致密砂岩储层。溶蚀作用改善了储层物性,形成了低孔渗有效储集层,溶蚀孔隙发育的有效储层多为三角洲水下分流河道、分流河道砂岩。
(2) 研究区扶余油层泥岩I∕S混层比介于25%~5%,且随着埋藏深度的增大,I∕S混层比逐渐降低,储层孔隙度、渗透率总体上也随埋深增大呈逐渐降低的趋势。在埋藏深度1 750~2 250 m,I∕S混层比为25%~15%,对应的成岩阶段为中成岩A2期,此深度带为次生溶蚀孔隙发育带,目前致密油开采多在本带;当埋藏深度大于2 250 m时,I∕S混层比小于15%,对应的成岩阶段为中成岩B期,储层进一步致密,孔隙迅速地减少。
(3) 将研究区扶余油层划分为常规储层及Ⅰ类致密油储层、Ⅱ类致密油储层与Ⅲ类致密油储层。纵向上,随埋藏深度的增加,各类储层依次出现。致密油勘探最有利的是Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类致密油储层,最有利的勘探深度范围为1 750~2 250 m。
Influence of Diagenesis on the Distribution of Tight Oil Reservoirs: A case study of the Fuyu reservoir, Rangzijing slope zone, southern Songliao Basin
-
摘要: 扶余油层是松辽盆地南部最主要的含油层系,目前已进入致密油勘探阶段,查明成岩作用对致密油储层形成和分布规律的影响,对致密油勘探有着至关重要的作用。以松南让字井斜坡带泉四段扶余油层为例,通过岩石薄片、黏土矿物X衍射、扫描电镜实验分析及物性、高压压汞等实验资料,开展成岩作用对致密油储层分布规律的影响研究。研究表明,研究区扶余油层溶蚀孔隙发育的有效储层多为三角洲水下分流河道、分流河道砂岩。在埋藏深度1 750~2 250 m,I/S混层比为25%~15%,对应的成岩阶段为中成岩A2期,此深度带为次生溶蚀孔隙发育带,目前致密油开采多在本带;当埋藏深度大于2 250 m时,I/S混层比小于15%,对应的成岩阶段为中成岩B期,储层进一步致密。将研究区扶余油层划分为常规储层及Ⅰ类致密油储层、Ⅱ类致密油储层与Ⅲ类致密油储层,在纵向上,随埋藏深度的增加,各类储层依次出现。研究区扶余油层致密油勘探最有利的是Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类致密油储层,最有利的勘探深度介于1 750~2 250 m。Abstract: The Fuyu reservoir in the Fourth member of the Quantou Formation is the most important oil-bearing reservoir in the southern Songliao Basin, and is currently being explored for tight oil resources. The diagenesis is highly influential in the formation and distribution of tight oil reservoirs. The Fuyu reservoir, located in the Rangzijing slope zone, was studied to determine the influence of diagenesis on the distribution of tight oil reservoirs using the methods of thin sections, clay mineral XRD, SEM observations, physical properties, high-pressure Hg injection and other experimental techniques. These showed that most of the effective reservoirs with dissolution pores in the study area comprise deltaic underwater distributary channels and resulting sandstone. At depths of 1 750⁃2 250 m, the mudstone I/S mixture ratio is 15%⁃25%, and the reservoir is at the mid-diagenetic A2 stage, with secondary dissolution pores. This is the main tight-oil exploitation zone. Below 2 250 m the mudstone I/S mixing ratio is less than 15%, and the reservoir is accordingly at mid-diagenetic stage B. In the study area the Fuyu reservoir is divided into conventional reservoir and tight-oil reservoir types I, II and III. Longitudinally, all reservoir types appear in turn with increasing depth. The most favorable reservoirs in the study area are types I and II. The most favorable exploration depth is between 1 750 m and 2 250 m.
-
Key words:
- diagenesis /
- tight oil /
- tight sandstone /
- reservoir distribution /
- Fuyu reservoir
-
图 2 研究区扶余油层致密油储层主要成岩作用特征
(a)强压实作用下颗粒间线—凹凸接触,塑性岩屑呈假杂基状,让53井,2 112.7 m,单偏光;(b)石英的次生加大,乾223井,2 204.9 m,正交偏光;(c)充填孔隙的自生石英,乾223井,2 185.0 m;(d)充填与颗粒之间或交代骨架颗粒的铁方解石胶结物,乾223井,2 185.6 m,单偏光;(e)充填孔隙的蠕虫状高岭石、丝状伊利石和石英胶结物,乾223井,2 203.5 m;(f)孔隙衬垫式产出的绿泥石胶结物,乾223井,2 185.6 m;(g)孔隙类型主要为次生溶蚀孔和残余原生孔,乾223井,2 204.9 m,单偏光;(h)孔隙类型主要为次生溶蚀孔和残余原生孔,让24井,1 875.6 m,单偏光;(i,j)钾长石沿其解理缝或双晶面溶蚀,让53井,2 113.7 m;(k,l)黏土矿物间微孔,让53井,2 113.7 m
Figure 2. Main diagenesis characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Fuyu reservoir in the study area
(a) concavo⁃convex contact between particles due to strong compaction, well R53, 2 112.7 m (single polarized light); (b) secondary enlargement of quartz, well Q223, 2 204.9 m (orthogonal polarized light); (c) authigenic quartz pore infill, well Q223, 2 185.0 m; (d) iron calcite cement intergrain infill or metasomatized skeleton grains, well Q223, 2 185.6 m (single polarized light); (e) vermicular kaolinite, filamentous illite and quartz cement pore infilling, well Q223, 2 203.5 m; (f) chlorite cement produced by pore pad type, well Q223, 2 185.6 m; (g) mainly granular dissolution pores and a few residual intergrain pores, well Q223, 2 204.9 m (single polarized light); (h) mainly granular dissolution pores and a few residual intergrain pores, well R24, 1 875.6 m (single polarized light); (i, j) potassium feldspar dissolved along cleavage joints or double crystal faces, well R53, 2 113.7 m; (k, l) micropores between clay minerals, well R53, 2 113.7 m
表 1 (I/S)混层比与成岩阶段关系表[28]
(I∕S)混层类型 混层转化带 (I∕S)混层比/(%) 有机质成熟度 碎屑岩成岩阶段划分标准 蒙皂石 蒙皂石带 >70 未成熟 早成岩A期 无序混层 渐变带 50~70 半成熟 早成岩B期 有序混层 部分有序 第一迅速转化带 35~50 低成熟 中成岩期 A A1 有序 第二迅速转化带 15~35 成熟 A2 超点阵 第三转化带 <15 高成熟 B 伊利石 过成熟 晚成岩期 -
[1] 贾承造,邹才能,李建忠,等. 中国致密油评价标准、主要类型、基本特征及资源前景[J]. 石油学报,2012,33(3):343-350. Jia Chengzao, Zou Caineng, Li Jianzhong, et al. Assessment criteria, main types, basic features and resource prospects of the tight oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3): 343-350. [2] 邹才能,陶士振,侯连华,等. 非常规油气地质[M]. 2版. 北京:地质出版社,2013. Zou Caineng, Tao Shizhen, Hou Lianhua, et al. Unconventional hydrocarbon geology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2013. [3] 赵志魁,张金亮,赵占银,等. 松辽盆地南部坳陷湖盆沉积相和储层研究[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2009. Zhao Zhikui, Zhang Jinliang, Zhao Zhanyin, et al. Reservoir sedimentology in southern Songliao Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2009. [4] 侯启军. 深盆油藏—松辽盆地扶杨油层油藏形成与分布[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2010. Hou Qijun. Distribution of deep basin oil: Fuyang layer in Songliao Basin for example[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010. [5] 陶士振,袁选俊,侯连华,等. 大型岩性地层油气田(区)形成与分布规律[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(11):1613-1624. Tao Shizhen, Yuan Xuanjun, Hou Lianhua, et al. The regularities of formation and distribution of giant litho-stratigraphic oil and gas fields[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(11): 1613-1624. [6] Ehrenberg S N. Relationship between diagenesis and reservoir quality in sandstones of the Garn Formation, Haltenbanken, Mid-Norwegian Continental Shelf[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(10): 1538-1558. [7] Taylor T R, Soule C H. Reservoir characterization and diagenesis of the Oligocene 64-zone sandstone, North Belridge Field, Kern County, California[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(9): 1549-1566. [8] Baker J C, Havord P J, Martin K R, et al. Diagenesis and petrophysics of the Early Permian Moogooloo sandstone, southern Carnarvon Basin, western Australia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(2): 250-265. [9] Salem A M, Morad S, Mato L F, et al. Diagenesis and reservoir-quality evolution of fluvial sandstones during progressive burial and uplift: Evidence from the Upper Jurassic Boipeba member, Reconcavo Basin, northeastern Brazil[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(7): 1015-1040. [10] Morad S, Al-Ramadan K, Ketzer J M, et al. The impact of diagenesis on the heterogeneity of sandstone reservoirs: A review of the role of depositional facies and sequence stratigraphy[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2010, 94(8): 1267-1309. [11] 应凤祥,罗平,何东博,等. 中国含油气盆地碎屑岩储集层成岩作用与成岩数值模拟[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2004. Ying Fengxiang, Luo Ping, He Dongbo, et al. Clastic reservoirs diagenesis and diagenetic numerical simulation of oil and gas bearing basins in China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004. [12] 于炳松,林畅松. 油气储层埋藏成岩过程中的地球化学热力学[J]. 沉积学报,2009,27(5):896-903. Yu Bingsong, Lin Changsong. Geochemical thermodynamics of diagenesis in reservoirs for oil and gas[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 896-903. [13] 张响响,邹才能,朱如凯,等. 川中地区上三叠统须家河组储层成岩相[J]. 石油学报,2011,32(2):257-264. Zhang Xiangxiang, Zou Caineng, Zhu Rukai, et al. Reservoir diagenetic facies of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 257-264. [14] 孟元林,焦金鹤,田伟志,等. 松辽盆地北部泉头组三、四段储层质量预测[J]. 沉积学报,2011,29(6):1023-1030. Meng Yuanlin, Jiao Jinhe, Tian Weizhi, et al. Reservoir quality prediction of the member 3 and member 4 of the Quantou Formation in the northern Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(6): 1023-1030. [15] 邓庆杰,胡明毅,胡忠贵,等. 浅水三角洲分流河道砂体沉积特征:以松辽盆地三肇凹陷扶Ⅱ—Ⅰ组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2015,36(1):118-127. Deng Qingjie, Hu Mingyi, Hu Zhonggui, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of shallow-water delta distributary channel sand bodies: A case from Ⅱ-Ⅰ Formation of Fuyu oil layer in the Sanzhao Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(1): 118-127. [16] 唐振兴,赵家宏,王天煦. 松辽盆地南部致密油“甜点区(段)”评价与关键技术应用[J]. 天然气地球科学,2019,30(8):1114-1124. Tang Zhenxing, Zhao Jiahong, Wang Tianxu. Evaluation and key technology application of "sweet area" of tight oil in southern Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(8): 1114-1124. [17] 田立柱,董清水,厚刚福,等. 松辽盆地南部扶余油层砂岩成岩作用研究:以扶余油田和新立油田为例[J]. 地质调查与研究,2007,30(1):27-32. Tian Lizhu, Dong Qingshui, Hou Gangfu, et al. Research on the Fuyu reservoir sandstone diagenesis in south of Songliao Basin: Exampled by the Fuyu and Xinli oilfields[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2007, 30(1): 27-32. [18] 操应长,葸克来,朱如凯,等. 松辽盆地南部泉四段扶余油层致密砂岩储层微观孔喉结构特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2015,39(5):7-17. Cao Yingchang, Xi Kelai, Zhu Rukai, et al. Microscopic pore throat characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs in Fuyu layer of the Fourth member of Quantou Formation in southern Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2015, 39(5): 7-17. [19] 操应长,葸克来,刘可禹,等. 陆相湖盆致密砂岩油气储层储集性能表征与成储机制:以松辽盆地南部下白垩统泉头组四段为例[J]. 石油学报,2018,39(3):247-265. Cao Yingchang, Xi Kelai, Liu Keyu, et al. Reservoir properties characterization and its genetic mechanism for tight sandstone oil and gas reservoir in lacustrine basin: The case of the Fourth member of Lower Cretaceous Quantou Formation in the southern Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(3): 247-265. [20] 李丹,董春梅,林承焰,等. 松南让字井斜坡带源下致密砂岩储集层控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2013,40(6):692-700. Li Dan, Dong Chunmei, Lin Chengyan, et al. Control factors on tight sandstone reservoirs below source rocks in the Rangzijing slope zone of southern Songliao Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(6): 692-700. [21] 朱筱敏,刘媛,方庆,等. 大型坳陷湖盆浅水三角洲形成条件和沉积模式:以松辽盆地三肇凹陷扶余油层为例[J]. 地学前缘,2012,19(1):89-99. Zhu Xiaomin, Liu Yuan, Fang Qing, et al. Formation and sedimentary model of shallow delta in large-scale lake: example from Cretaceous Quantou Formation in Sanzhao Sag, Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(1): 89-99. [22] 赵占银,李洪革,王兴光,等. 松辽盆地南部中浅层成藏机制研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2004,31(6):17-19. Zhao Zhanyin, Li Hongge, Wang Xingguang, et al. Pool formation mechanism of medium shallow layer in south Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(6): 17-19. [23] 郭宏莉,王大锐. 塔里木油气区砂岩储集层碳酸盐胶结物的同位素组成与成因分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发,1999,26(3):31-32. Guo Hongli, Wang Darui. Stable isotopic composition and origin analysis of the carbonate cements within sandstone reservoirs of Tarim oil-gas bearing area[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1999, 26(3): 31-32. [24] 姚泾利,王琪,张瑞,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中部延长组砂岩中碳酸盐胶结物成因与分布规律研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2011,22(6):943-950. Yao Jingli, Wang Qi, Zhang Rui, et al. Origin and spatial distribution of carbonate cements in Yanchang Fm. (Triassic) sandstones within the lacustrine center of Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(6): 943-950. [25] 宋丽红,朱如凯,朱德升,等. 粘土矿物对广安须家河组致密砂岩物性影响[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),2011,33(2):73-78. Song Lihong, Zhu Rukai, Zhu Desheng, et al. Influences of clay minerals on physical properties of tight sandstones of Xujiahe Formation in Guang’an area[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2011, 33(2): 73-78. [26] Ehrenberg S N. Preservation of anomalously high porosity in deeply buried sandstones by grain-coating chlorite: Examples from the Norwegian Continental Shelf[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(7): 1260-1286. [27] 黄思静,谢连文,张萌,等. 中国三叠系陆相砂岩中自生绿泥石的形成机制及其与储层孔隙保存的关系[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2004,31(3):273-281. Huang Sijing, Xie Lianwen, Zhang Meng, et al. Formation mechanism of authigenic chlorite and relation to preservation of porosity in nonmarine Triassic reservoir sandstones, Ordos Basin and Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2004, 31(3): 273-281. [28] 国家经济贸易委员会. SY/T 5477—2003 碎屑岩成岩阶段划分 [S]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2003:1-5. [State Economic and Trade Commission. SY/ T5477-2003 The division of diagenetic stages in clastic rocks[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003: 1-5.] -





 下载:
下载: